NH 2
... Describe the four levels of protein organization with reference to primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins using haemoglobin as example Explain how structure of protein determines its function by looking at examples Differentiate between globular and structural proteins wit ...
... Describe the four levels of protein organization with reference to primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins using haemoglobin as example Explain how structure of protein determines its function by looking at examples Differentiate between globular and structural proteins wit ...
Human Genome Project
... (polygenic), and gene-environment interaction – Multifactorial • refers to a trait that is affected by many factors, both genetic and environmental – The Human Genome Project is an international effort to map the entire human genome • researchers have found that humans have only about 25,000 genes, ...
... (polygenic), and gene-environment interaction – Multifactorial • refers to a trait that is affected by many factors, both genetic and environmental – The Human Genome Project is an international effort to map the entire human genome • researchers have found that humans have only about 25,000 genes, ...
3D structures of RNA
... helix of type A. The ability of being both informational and diverse in structure suggests that RNA was the prebiotic molecule that could function in both replication and catalysis (The RNA World Hypothesis). In fact, some viruses encode their genetic materials by RNA (retrovirus) ...
... helix of type A. The ability of being both informational and diverse in structure suggests that RNA was the prebiotic molecule that could function in both replication and catalysis (The RNA World Hypothesis). In fact, some viruses encode their genetic materials by RNA (retrovirus) ...
Proteins and Mutations – Revision Pack (B3)
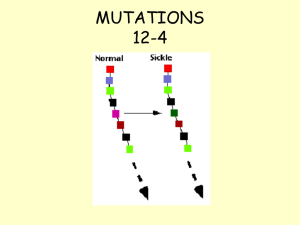
... Gene mutations may lead to the production of different proteins. Mutation may occur spontaneously but can be made to occur more often by radiation or chemicals. Mutations are often harmful but may be beneficial or have no effect. Only some of the full set of genes is used in any one cell; some genes ...
... Gene mutations may lead to the production of different proteins. Mutation may occur spontaneously but can be made to occur more often by radiation or chemicals. Mutations are often harmful but may be beneficial or have no effect. Only some of the full set of genes is used in any one cell; some genes ...
Supplement 2
... SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the plasmids expressed corresponding sizes of recombinant proteins (SFig. 2a). SFig. 2b illustrates the amino acid sequences of the 4 recombinant fragments deduced from DNA sequencing after cloning into the vectors. 3. Discussion and Conclusion By successfully cloning a ...
... SDS-PAGE analysis showed that the plasmids expressed corresponding sizes of recombinant proteins (SFig. 2a). SFig. 2b illustrates the amino acid sequences of the 4 recombinant fragments deduced from DNA sequencing after cloning into the vectors. 3. Discussion and Conclusion By successfully cloning a ...
Macromolecules of Life
... DNA and RNA, can always be found in all cells of everything from bacteria to humans. DNA is always found in the nucleus of the cell. RNA can also be found in the nucleus but also throughout the cell. RNA is broken down into three subcategories: messenger RNA (mRNA) - carries the genetic code from th ...
... DNA and RNA, can always be found in all cells of everything from bacteria to humans. DNA is always found in the nucleus of the cell. RNA can also be found in the nucleus but also throughout the cell. RNA is broken down into three subcategories: messenger RNA (mRNA) - carries the genetic code from th ...
How do bacteria respond to their environment?
... Experiment • Add uncharged tRNA to ribosomes • See if pppGpp increases Need: • In vitro system where charging of tRNA can be controlled • Assay for level of pppGpp ...
... Experiment • Add uncharged tRNA to ribosomes • See if pppGpp increases Need: • In vitro system where charging of tRNA can be controlled • Assay for level of pppGpp ...
Chemistry of Life
... The amount of energy required to make the reaction begin – Act as a catalyst A part of the reaction that is not consumed or changed ...
... The amount of energy required to make the reaction begin – Act as a catalyst A part of the reaction that is not consumed or changed ...
Protein Engineering
... • N-linked carbohydrate is attached to the polypeptide backbone at a consens us sequence for carbohydrate addition: Asn-Xxx-Ser/Thr -The middle amino acid can not be proline (Pro). • Critical factors: - Local protein folding and conformation during biosynthesis: Co-translation - No interference with ...
... • N-linked carbohydrate is attached to the polypeptide backbone at a consens us sequence for carbohydrate addition: Asn-Xxx-Ser/Thr -The middle amino acid can not be proline (Pro). • Critical factors: - Local protein folding and conformation during biosynthesis: Co-translation - No interference with ...
91159 Demonstrate understanding of gene expression
... Demonstrate understanding involves defining, using annotated diagrams or models to explain, and giving characteristics of, or an account of, gene expression. Demonstrate in-depth understanding involves providing a reason as to how or why biological ideas and processes affect gene expression. Demonst ...
... Demonstrate understanding involves defining, using annotated diagrams or models to explain, and giving characteristics of, or an account of, gene expression. Demonstrate in-depth understanding involves providing a reason as to how or why biological ideas and processes affect gene expression. Demonst ...
Powerpoint
... Why is it a good molecule to store energy? It takes a lot of energy to put two phosphate molecules together (both –’ve). So when you break that bond, a lot of energy is released. C6H12O6 + 6O2 -----> 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy (heat and ATP) ...
... Why is it a good molecule to store energy? It takes a lot of energy to put two phosphate molecules together (both –’ve). So when you break that bond, a lot of energy is released. C6H12O6 + 6O2 -----> 6CO2 + 6H20 + energy (heat and ATP) ...
pages 46-50
... fatty acids are shown in figure 3.4. Many lipids, both fats and oils, contain three fatty acids bonded to glycerol. They are called triglycerides. Most animal fats are saturated fats, which means they have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible. That is, every place that a hydrogen atom can ...
... fatty acids are shown in figure 3.4. Many lipids, both fats and oils, contain three fatty acids bonded to glycerol. They are called triglycerides. Most animal fats are saturated fats, which means they have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible. That is, every place that a hydrogen atom can ...
A1993KM59500002
... [Department of Zoology, University of Texas, Austin. TX] An analysis by enzyme electrophoresis of allelic variation in 32 structural genes revealed that populations inhabiting beaches on Santa Rosa Island and several peninsulas on the Ronda Gulf coast were only ¼ to ½ as variable as those on the mai ...
... [Department of Zoology, University of Texas, Austin. TX] An analysis by enzyme electrophoresis of allelic variation in 32 structural genes revealed that populations inhabiting beaches on Santa Rosa Island and several peninsulas on the Ronda Gulf coast were only ¼ to ½ as variable as those on the mai ...
Protein Basics
... right-handed alpha helix and beta sheet) • Yellow = sterically allowed if shorter radii are used (i.e. atoms allowed closer together; brings out left-handed helix) ...
... right-handed alpha helix and beta sheet) • Yellow = sterically allowed if shorter radii are used (i.e. atoms allowed closer together; brings out left-handed helix) ...
Complete genomic sequence of viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus
... Within the P gene of VSV, an additional overlapping reading frame was detected (14) encoding a deduced protein C, which is localized in cytoplasmic compartiments of virus infected cells. In the VHSV and IHNV genomes, an additional second ORF contained in the P gene is also present. The deduced hypot ...
... Within the P gene of VSV, an additional overlapping reading frame was detected (14) encoding a deduced protein C, which is localized in cytoplasmic compartiments of virus infected cells. In the VHSV and IHNV genomes, an additional second ORF contained in the P gene is also present. The deduced hypot ...
Gene Section TACC2 (transforming, acidic coiled-coil containing protein 2)
... often shows species 65-70 kDa (corresponding in size to ORF-BC015736 and AAF63433 isoforms), however the variability in intensity in different preparations from the same cell type suggests that these species could also arise as a product of degradation (PEST sequences support that TACC2 is subject t ...
... often shows species 65-70 kDa (corresponding in size to ORF-BC015736 and AAF63433 isoforms), however the variability in intensity in different preparations from the same cell type suggests that these species could also arise as a product of degradation (PEST sequences support that TACC2 is subject t ...
Biochemistry Biochemistry is a science concerning the chemical
... aromatic; sulfur-containing; charged, uncharged; acidic, basic). The amphoteric properties of amino acids, zwitterions. The structure of some modified amino acids (as selenocysteine, 4-hydroxyproline, 5hydroxylysine). The structure of some physiologically important nonprotein amino acids. The format ...
... aromatic; sulfur-containing; charged, uncharged; acidic, basic). The amphoteric properties of amino acids, zwitterions. The structure of some modified amino acids (as selenocysteine, 4-hydroxyproline, 5hydroxylysine). The structure of some physiologically important nonprotein amino acids. The format ...
Biochemistry Biochemistry is a science concerning the chemical
... aromatic; sulfur-containing; charged, uncharged; acidic, basic). The amphoteric properties of amino acids, zwitterions. The structure of some modified amino acids (as selenocysteine, 4-hydroxyproline, 5hydroxylysine). The structure of some physiologically important nonprotein amino acids. The format ...
... aromatic; sulfur-containing; charged, uncharged; acidic, basic). The amphoteric properties of amino acids, zwitterions. The structure of some modified amino acids (as selenocysteine, 4-hydroxyproline, 5hydroxylysine). The structure of some physiologically important nonprotein amino acids. The format ...
Acid-Base Principles to Organic Acids
... Inflammation causes or exacerbates heart, lung, and kidney disease ...
... Inflammation causes or exacerbates heart, lung, and kidney disease ...
Slide 1
... RNA has a hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon of the sugar. Not like DNA uses thymine (T), RNA uses uracil (U). Because of the extra hydroxyl group on the sugar, RNA is too bulky to form a stable double helix. RNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form wher ...
... RNA has a hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon of the sugar. Not like DNA uses thymine (T), RNA uses uracil (U). Because of the extra hydroxyl group on the sugar, RNA is too bulky to form a stable double helix. RNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form wher ...
Biochemistry Biochemistry is a science concerning the chemical
... nonpolar; aliphatic, aromatic; sulfur-containing; charged, uncharged; acidic, basic). The amphoteric properties of amino acids, zwitterions. The structure of some modified amino acids (as selenocysteine, 4-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine). The structure of some physiologically important nonprotein a ...
... nonpolar; aliphatic, aromatic; sulfur-containing; charged, uncharged; acidic, basic). The amphoteric properties of amino acids, zwitterions. The structure of some modified amino acids (as selenocysteine, 4-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine). The structure of some physiologically important nonprotein a ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.