2.3 and 2.4 Notes
... What are carbohydrates? What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Give an example of a monomer of carbohydrates. What is the reaction called when you make a larger molecule? What has to happen for this to occur? ...
... What are carbohydrates? What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Give an example of a monomer of carbohydrates. What is the reaction called when you make a larger molecule? What has to happen for this to occur? ...
Blueprint of Life notes
... within each separate population, different mutations occur, and therefore, different variations are produced natural selection acts differently on each isolated population, as there are different environmental conditions and selections pressures over time the populations differ so much that they no ...
... within each separate population, different mutations occur, and therefore, different variations are produced natural selection acts differently on each isolated population, as there are different environmental conditions and selections pressures over time the populations differ so much that they no ...
Human Monoclonal Antibodies
... that recognize tyrosine were randomly mutagenized to form a library of different tRNA synthetases that still recognize the same tRNA, but might attach different amino acids. Next, these library clones (MutTyrRS) were expressed in a cell containing another plasmid carrying genes for the amber tRNA (M ...
... that recognize tyrosine were randomly mutagenized to form a library of different tRNA synthetases that still recognize the same tRNA, but might attach different amino acids. Next, these library clones (MutTyrRS) were expressed in a cell containing another plasmid carrying genes for the amber tRNA (M ...
MOLECULAR MARKERS APPLICATION FOR GENETIC RESOURCES CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFERENT PLANT SPECIES
... recommended. Red pepper. Grouping of red - pepper accessions belonging to different taxonomic units, revealed by the analysis of seed proteins, does not completely agree with classification based on morphological traits. Protein pattern of accessions belonging to the species Capsicum annuum L., coul ...
... recommended. Red pepper. Grouping of red - pepper accessions belonging to different taxonomic units, revealed by the analysis of seed proteins, does not completely agree with classification based on morphological traits. Protein pattern of accessions belonging to the species Capsicum annuum L., coul ...
HCl + NaOH --» NaCl + H2O
... chemically in the digestive system by a process called hydrolysis. Substances broken down by hydrolysis have been hydrolyzed. (example) Maltose + Water ------ » Glucose C12H22O11 + H2O ------ » 2C6H12O6 Nutrients such as glucose and amino acids are absorbed through cell membranes and into the bloods ...
... chemically in the digestive system by a process called hydrolysis. Substances broken down by hydrolysis have been hydrolyzed. (example) Maltose + Water ------ » Glucose C12H22O11 + H2O ------ » 2C6H12O6 Nutrients such as glucose and amino acids are absorbed through cell membranes and into the bloods ...
2015FallNSC408
... 2. In which of the following tissue does gluconeogenesis take place? a. Muscle b. Liver c. Adipose 3. Gluconeogenesis produces glucose from amino acids. a. True b. False 4. When an amino acid is metabolized to Acetyl CoA, how many net carbons are contributed for the synthesis of glucose via gluconeo ...
... 2. In which of the following tissue does gluconeogenesis take place? a. Muscle b. Liver c. Adipose 3. Gluconeogenesis produces glucose from amino acids. a. True b. False 4. When an amino acid is metabolized to Acetyl CoA, how many net carbons are contributed for the synthesis of glucose via gluconeo ...
UNIT 10 NOTES PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Note: DNA in eukaryotes never leaves the nucleus RNA does leave the nucleus Note: RNA acts as a go between between DNA and ribosomes. Note: Ribosomes found in the cytosol on the RER. ...
... Note: DNA in eukaryotes never leaves the nucleus RNA does leave the nucleus Note: RNA acts as a go between between DNA and ribosomes. Note: Ribosomes found in the cytosol on the RER. ...
1 UNIT 10 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA contains genetic information
... Note: DNA in eukaryotes never leaves the nucleus RNA does leave the nucleus Note: RNA acts as a go between between DNA and ribosomes. Note: Ribosomes found in the cytosol on the RER. ...
... Note: DNA in eukaryotes never leaves the nucleus RNA does leave the nucleus Note: RNA acts as a go between between DNA and ribosomes. Note: Ribosomes found in the cytosol on the RER. ...
Chapter 5: Structure and function of macromolecules
... In addition to primary structure, protein conformation is also dependent on protein's environment (e.g. changes in temp, pH, of salt concentration can lead to protein denaturation ( unfolding of protein with resultant loss of function) (Fig 5.23) We still can not fully predict the 3-D conformation b ...
... In addition to primary structure, protein conformation is also dependent on protein's environment (e.g. changes in temp, pH, of salt concentration can lead to protein denaturation ( unfolding of protein with resultant loss of function) (Fig 5.23) We still can not fully predict the 3-D conformation b ...
50. and 51. Natural Selection
... species. All humans are members of the species Homo sapiens, and share a majority of their DNA, but no two individuals are exactly alike. That's variation! For the global population, there are many genetic variations among people, including things like eye color, hair color, and blood type. For exam ...
... species. All humans are members of the species Homo sapiens, and share a majority of their DNA, but no two individuals are exactly alike. That's variation! For the global population, there are many genetic variations among people, including things like eye color, hair color, and blood type. For exam ...
Nucleic Acid structure - part 1
... Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids Chargaff’s rules 1940s 1. Base composition of DNA varies from one species to another 2. DNA from different tissues of same species have same base composition 3. Base composition of DNA in given species does not change with age, nutritional state, environment 4. In all ce ...
... Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids Chargaff’s rules 1940s 1. Base composition of DNA varies from one species to another 2. DNA from different tissues of same species have same base composition 3. Base composition of DNA in given species does not change with age, nutritional state, environment 4. In all ce ...
Nucleic Acid structure
... Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids Chargaff’s rules 1940s 1. Base composition of DNA varies from one species to another 2. DNA from different tissues of same species have same base composition 3. Base composition of DNA in given species does not change with age, nutritional state, environment 4. In all ce ...
... Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids Chargaff’s rules 1940s 1. Base composition of DNA varies from one species to another 2. DNA from different tissues of same species have same base composition 3. Base composition of DNA in given species does not change with age, nutritional state, environment 4. In all ce ...
A1986A777600001
... of pyridoxal and the amino acid. The powerful electron-withdrawing ability of the N-protonated pyridine ring was also needed for catalysis. Taking some clues from the newly published Chemistry of the Metal 2Chelate Compounds, by Martell and Calvin, we quickly deduced the common mechanism for all of ...
... of pyridoxal and the amino acid. The powerful electron-withdrawing ability of the N-protonated pyridine ring was also needed for catalysis. Taking some clues from the newly published Chemistry of the Metal 2Chelate Compounds, by Martell and Calvin, we quickly deduced the common mechanism for all of ...
MUTATIONS
... to be different, so all codons after the mutation will code for different amino acids. Furthermore, the stop codon "UAA, UGA, or UAG" will not be read, or a stop codon could be created at an earlier or later site. The protein being created could be abnormally short, abnormally long, and/or contain ...
... to be different, so all codons after the mutation will code for different amino acids. Furthermore, the stop codon "UAA, UGA, or UAG" will not be read, or a stop codon could be created at an earlier or later site. The protein being created could be abnormally short, abnormally long, and/or contain ...
Bio 101 Homework #3 Prof. Fournier
... 74. Scientists have successfully cloned sheep and cattle for several years. A farmer is considering the advantages and disadvantages of having a flock of sheep cloned from a single individual. Discuss the issues the farmer should take into account before making a decision. Your response should inclu ...
... 74. Scientists have successfully cloned sheep and cattle for several years. A farmer is considering the advantages and disadvantages of having a flock of sheep cloned from a single individual. Discuss the issues the farmer should take into account before making a decision. Your response should inclu ...
genetic code table
... 1. The enzyme site into which you cloned your fragment of DNA is __________. NOTE: ...
... 1. The enzyme site into which you cloned your fragment of DNA is __________. NOTE: ...
Lecture 6 S - BEHESHTI MAAL
... Spontaneous Mutation: Base-pair deletion or insertion Insert or delete a nucleotide- very disastrous Shifts codons of DNA when transcribed into RNA (also called frameshift mutation) All nucleotides downstream of mutation will be grouped into improper codons, and wrong amino acids will be added Prot ...
... Spontaneous Mutation: Base-pair deletion or insertion Insert or delete a nucleotide- very disastrous Shifts codons of DNA when transcribed into RNA (also called frameshift mutation) All nucleotides downstream of mutation will be grouped into improper codons, and wrong amino acids will be added Prot ...
Kinetic proofreading - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Kinetic proofreading tRNA – Ribosome analogy ...
... Kinetic proofreading tRNA – Ribosome analogy ...
proteins - MBBS Students Club
... These are soluble in 70 to 80% ethanol but insoluble in water and absolute alcohol Examples are gliadin of wheat and zein of maize. These are rich in the amino acid praline but deficient in lysine. ...
... These are soluble in 70 to 80% ethanol but insoluble in water and absolute alcohol Examples are gliadin of wheat and zein of maize. These are rich in the amino acid praline but deficient in lysine. ...
Chapter 8 How Genes Work
... amino acids into proteins on ribosomes Order of amino acid determines protein ...
... amino acids into proteins on ribosomes Order of amino acid determines protein ...
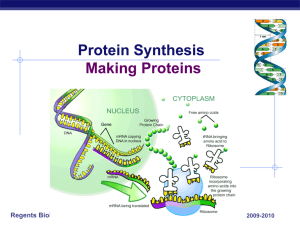
Protein Synthesis
... act as chemical messengers to keep your body functioning correctly, they help to determine how tall you will become, and they form the structure for building your body. Proteins are found almost everywhere in a living organism. The human body contains about 50,000 different kinds of protein. Protein ...
... act as chemical messengers to keep your body functioning correctly, they help to determine how tall you will become, and they form the structure for building your body. Proteins are found almost everywhere in a living organism. The human body contains about 50,000 different kinds of protein. Protein ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.