Document
... one in every 25 bases is edited on average, which leads to about 1 in every 8 codons being edited on average. In plant mitochondrial mRNAs, about 2% of the nucleotides are edited on average. In the remainder of this article, we briefly describe the editing events in these organisms. Then we focus fi ...
... one in every 25 bases is edited on average, which leads to about 1 in every 8 codons being edited on average. In plant mitochondrial mRNAs, about 2% of the nucleotides are edited on average. In the remainder of this article, we briefly describe the editing events in these organisms. Then we focus fi ...
Protein: Amino Acids - Resource Sites
... – Maillard Reaction • Browning when sugar combines with protein p. 176 ...
... – Maillard Reaction • Browning when sugar combines with protein p. 176 ...
Honors Biology Unit 6 Ch. 10 “DNA, RNA & Protein synthesis”
... I can describe what happens during transcription. I can describe what happens during translation. I can explain how transcription and translation work together to make a protein. b. I can identify how each type of RNA is involved in protein synthesis. c. I can describe the functions of protein ...
... I can describe what happens during transcription. I can describe what happens during translation. I can explain how transcription and translation work together to make a protein. b. I can identify how each type of RNA is involved in protein synthesis. c. I can describe the functions of protein ...
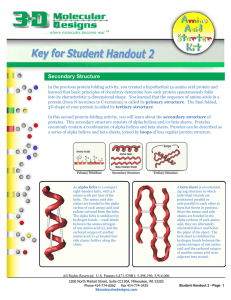
Secondary Structure - 3D Molecular Designs
... Fold the beta sheet and alpha helix into the final tertiary structure of the zinc finger. In its final tertiary structure, the seven side chains will be positioned such that: • The two cysteine and two histidine side chains will be oriented to simultaneously bind to a single zinc atom (not included ...
... Fold the beta sheet and alpha helix into the final tertiary structure of the zinc finger. In its final tertiary structure, the seven side chains will be positioned such that: • The two cysteine and two histidine side chains will be oriented to simultaneously bind to a single zinc atom (not included ...
Endoplasmic reticulum - Protein synthesis
... ER, Golgi retrieved by the KDEL-receptors. They recognize the KDEL signal (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu at C-terminus). ...
... ER, Golgi retrieved by the KDEL-receptors. They recognize the KDEL signal (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu at C-terminus). ...
HPER 334 Nutrition Exam 2
... 43. Exercise has a very strong insulin-like effect. 44. An example of a food that contains a complete protein is peanut butter. 45. The catabolism of protein can produce ammonia, a product that is toxic to the body. 46. It has been proven that protein supplements are more effective than food protein ...
... 43. Exercise has a very strong insulin-like effect. 44. An example of a food that contains a complete protein is peanut butter. 45. The catabolism of protein can produce ammonia, a product that is toxic to the body. 46. It has been proven that protein supplements are more effective than food protein ...
Lecture 02 - Natural products & biosynthesis, web
... - Synthesize compounds that are unique to a particular species or genus (unlike common proteins, lipids, etc.) - Molecules may have extremely complex structures - These molecules typically have no effect on the producing organism, but are often highly biologically active against other organisms (com ...
... - Synthesize compounds that are unique to a particular species or genus (unlike common proteins, lipids, etc.) - Molecules may have extremely complex structures - These molecules typically have no effect on the producing organism, but are often highly biologically active against other organisms (com ...
ORGANIC ACID DISORDERS This disorder is caused by a
... glucose can be used when child is vomiting or has a fever. Monitor urinary ketones for metabolic crisis. Incidence: Very rare- < 50 cases reported since 1971 Isovaleric Acidemia (IVA) IVA results from a defect in metabolism of the amino acid, Leucine. There are 2 types of this disorder. The acute ne ...
... glucose can be used when child is vomiting or has a fever. Monitor urinary ketones for metabolic crisis. Incidence: Very rare- < 50 cases reported since 1971 Isovaleric Acidemia (IVA) IVA results from a defect in metabolism of the amino acid, Leucine. There are 2 types of this disorder. The acute ne ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provides the construction site for polypeptide assembly snRNA: small nuclear RNA involved in modification of mRNA molecules The purpose of TRANSCRIPTION: produce a copy of a small section of DNA. Similar in euka ...
... rRNA: structural component of ribosome, along with a protein it forms the ribosome which provides the construction site for polypeptide assembly snRNA: small nuclear RNA involved in modification of mRNA molecules The purpose of TRANSCRIPTION: produce a copy of a small section of DNA. Similar in euka ...
Talking to Couples about Genetic Screening JScreen is a national
... population. As an enhanced option, you can also choose the expanded panel to learn whether you carry other disease genes seen in the general population. The expanded panel includes more than 80 genetic conditions. For either panel, JScreen offers two different testing methods. Genotyping, the standa ...
... population. As an enhanced option, you can also choose the expanded panel to learn whether you carry other disease genes seen in the general population. The expanded panel includes more than 80 genetic conditions. For either panel, JScreen offers two different testing methods. Genotyping, the standa ...
Amino Acid Metabolism 1. Explain the role of glutamate in amino
... 1. Explain the role of glutamate in amino acid biosynthesis and degradation. 2. How is it possible for the amino group of some amino acids to end up in urea without first being converted to ammonium? 3. Glyphosate, also known as Round-Up, is an herbicide that kills plants by inhibiting an enzyme in ...
... 1. Explain the role of glutamate in amino acid biosynthesis and degradation. 2. How is it possible for the amino group of some amino acids to end up in urea without first being converted to ammonium? 3. Glyphosate, also known as Round-Up, is an herbicide that kills plants by inhibiting an enzyme in ...
Biological Molecules continued
... The monomer building blocks of proteins are called amino acids. Most of these amino acids share a common structure. Two amino acids can bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. These amino acids can bond to each other in a long chain to form what is commonly called a polypeptide. These ...
... The monomer building blocks of proteins are called amino acids. Most of these amino acids share a common structure. Two amino acids can bond to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction. These amino acids can bond to each other in a long chain to form what is commonly called a polypeptide. These ...
ppt
... IMAC takes advantage of the ability to histidine residues to interaction with various transition metal ions including Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ ...
... IMAC takes advantage of the ability to histidine residues to interaction with various transition metal ions including Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ ...
Case presentation
... Genetic analysis of several affected families (kindreds) suggests that the disorder may result from changes (mutations) of a gene that regulates production of an enzyme known as cathespin ...
... Genetic analysis of several affected families (kindreds) suggests that the disorder may result from changes (mutations) of a gene that regulates production of an enzyme known as cathespin ...
Answer
... 39. Hydrogen bonding among individual amino acids in a chain cause what effect on the protein's shape? Coiling or pleating (primary structure) or folding (tertiary) 40. What is the effect of temperature on protein shape? Give an example of this. Denaturing = unfolding of a protein and a loss of func ...
... 39. Hydrogen bonding among individual amino acids in a chain cause what effect on the protein's shape? Coiling or pleating (primary structure) or folding (tertiary) 40. What is the effect of temperature on protein shape? Give an example of this. Denaturing = unfolding of a protein and a loss of func ...
1. What happens during the digestion of proteins, and what are the
... Essential amino acid: An amino acid that cannot be synthesized by the body and thus must be obtained in the diet. Meats contain all of the essential amino acids. The foods that do not have all of them are described as having incomplete amino acids. Food combinations that together contain all of the ...
... Essential amino acid: An amino acid that cannot be synthesized by the body and thus must be obtained in the diet. Meats contain all of the essential amino acids. The foods that do not have all of them are described as having incomplete amino acids. Food combinations that together contain all of the ...
Working with Data Primary Structure Specifies Tertiary Structure
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
The Folding and Assembly of Proteins
... • Gln is a relatively indifferent, plain vanilla residue that goes reasonably well with almost anything and has no extreme properties or violent preferences or aversion. Asn, in contrast, is an interesting, quirky, residue with many unique properties. ...
... • Gln is a relatively indifferent, plain vanilla residue that goes reasonably well with almost anything and has no extreme properties or violent preferences or aversion. Asn, in contrast, is an interesting, quirky, residue with many unique properties. ...
No Slide Title
... DNA- must be copied exactly like blueprints. It does this by “UNZIPPING” each side of the double helix. DNA helicase (an enzyme) breaks the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases. Polymerase catalyses the new bonds. *DNA can be easily damaged by certain things. What are some of the factors that can d ...
... DNA- must be copied exactly like blueprints. It does this by “UNZIPPING” each side of the double helix. DNA helicase (an enzyme) breaks the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases. Polymerase catalyses the new bonds. *DNA can be easily damaged by certain things. What are some of the factors that can d ...
LS ch. 8 surgeon_brooks
... genetic material. Example: Albinism - pigment 2. Mutations happen any time, randomly 3. Mutations are mostly harmful 4. Lethal mutations – cause death before or after birth ...
... genetic material. Example: Albinism - pigment 2. Mutations happen any time, randomly 3. Mutations are mostly harmful 4. Lethal mutations – cause death before or after birth ...
Chapter 6 study guide key
... 4. State the principle that explains why there must be the same number of atoms of each element on each side of an equation. conservation of mass; Matter cannot be created or destroyed. ...
... 4. State the principle that explains why there must be the same number of atoms of each element on each side of an equation. conservation of mass; Matter cannot be created or destroyed. ...
Chapter 17. - Cloudfront.net
... How can you code for 20 amino acids with only 4 nucleotide bases (A,U,G,C)? ...
... How can you code for 20 amino acids with only 4 nucleotide bases (A,U,G,C)? ...
Document
... tRNA insert its first amino acid The start codon is usually AUG and codes for methionine So almost all proteins begin with methionine as its first amino acid The stop codon is the one that makes the tRNA stop inserting amino acids UAA, UAG, UGA are all stop codons ...
... tRNA insert its first amino acid The start codon is usually AUG and codes for methionine So almost all proteins begin with methionine as its first amino acid The stop codon is the one that makes the tRNA stop inserting amino acids UAA, UAG, UGA are all stop codons ...
Exam 3 Study Guide
... Explain what is meant when we say that the strands of DNA serve as templates during their replication. List the steps of replication. If given a diagram of “incomplete” replication, you should be able to fill in the missing bases. Describe the two steps in gene expression including the following: ...
... Explain what is meant when we say that the strands of DNA serve as templates during their replication. List the steps of replication. If given a diagram of “incomplete” replication, you should be able to fill in the missing bases. Describe the two steps in gene expression including the following: ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.