Monomer polymer2011
... Monomer A small repeating unit that can make larger more complex molecules. ...
... Monomer A small repeating unit that can make larger more complex molecules. ...
Science 1.5 Acids and Bases
... These are organised into small chunks of each topic. Check the contents list at the front of your workbook and focus on one section at a time. Read the notes in the workbook, read the relevant notes you made in class, attempt the questions. Complete the revision questions at the end of each section. ...
... These are organised into small chunks of each topic. Check the contents list at the front of your workbook and focus on one section at a time. Read the notes in the workbook, read the relevant notes you made in class, attempt the questions. Complete the revision questions at the end of each section. ...
... The study evaluated the performance and carcass composition index of Nile tilapia ( Oreochromis niloticus ) fed with diets containing increasing levels of spray-dried blood meal (SDBM) and vat-dried blood meal (VDBM) and formulated based on digestible amino acids. Two hundred and fifty-two fingerlin ...
Chapter 2
... Amino acids can be linked in any sequence. The linkage of several amino acids together results in a larger molecule called a polypeptide. After the polypeptide chain reaches a certain length, 50 or more amino acids, it may take on the more complex structure of a protein. A given protein can contain ...
... Amino acids can be linked in any sequence. The linkage of several amino acids together results in a larger molecule called a polypeptide. After the polypeptide chain reaches a certain length, 50 or more amino acids, it may take on the more complex structure of a protein. A given protein can contain ...
Amphibolic nature of Krebs Cycle
... intermediates of the TCA cycle are shown at the points at which they enter the TCA. ...
... intermediates of the TCA cycle are shown at the points at which they enter the TCA. ...
Vicia species belonging to the subgenus Cracca are
... However, there is a big difference in canavanine content in these two species, 0.4 % in ...
... However, there is a big difference in canavanine content in these two species, 0.4 % in ...
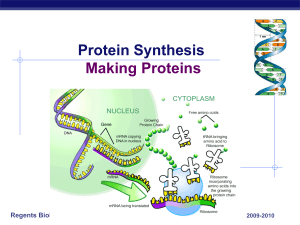
Protein Synthesis Making Proteins
... aa made by a “protein factory” in cytoplasm aa protein factory = ribosome aa ...
... aa made by a “protein factory” in cytoplasm aa protein factory = ribosome aa ...
Water as a Solvent
... becomes obvious if someone attempts to shake the right hand of a person using his left hand, or if a left‐handed glove is placed on a right hand. The term chirality is derived from the Greek word for hand. It is a mathematical ...
... becomes obvious if someone attempts to shake the right hand of a person using his left hand, or if a left‐handed glove is placed on a right hand. The term chirality is derived from the Greek word for hand. It is a mathematical ...
Genetic cause
... is inability to conceive a child during one up to two years of frequent intercourse without the use of contraceptives ...
... is inability to conceive a child during one up to two years of frequent intercourse without the use of contraceptives ...
8102 Explain genetic change
... Ethical implications of genetic engineering are described for a specific example. ...
... Ethical implications of genetic engineering are described for a specific example. ...
MUTATIONS
... to be different, so all codons after the mutation will code for different amino acids. Furthermore, the stop codon "UAA, UGA, or UAG" will not be read, or a stop codon could be created at an earlier or later site. The protein being created could be abnormally short, abnormally long, and/or contain ...
... to be different, so all codons after the mutation will code for different amino acids. Furthermore, the stop codon "UAA, UGA, or UAG" will not be read, or a stop codon could be created at an earlier or later site. The protein being created could be abnormally short, abnormally long, and/or contain ...
video slide
... Sickle-Cell Disease • A slight change in primary structure can drastically change the entire shape of the protein. • When a protein changes shape, it will not work the same. • Sickle-cell anemia is a genetic disease that occurs when red blood cells are shaped like crescents or sickles instead of sa ...
... Sickle-Cell Disease • A slight change in primary structure can drastically change the entire shape of the protein. • When a protein changes shape, it will not work the same. • Sickle-cell anemia is a genetic disease that occurs when red blood cells are shaped like crescents or sickles instead of sa ...
Do universal codon-usage patterns minimize the effects of mutation
... codon usage as well as their genetic code: codons with low error values might be used in preference to those with high error values, to reduce the overall probability of error. Different organisms use the four bases in varying amounts at each of the three positions within the codon (that is, the ave ...
... codon usage as well as their genetic code: codons with low error values might be used in preference to those with high error values, to reduce the overall probability of error. Different organisms use the four bases in varying amounts at each of the three positions within the codon (that is, the ave ...
Awan, Ali: In Silico Transfer of Ligand Binding Function between Structurally Analogous Proteins
... one can explore in silico. Amino acid sequences in natural proteins result from natural selection, and thus are likely to be situated on ‘evolutionary peaks’. It is unlikely that other amino acid sequences which are equally functional but situated on different evolutionary peaks are present in natur ...
... one can explore in silico. Amino acid sequences in natural proteins result from natural selection, and thus are likely to be situated on ‘evolutionary peaks’. It is unlikely that other amino acid sequences which are equally functional but situated on different evolutionary peaks are present in natur ...
Modeling DNA Structure and Function
... III. Transcription Using the DNA molecule that you've just created, do the following: Build an mRNA molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands -- the so called template strand. That is, show your instructor what would happen if the DNA was being transcribed. ...
... III. Transcription Using the DNA molecule that you've just created, do the following: Build an mRNA molecule that is complementary to one of the DNA strands -- the so called template strand. That is, show your instructor what would happen if the DNA was being transcribed. ...
Protein and DNA sequence determinants of
... alternative signatures such as purine loading index as suggested by others (19)? For proteomic compositions is it excess of charge residues or hydrophobic or both and which amino acids specifically are most sensitive to thermal adaptation? On a more fundamental ...
... alternative signatures such as purine loading index as suggested by others (19)? For proteomic compositions is it excess of charge residues or hydrophobic or both and which amino acids specifically are most sensitive to thermal adaptation? On a more fundamental ...
cheese - Genootschap Melkkunde
... - Carboxypeptidase catalyses the removal of one or two amino acid residues from the C-terminus of the protein. - Aminopeptidase catalyses the removal of one or two single amino acid residue from the N-terminus of the protein. Aminopeptidase ...
... - Carboxypeptidase catalyses the removal of one or two amino acid residues from the C-terminus of the protein. - Aminopeptidase catalyses the removal of one or two single amino acid residue from the N-terminus of the protein. Aminopeptidase ...
Document
... prevent the spread of the disease. If you have or may have CJD, you should not donate organs or tissue, including corneal tissue. Newer regulations that govern the handling and feeding of cows may help prevent the spread of prion diseases. ...
... prevent the spread of the disease. If you have or may have CJD, you should not donate organs or tissue, including corneal tissue. Newer regulations that govern the handling and feeding of cows may help prevent the spread of prion diseases. ...
What is natural immunity?
... • One "PAM" corresponds to an average change in 1% of all amino acid positions. After 100 PAMs of evolution, not every residue will have changed: some will have mutated several times, perhaps returning to their original state, and others not at all. Thus it is possible to recognize as homologous pro ...
... • One "PAM" corresponds to an average change in 1% of all amino acid positions. After 100 PAMs of evolution, not every residue will have changed: some will have mutated several times, perhaps returning to their original state, and others not at all. Thus it is possible to recognize as homologous pro ...
Exam-2 review
... - 16.Understand what essential amino acids (EAA's), nonessential amino acids (NEAA's) and conditionally essential amino acids are. - 17. What differentiates one protein from another? What dictates the 3-d shape of a protein - 18. Understand what protein denaturation is, be able to give some examples ...
... - 16.Understand what essential amino acids (EAA's), nonessential amino acids (NEAA's) and conditionally essential amino acids are. - 17. What differentiates one protein from another? What dictates the 3-d shape of a protein - 18. Understand what protein denaturation is, be able to give some examples ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... ● Ammonia secretion (5-10% of whole N turnover) in kidney tubules from glutamine (Chinese Restaurant) ● Nucleotide (pyrimidine) degradation ● Intestinal bacteria produce it from amino acids and urea Ammonia is very toxic → cerebral edema, increased cranial pressure (depletion of ATP in brain cells?) ...
... ● Ammonia secretion (5-10% of whole N turnover) in kidney tubules from glutamine (Chinese Restaurant) ● Nucleotide (pyrimidine) degradation ● Intestinal bacteria produce it from amino acids and urea Ammonia is very toxic → cerebral edema, increased cranial pressure (depletion of ATP in brain cells?) ...
Integrated Teaching Area (ITA) Scenarios for Semester One
... Crossing over at meiosis. Two loci close together on one chromosome may segregate together as crossing over is less likely to happen between them (they are said to be in linkage disequilibrium). Why are people different – how does the genome of one person vary from that of another person? Single bas ...
... Crossing over at meiosis. Two loci close together on one chromosome may segregate together as crossing over is less likely to happen between them (they are said to be in linkage disequilibrium). Why are people different – how does the genome of one person vary from that of another person? Single bas ...
Hydrolysis of Aspartame
... butan-1ol:ethanoic acid:distilled water (prepared as instructions). This solvent is known as the eluent. Make sure the bottom of the paper is in the eluent but the spots are not. Cover the beaker with foil to prevent evaporation. Remove from the beaker when the solvent front is just at the top of th ...
... butan-1ol:ethanoic acid:distilled water (prepared as instructions). This solvent is known as the eluent. Make sure the bottom of the paper is in the eluent but the spots are not. Cover the beaker with foil to prevent evaporation. Remove from the beaker when the solvent front is just at the top of th ...
Protein Structure Prediction
... Definition of -turn A -turn is defined by four consecutive residues i, i+1, i+2 and i+3 that do not form a helix and have a C(i)-C(i+3) distance less than 7Å and the turn lead to reversal in the protein chain. (Richardson, ...
... Definition of -turn A -turn is defined by four consecutive residues i, i+1, i+2 and i+3 that do not form a helix and have a C(i)-C(i+3) distance less than 7Å and the turn lead to reversal in the protein chain. (Richardson, ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.