Lecture 5: Basic Plant Biochemistry: Carbohydrates, Proteins
... heat. Water absorbs the heat with only slight change in its own temperature. This is because of high specific heat of water 4. Evaporative cooling: As water evaporates, the surface of the liquid that remains behind cools down. This is due to water’s high heat of vaporization (quantity of hear requir ...
... heat. Water absorbs the heat with only slight change in its own temperature. This is because of high specific heat of water 4. Evaporative cooling: As water evaporates, the surface of the liquid that remains behind cools down. This is due to water’s high heat of vaporization (quantity of hear requir ...
Sickle Cell Anemia: Example of a Point Mutation
... be put in proper order by overlapping the ends of fragments produced when a different protease was used in the initial digestion. The fragment sequences shown above turned out to be the first seven amino acids (Nterminal) of the beta-globin chain. Thus it was shown that the difference between sickle ...
... be put in proper order by overlapping the ends of fragments produced when a different protease was used in the initial digestion. The fragment sequences shown above turned out to be the first seven amino acids (Nterminal) of the beta-globin chain. Thus it was shown that the difference between sickle ...
KEY Honors Biology Chapter 10
... b. An amino acid will be missing from each of its kinds of proteins. c. One of its kinds of proteins might contain an incorrect amino acid. d. An amino acid will be missing from one of its kinds of proteins. e. The amino acid sequence of one of its kinds of proteins will be completely changed. 22. A ...
... b. An amino acid will be missing from each of its kinds of proteins. c. One of its kinds of proteins might contain an incorrect amino acid. d. An amino acid will be missing from one of its kinds of proteins. e. The amino acid sequence of one of its kinds of proteins will be completely changed. 22. A ...
Mutations - Bensalem High School
... Type of point mutation Results in a premature stop codon and usually a nonfunctional protein ...
... Type of point mutation Results in a premature stop codon and usually a nonfunctional protein ...
Phage Lab III - Generic Genome Browser of WUSTL Phages
... start codons any one of which could be the one used by the phage. Remember from your reading that Mycobacteria can use ATG, TTG and GTG for start codons. Since some start codons are used much ...
... start codons any one of which could be the one used by the phage. Remember from your reading that Mycobacteria can use ATG, TTG and GTG for start codons. Since some start codons are used much ...
Alternative Approaches to Molecular Biology
... With a circular chromosome, the DNA is continuous – it has no "end". This means that there will always be DNA from which to make the RNA primer for the lagging strand. d) Other organisms have non-coding sequences at the ends of linear chromosomes called telomeres. A telomere is simply a long stretch ...
... With a circular chromosome, the DNA is continuous – it has no "end". This means that there will always be DNA from which to make the RNA primer for the lagging strand. d) Other organisms have non-coding sequences at the ends of linear chromosomes called telomeres. A telomere is simply a long stretch ...
Organic Macromolecules
... • By the end of the lesson, students will be able to – Describe basic chemistry principles including different organic molecules – By understanding basic chemistry concepts, you will be able to grasp the various interactions between a microorganism and its environment ...
... • By the end of the lesson, students will be able to – Describe basic chemistry principles including different organic molecules – By understanding basic chemistry concepts, you will be able to grasp the various interactions between a microorganism and its environment ...
Questions - Vanier College
... 35. Imagine that a novel life-form is found deep within Earth’s crust. Evaluation of its DNA yields no surprises. However, it is found that a codon for this life-form is just two bases in length. How many different amino acids could this organism be composed of? a. 4 c. 16 e. 64 b. 8 d. 32 36. The ...
... 35. Imagine that a novel life-form is found deep within Earth’s crust. Evaluation of its DNA yields no surprises. However, it is found that a codon for this life-form is just two bases in length. How many different amino acids could this organism be composed of? a. 4 c. 16 e. 64 b. 8 d. 32 36. The ...
Document
... • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or ____________ • The other regions are called ____________ because they are eventually expressed, usually translated into amino acid sequences • _____________________removes introns and joins exons, creating an mRNA molecule with a ...
... • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or ____________ • The other regions are called ____________ because they are eventually expressed, usually translated into amino acid sequences • _____________________removes introns and joins exons, creating an mRNA molecule with a ...
Evolutionary Computation
... simply to maximize the number of 1’s in a bitstring. (Also “Onemax”) Building Block: in the traditional GA, a collection of bits and their corresponding positions (i.e., a hyperplane) such that (1) individuals having those bits in those positions tend to have higher fitness; (2) the number of bits i ...
... simply to maximize the number of 1’s in a bitstring. (Also “Onemax”) Building Block: in the traditional GA, a collection of bits and their corresponding positions (i.e., a hyperplane) such that (1) individuals having those bits in those positions tend to have higher fitness; (2) the number of bits i ...
Mutations
... and the protein may fail to function. 5. More or fewer Amino acids: • If an insertion or deletion is a multiple of 3, the reading frame will be preserved. It causes the resulting protein to have more or less amino acids than originally. • An insertion or deletion of many codons is likely to disrupt ...
... and the protein may fail to function. 5. More or fewer Amino acids: • If an insertion or deletion is a multiple of 3, the reading frame will be preserved. It causes the resulting protein to have more or less amino acids than originally. • An insertion or deletion of many codons is likely to disrupt ...
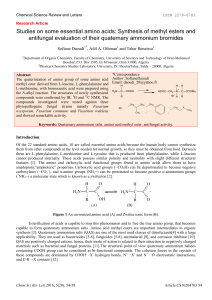
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
... capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are one of the most used classes of disinfectants[4] with a large applicability. They are used as bactericides [5-6], fungicides [5-8], antimalari ...
... capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are one of the most used classes of disinfectants[4] with a large applicability. They are used as bactericides [5-6], fungicides [5-8], antimalari ...
Functional Control by Codon Bias in Magnetic Bacteria
... magnetic bacterial genome. This is so since IRPs in magnetic bacteria are clearly expected to play a role in iron transport towards nanomagnet formation, a functional feature absent in other sources. Once again, to our pleasant surprise, we found that primary sequences of IRPs identical to those fou ...
... magnetic bacterial genome. This is so since IRPs in magnetic bacteria are clearly expected to play a role in iron transport towards nanomagnet formation, a functional feature absent in other sources. Once again, to our pleasant surprise, we found that primary sequences of IRPs identical to those fou ...
Metabolism of amino acids
... b) aspartate aminotransferase (AST) transforms aspartate to -ketoglutarate c) glutamine synthetase transforms glutamate to glutamine d) glutaminase catylyzes conversion of glutamine to ammonia and -ketoglutarate ...
... b) aspartate aminotransferase (AST) transforms aspartate to -ketoglutarate c) glutamine synthetase transforms glutamate to glutamine d) glutaminase catylyzes conversion of glutamine to ammonia and -ketoglutarate ...
Метод поиска SDP
... ---------MFRKLSVEFLGTFWLVLGGCGSAVLAA--AFP ---------MGRKLLAEFFGTFWLVFGGCGSAVFAA--AFP ---------MFRKLAAECFGTFWLVFGGCGSAVLAA--GFP ...
... ---------MFRKLSVEFLGTFWLVLGGCGSAVLAA--AFP ---------MGRKLLAEFFGTFWLVFGGCGSAVFAA--AFP ---------MFRKLAAECFGTFWLVFGGCGSAVLAA--GFP ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 35. Which of the following illustrates a deamination reaction? a. Removal of the amino group from an amino acid. b. Separation of an amino acid from a peptide chain. c. Addition of an amino group to form a new amino acid. d. Addition of an amino acid to form a larger peptide chain. 36. A deficiency ...
... 35. Which of the following illustrates a deamination reaction? a. Removal of the amino group from an amino acid. b. Separation of an amino acid from a peptide chain. c. Addition of an amino group to form a new amino acid. d. Addition of an amino acid to form a larger peptide chain. 36. A deficiency ...
BIOLOGY Cells Unit GUIDE SHEET
... 13. Explain why a point mutation (the replacement of one nucleotide and its base-pairing partner with another pair of nucleotides) may or may not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein. In your answer use and define the terms silent mutation, missense mutation, and nonsense mutat ...
... 13. Explain why a point mutation (the replacement of one nucleotide and its base-pairing partner with another pair of nucleotides) may or may not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein. In your answer use and define the terms silent mutation, missense mutation, and nonsense mutat ...
division - IRIS - Lake Land College
... ketones, and carbohydrates. Write chemical equations for the reactions of aldehydes, ketones and carbohydrates. Name and write structural formulas for carboxylic acids, esters, and lipids. Write chemical equations for the reactions of carboxylic acids, esters, and lipids. Name and write structural f ...
... ketones, and carbohydrates. Write chemical equations for the reactions of aldehydes, ketones and carbohydrates. Name and write structural formulas for carboxylic acids, esters, and lipids. Write chemical equations for the reactions of carboxylic acids, esters, and lipids. Name and write structural f ...
Chapter 6: Genetic Control: DNA and RNA
... • Property 1 - it must contain, in a stable form, information encoding the organism’s structure, function, development and reproduction • Property 2 - it must replicate accurately so progeny cells have the same genetic makeup • Property 3 - it must be capable of some variation (mutation) to permit e ...
... • Property 1 - it must contain, in a stable form, information encoding the organism’s structure, function, development and reproduction • Property 2 - it must replicate accurately so progeny cells have the same genetic makeup • Property 3 - it must be capable of some variation (mutation) to permit e ...
Final Practice Exam
... b. Separation of an amino acid from a peptide chain. c. Addition of an amino group to form a new amino acid. d. Addition of an amino acid to form a larger peptide chain. 36. A deficiency in iodine is called what? a. Ariboflavinosis b. Goiter c. Beri Beri d. Scurvy 37. What system do the fat-soluble ...
... b. Separation of an amino acid from a peptide chain. c. Addition of an amino group to form a new amino acid. d. Addition of an amino acid to form a larger peptide chain. 36. A deficiency in iodine is called what? a. Ariboflavinosis b. Goiter c. Beri Beri d. Scurvy 37. What system do the fat-soluble ...
Milan Manchandia - Werner Syndrome
... Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor for associated osteoporosis ...
... Recombinant human insulin-like growth factor for associated osteoporosis ...
Lec. # 2
... solution to produce their respective conjugate bases and acids. ý They undergo 100% dissociation in water with equilibrium shifted completely to the right side. ý Many different organic functional groups behave as acids or bases, and these are listed in table 1 and 2 respectively. ý Organic function ...
... solution to produce their respective conjugate bases and acids. ý They undergo 100% dissociation in water with equilibrium shifted completely to the right side. ý Many different organic functional groups behave as acids or bases, and these are listed in table 1 and 2 respectively. ý Organic function ...
WEEK 10
... glutaraldehyde does not join every peptide linkage, as is possible with formaldehyde. The size of the five-carbon glutaraldehyde sterically prevents a reaction at every peptide site. Tissue embalmed with glutaraldehyde is not as hard as that embalmed with formaldehyde. A possible explanation for thi ...
... glutaraldehyde does not join every peptide linkage, as is possible with formaldehyde. The size of the five-carbon glutaraldehyde sterically prevents a reaction at every peptide site. Tissue embalmed with glutaraldehyde is not as hard as that embalmed with formaldehyde. A possible explanation for thi ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.