RNA interference 1. The central dogma 3. The RNAi mechanism
... dsRNA molecules are tailor-made to activate the RISC complex to degrade mRNA for a specific gene. ...
... dsRNA molecules are tailor-made to activate the RISC complex to degrade mRNA for a specific gene. ...
Lecture genes to proteins translation - IIT
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
A1980JQ46200001
... spectroscopy was at the Carlsberg Laboratory where I was a postdoctoral visitor with K. Linderstrøm-Lang. I applied the then rather new technique of difference spectroscopy in model compound studies to test Crammer and Neuberger’s suggestion that some of ovalbumin’s tyrosyl residues were Hbonded to ...
... spectroscopy was at the Carlsberg Laboratory where I was a postdoctoral visitor with K. Linderstrøm-Lang. I applied the then rather new technique of difference spectroscopy in model compound studies to test Crammer and Neuberger’s suggestion that some of ovalbumin’s tyrosyl residues were Hbonded to ...
Biology 164 Laboratory Introduction to Bioinformatics and Molecular
... The Clustalx software runs a mathematical algorithm that aligns multiple sequences in ways that minimize the differences between them. If you think about the types of changes that occur to genes over time, e.g., point mutations, reading frame shifts, codon transpositions or deletions, etc., you begi ...
... The Clustalx software runs a mathematical algorithm that aligns multiple sequences in ways that minimize the differences between them. If you think about the types of changes that occur to genes over time, e.g., point mutations, reading frame shifts, codon transpositions or deletions, etc., you begi ...
Biochemistry Assessment
... A Proteins, carbohydrates, amino acids, steroids B Amino acids, lipids, carbohydrates, fats C Lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates D Steroids, nucleic acids, amino acids, lipids _______13. A common name for lipids is _____________. A Monosaccharide B Carbohydrates C Fats D Amino acids (Con ...
... A Proteins, carbohydrates, amino acids, steroids B Amino acids, lipids, carbohydrates, fats C Lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates D Steroids, nucleic acids, amino acids, lipids _______13. A common name for lipids is _____________. A Monosaccharide B Carbohydrates C Fats D Amino acids (Con ...
Simple and efficient method for isolating cDNA - Funpec-RP
... kDa) proteins, that are involved in protecting higher plants from damage caused by environmental stress especially drought. Based on their amino acid sequences, LEA proteins are basically divided into five groups (Dure, 1993; Zhang and Zhao, 2003). To date, there have been some reports about the lea ...
... kDa) proteins, that are involved in protecting higher plants from damage caused by environmental stress especially drought. Based on their amino acid sequences, LEA proteins are basically divided into five groups (Dure, 1993; Zhang and Zhao, 2003). To date, there have been some reports about the lea ...
Module III.4.1-Stochastic hereditary effects
... mutations, doubling dose, UNCEAR and ICRP approaches for genetic risk Comments are welcomed Add module code number and lesson title ...
... mutations, doubling dose, UNCEAR and ICRP approaches for genetic risk Comments are welcomed Add module code number and lesson title ...
Lecture 5: Major Nutrient Groups
... don’t effectively use crystalline sources, experimental conditions allow cannibalism, extrinsic sources of EAA (bacteria) difficult to formulate reasonable diet and vary only one EAA ...
... don’t effectively use crystalline sources, experimental conditions allow cannibalism, extrinsic sources of EAA (bacteria) difficult to formulate reasonable diet and vary only one EAA ...
Protein Synthesis Card Sort
... to take out of the nucleus. This copy is called “mRNA” (messenger RNA). Thymine is replaced with Uracil. ...
... to take out of the nucleus. This copy is called “mRNA” (messenger RNA). Thymine is replaced with Uracil. ...
Chemical Elements and water
... This is the linear sequence of amino acids, which form a polypeptide protein chain connected by covalent-peptide bonds. This is determined by the DNA base sequence of the gene that codes for the polypeptide. The amino acid sequence of a protein determines the higher levels of structure of the molecu ...
... This is the linear sequence of amino acids, which form a polypeptide protein chain connected by covalent-peptide bonds. This is determined by the DNA base sequence of the gene that codes for the polypeptide. The amino acid sequence of a protein determines the higher levels of structure of the molecu ...
"Amino Acid Substitutions: Effects on Protein Stability". In
... strength near 0.15 mol L 2 1). Its three-dimensional structure under these conditions invariably consists of a congeries of compactly folded stretches of regular secondary structure. Environmental stress can cause a protein to lose its native structure and hence to denature to a state that is much l ...
... strength near 0.15 mol L 2 1). Its three-dimensional structure under these conditions invariably consists of a congeries of compactly folded stretches of regular secondary structure. Environmental stress can cause a protein to lose its native structure and hence to denature to a state that is much l ...
Document
... 3. Ketone body biogenesis and cholesterol synthesis are related in that they share the metabolic intermediate, _HMG-CoA/acetoacetyl-CoA_, and utilize _acetyl-CoA__ as a substrate for their biogenesis. The synthetic pathway for ketone bodies takes place in the __mitochondria__ (subcellular compartmen ...
... 3. Ketone body biogenesis and cholesterol synthesis are related in that they share the metabolic intermediate, _HMG-CoA/acetoacetyl-CoA_, and utilize _acetyl-CoA__ as a substrate for their biogenesis. The synthetic pathway for ketone bodies takes place in the __mitochondria__ (subcellular compartmen ...
Protein Synthesis 2
... • Translation is the process of making protein from an RNA template • Fidelity is affected by several steps • tRNAs are the “adapters” that translate the 4-nucleotide language of DNA/RNA into the 20-amino acid language of proteins. • Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are ancient, but accurate enzymes. • Ri ...
... • Translation is the process of making protein from an RNA template • Fidelity is affected by several steps • tRNAs are the “adapters” that translate the 4-nucleotide language of DNA/RNA into the 20-amino acid language of proteins. • Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are ancient, but accurate enzymes. • Ri ...
The Biochemistry of Movement
... In the cell, energy released by the oxidation of biochemical fuels such as glucose is converted into chemical potential energy stored in adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP occurs in all known living species. It is the major energy source for cellular metabolic processes. The process of cellular respi ...
... In the cell, energy released by the oxidation of biochemical fuels such as glucose is converted into chemical potential energy stored in adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP occurs in all known living species. It is the major energy source for cellular metabolic processes. The process of cellular respi ...
Life and Chemistry: Large Molecules
... • Waxes are highly nonpolar molecules consisting of saturated long fatty acids bonded to long fatty alcohols via an ester linkage. • A fatty alcohol is similar to a fatty acid, except for the last carbon, which has an —OH group instead of a —COOH group. ...
... • Waxes are highly nonpolar molecules consisting of saturated long fatty acids bonded to long fatty alcohols via an ester linkage. • A fatty alcohol is similar to a fatty acid, except for the last carbon, which has an —OH group instead of a —COOH group. ...
Introduction to Protein-protein Interaction
... Useful for isolating groups of interacting proteins that participate in the same biological process Helps to understand the mechanism of ...
... Useful for isolating groups of interacting proteins that participate in the same biological process Helps to understand the mechanism of ...
AMINO ACIDS METABOLISM ** Dr. Mohammed Abdullateef **
... Due to accumulation of metabolites, often they cause mental retardation and other defects. Mostly enzymes are absent or deficient. More common include Hyperphenylalaninaemia. Phenylketonuria is the most common form of elevated phenylalanine levels. It is caused by a deficiency in phenylalani ...
... Due to accumulation of metabolites, often they cause mental retardation and other defects. Mostly enzymes are absent or deficient. More common include Hyperphenylalaninaemia. Phenylketonuria is the most common form of elevated phenylalanine levels. It is caused by a deficiency in phenylalani ...
Chemical constituents
... c) As structural material : cellulose is the chief component forming the cell wall of the plant cells and thus giving strength to these cells. Chitin forms the exoskeleton of the insects C. Tests for carbohydrates a) Reducing sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides except sucrose) (i) Benedict’s t ...
... c) As structural material : cellulose is the chief component forming the cell wall of the plant cells and thus giving strength to these cells. Chitin forms the exoskeleton of the insects C. Tests for carbohydrates a) Reducing sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides except sucrose) (i) Benedict’s t ...
11.4 How Is The Information In A Gene
... marks that indicate the end of one protein sequence and the start of another. • All proteins begin with the start codon AUG (methionine), and all end with UAG, UAA, or UGA, called stop codons. • Almost all amino acids are coded for by more than one codon (e.g., six codons code for leucine). Copyrigh ...
... marks that indicate the end of one protein sequence and the start of another. • All proteins begin with the start codon AUG (methionine), and all end with UAG, UAA, or UGA, called stop codons. • Almost all amino acids are coded for by more than one codon (e.g., six codons code for leucine). Copyrigh ...
Topic 2
... vii. Codons of three bases on mRNA correspond to one amino acid in a polypeptide • There are 4 different bases & 20 amino acids so a single base cannot code for an amino acid • Every 3 bases therefore code for an amino acid • These groups of 3 bases that are found on the mRNA is referred to as a co ...
... vii. Codons of three bases on mRNA correspond to one amino acid in a polypeptide • There are 4 different bases & 20 amino acids so a single base cannot code for an amino acid • Every 3 bases therefore code for an amino acid • These groups of 3 bases that are found on the mRNA is referred to as a co ...
Ch11_lecture - Dr Owen class material
... marks that indicate the end of one protein sequence and the start of another. • All proteins begin with the start codon AUG (methionine), and all end with UAG, UAA, or UGA, called stop codons. • Almost all amino acids are coded for by more than one codon (e.g., six codons code for leucine). Copyrigh ...
... marks that indicate the end of one protein sequence and the start of another. • All proteins begin with the start codon AUG (methionine), and all end with UAG, UAA, or UGA, called stop codons. • Almost all amino acids are coded for by more than one codon (e.g., six codons code for leucine). Copyrigh ...
MODULE 1 The Central Dogma Objective 1.4 LESSON A
... gene expression. Complete the assignment below. 1. Screen capture or draw an image related to the gene. (1 point) 2. What is the scientific and common name of the gene? (1 point) 4. What organism is the gene located in? (1point) 5. Explain how the gene is normally expressed using terms associated wi ...
... gene expression. Complete the assignment below. 1. Screen capture or draw an image related to the gene. (1 point) 2. What is the scientific and common name of the gene? (1 point) 4. What organism is the gene located in? (1point) 5. Explain how the gene is normally expressed using terms associated wi ...
Herbicide Mode of Action - Montana State University
... Plant Growth Regulators (PGR) Tordon 22K, Transline, Curtail, Redeem, Banvel, 2,4-D Referred to as synthetic auxins (regulate growth in plant tissues) Translocate in both xylem and phloem. Can act at multiple sites in a plant to disrupt hormone balance and protein synthesis Abnormal growth ...
... Plant Growth Regulators (PGR) Tordon 22K, Transline, Curtail, Redeem, Banvel, 2,4-D Referred to as synthetic auxins (regulate growth in plant tissues) Translocate in both xylem and phloem. Can act at multiple sites in a plant to disrupt hormone balance and protein synthesis Abnormal growth ...
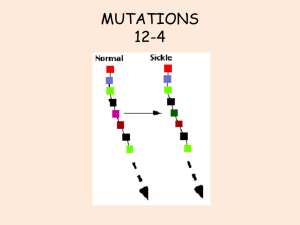
MUTATIONS 12-4 - Somers Public School District
... Segment breaks off and joins a different non-homologous chromosome ...
... Segment breaks off and joins a different non-homologous chromosome ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.