Intracerebral Microdialysis of Extracellular Amino Acids in the
... alyzed, including TAU, showed small changes. The re sults support the hypothesis that ASP, GLU, GLY, and possibly SER, play an important role in the mechanism of seizure activity and seizure-related brain damage in the human epileptic focus. Key Words: Brain-Human Epilepsy-Microdialysis-Amino acid ...
... alyzed, including TAU, showed small changes. The re sults support the hypothesis that ASP, GLU, GLY, and possibly SER, play an important role in the mechanism of seizure activity and seizure-related brain damage in the human epileptic focus. Key Words: Brain-Human Epilepsy-Microdialysis-Amino acid ...
Chapter 15: Genes and How They Work
... Crick and his colleagues reasoned that the genetic code most likely consisted of a series of blocks of information called codons, each corresponding to an amino acid in the encoded protein. They further hypothesized that the information within one codon was probably a sequence of three nucleotides s ...
... Crick and his colleagues reasoned that the genetic code most likely consisted of a series of blocks of information called codons, each corresponding to an amino acid in the encoded protein. They further hypothesized that the information within one codon was probably a sequence of three nucleotides s ...
protein - Portal UniMAP
... Proteins consist of two or more polypeptide chains aggregated into one functional macromolecules Many proteins, esp those with high molecular weight are composed of several polypeptide chains. In proteins that consist of more than 1 polypeptide chain, each polypeptide is called subunit Polypeptide s ...
... Proteins consist of two or more polypeptide chains aggregated into one functional macromolecules Many proteins, esp those with high molecular weight are composed of several polypeptide chains. In proteins that consist of more than 1 polypeptide chain, each polypeptide is called subunit Polypeptide s ...
Study Detects Recent Instance of Human Evolution
... digest milk in adulthood, conferred by genetic changes that occurred as recently as 3,000 years ago, a team of geneticists has found. The finding is a striking example of a cultural practice — the raising of dairy cattle — feeding back into the human genome. It also seems to be one of the first inst ...
... digest milk in adulthood, conferred by genetic changes that occurred as recently as 3,000 years ago, a team of geneticists has found. The finding is a striking example of a cultural practice — the raising of dairy cattle — feeding back into the human genome. It also seems to be one of the first inst ...
Click here for the LOs of the first 4 key areas
... (d) Translation of mRNA into a polypeptide by tRNA at the ribosome. tRNA folds due to base pairing to form a triplet anticodon site and an attachment site for a specific amino acid. Triplet codons on mRNA and anticodons translate the genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. Start and stop codons ...
... (d) Translation of mRNA into a polypeptide by tRNA at the ribosome. tRNA folds due to base pairing to form a triplet anticodon site and an attachment site for a specific amino acid. Triplet codons on mRNA and anticodons translate the genetic code into a sequence of amino acids. Start and stop codons ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA - Northwestern High School
... • Pg 208 (know process, find tRNA, mRNA, ribosome, nucleus, polypeptide chain, ...
... • Pg 208 (know process, find tRNA, mRNA, ribosome, nucleus, polypeptide chain, ...
BIO2093_DMS4_sequence_similarity
... of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. Gaps are inserted between the residues so that residues with identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. ...
... of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. Gaps are inserted between the residues so that residues with identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. ...
Topic 2 & 3: Genetics Review
... ribose. Ribose has one more hydroxyl than deoxyribose. b) Uracil, a pyrimidine, is unique to RNA and is similar to thymine (A, C, G, U). c) RNA is single stranded. ...
... ribose. Ribose has one more hydroxyl than deoxyribose. b) Uracil, a pyrimidine, is unique to RNA and is similar to thymine (A, C, G, U). c) RNA is single stranded. ...
National Research Program
... Brian Liddicoat is investigating the role of ribonucleic acid (RNA) editing in the development of blood cells and leukaemia. RNA plays an important role in translating the genetic information contained in the DNA. RNA is produced when a single-stranded, complementary ‘copy’ of a gene’s DNA sequence ...
... Brian Liddicoat is investigating the role of ribonucleic acid (RNA) editing in the development of blood cells and leukaemia. RNA plays an important role in translating the genetic information contained in the DNA. RNA is produced when a single-stranded, complementary ‘copy’ of a gene’s DNA sequence ...
Biochemistry
... ATP (adenosine triphosphate) - high energy molecule that contains three phosphate bonds that are easily broken to release energy (this energy drives the reactions in our ...
... ATP (adenosine triphosphate) - high energy molecule that contains three phosphate bonds that are easily broken to release energy (this energy drives the reactions in our ...
Ribosome binding site Polysomes (多聚核糖体)
... often determined by specific, relatively short amino acid sequence within the proteins themselves. These sequences can be responsible for proteins being secreted, imported into the nucleus or targeted to other organelles. ...
... often determined by specific, relatively short amino acid sequence within the proteins themselves. These sequences can be responsible for proteins being secreted, imported into the nucleus or targeted to other organelles. ...
Prediction of Protein Structure Using Backbone Fragment
... protein sequence with a template structure or (ii) ab initio prediction methods. These methods suffer from the disadvantages of (a) lack of homologous template structure for a majority of new sequences or (b) untractably large conformational search space for ab initio predictions. We propose a metho ...
... protein sequence with a template structure or (ii) ab initio prediction methods. These methods suffer from the disadvantages of (a) lack of homologous template structure for a majority of new sequences or (b) untractably large conformational search space for ab initio predictions. We propose a metho ...
Biol 1107 Biomolecules Lab Fall 2003
... The synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids requires specific enzymes called desaturases that produce the double bonds between specific carbons in the acyl chains. Animals do not have a desaturase necessary to produce a double bond below the 10th carbon in an acyl chain. Nevertheless, animals require s ...
... The synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids requires specific enzymes called desaturases that produce the double bonds between specific carbons in the acyl chains. Animals do not have a desaturase necessary to produce a double bond below the 10th carbon in an acyl chain. Nevertheless, animals require s ...
PTM
... Mononucleotide addition is used to regulate the activity of some enzymes. Two different examples are found among the system that regulates Nitrogen utilization in E. coli: • Glutamine synthetase is adenylylated (i.e. AMP is added) at a specific tyrosine residue. The enzyme is inactive when it is ade ...
... Mononucleotide addition is used to regulate the activity of some enzymes. Two different examples are found among the system that regulates Nitrogen utilization in E. coli: • Glutamine synthetase is adenylylated (i.e. AMP is added) at a specific tyrosine residue. The enzyme is inactive when it is ade ...
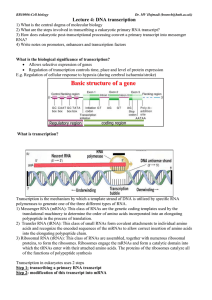
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... E.g. Regulation of cellular response to hypoxia (during cerebral ischaemia/stroke) ...
... E.g. Regulation of cellular response to hypoxia (during cerebral ischaemia/stroke) ...
File
... • Even if the aa is substituted for another, it may not have a significant function in the final structure • This is called a silent mutation • Example: UAU and UAC • Mis-sense mutation • Results in an altered protein • Ex sickle cell disease is a point mutation that is very harmful ...
... • Even if the aa is substituted for another, it may not have a significant function in the final structure • This is called a silent mutation • Example: UAU and UAC • Mis-sense mutation • Results in an altered protein • Ex sickle cell disease is a point mutation that is very harmful ...
biomolecule
... mono-, di-, oligo-, and poly mean? Each of these roots can be added to the word saccharide to describe the type of carbohydrate you have. ...
... mono-, di-, oligo-, and poly mean? Each of these roots can be added to the word saccharide to describe the type of carbohydrate you have. ...
DNA, RNA and Protein
... produce a new chain •Each new DNA helix contains one “old” and one “new” chain ...
... produce a new chain •Each new DNA helix contains one “old” and one “new” chain ...
Detailed Objectives
... reaction type. Understand the stoichiometry of each pathway from the overall reaction. Understand the free energy considerations (production and use of ATP) and oxidation-reduction considerations (the general flow of electrons (H·, H:-, or e-)) for each pathway. You should understand the basic princ ...
... reaction type. Understand the stoichiometry of each pathway from the overall reaction. Understand the free energy considerations (production and use of ATP) and oxidation-reduction considerations (the general flow of electrons (H·, H:-, or e-)) for each pathway. You should understand the basic princ ...
Most molecules of human vasopressin have a net charge of _____
... a. What errors in the drawing would cause you to deduct points? List each error. If there are no errors, list ‘none.’ b. The exam also asks the students to calculate the average charge of this peptide at pH 7. What is the correct answer? (Show your work.) ...
... a. What errors in the drawing would cause you to deduct points? List each error. If there are no errors, list ‘none.’ b. The exam also asks the students to calculate the average charge of this peptide at pH 7. What is the correct answer? (Show your work.) ...
Transcription 12.06.21 lec
... starts to split. [process for creating a new DNA chain – two new sets, each set has one of the original chains of DNA in it][thymine can turn into uracil, but there are ...
... starts to split. [process for creating a new DNA chain – two new sets, each set has one of the original chains of DNA in it][thymine can turn into uracil, but there are ...
Proteins - churchillcollegebiblio
... • Some protein chains are attracted to other protein chains. • Work with the other team and try putting your protein model next to their protein model in a way that still follows the rules of protein folding. • Make a drawing to show the quaternary structure of your protein model (Step D of your ...
... • Some protein chains are attracted to other protein chains. • Work with the other team and try putting your protein model next to their protein model in a way that still follows the rules of protein folding. • Make a drawing to show the quaternary structure of your protein model (Step D of your ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.