Nucleotides and nucleic acids Structure of nucleotides Structure of
... DNA strands • The antiparallel strands of DNA are not identical, but are complementary. • This means that they are positioned to align complementary base pairs: C with G, and A with T. • So you can predict the sequence of one strand given the sequence of its complement. • Useful for information sto ...
... DNA strands • The antiparallel strands of DNA are not identical, but are complementary. • This means that they are positioned to align complementary base pairs: C with G, and A with T. • So you can predict the sequence of one strand given the sequence of its complement. • Useful for information sto ...
Building 3D models of proteins Why make a structural model for your
... This field is of great theoretical interest but, so far, of very little practical applications. Here there is no use of sequence alignments and no direct use of known structures The basic idea is to build empirical function that simulates real physical forces and potentials of chemical contacts If w ...
... This field is of great theoretical interest but, so far, of very little practical applications. Here there is no use of sequence alignments and no direct use of known structures The basic idea is to build empirical function that simulates real physical forces and potentials of chemical contacts If w ...
Biology - Meester Martinez
... A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the...: "proteins coded directly by genes." ...
... A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the...: "proteins coded directly by genes." ...
Nucleic Acids Notes
... One reason (out of many) why it is important to know how the DNA is folded up in the cell. The DNA in all your cells is identical. Yet cells are different. For instance, the DNA in the eye cells is exactly the same as in the tongue cells. But it is packed differently, exposing different parts for r ...
... One reason (out of many) why it is important to know how the DNA is folded up in the cell. The DNA in all your cells is identical. Yet cells are different. For instance, the DNA in the eye cells is exactly the same as in the tongue cells. But it is packed differently, exposing different parts for r ...
DNA (Gene) Mutations
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
... more) missing, added, or incorrect A mistake in the genetic code Wrong instructions wrong building materials wrong structure. ...
BOTANY DEPARTMENT - university of nairobi staff profiles
... the intricate nature of life. Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactio ...
... the intricate nature of life. Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactio ...
CATABOLISM OF PROTEINS AND AMINO ACIDS1.36 MB
... • NH3 production from intracellular renal glutamine increases in metabolic acidosis, decreases in ...
... • NH3 production from intracellular renal glutamine increases in metabolic acidosis, decreases in ...
MUTATIONS
... Types of mutations Point mutations (gene mutations) change in a single DNA base pair. Frameshift mutation single base added and deleted from DNA Chromosomal mutations changes in chromosomes. Insertion, deletion, inversion and translocation. ...
... Types of mutations Point mutations (gene mutations) change in a single DNA base pair. Frameshift mutation single base added and deleted from DNA Chromosomal mutations changes in chromosomes. Insertion, deletion, inversion and translocation. ...
Nucleic Acids and Nucleotides
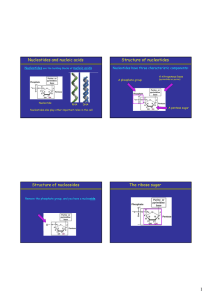
... adenine (A), guanine (G) cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Adenine and guanine are classi ed as purines. The primary structure of a purine is two carbon-nitrogen rings. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are classi ed as pyrimidines which have a single carbon-nitrogen ring as their primary structure (Figure ...
... adenine (A), guanine (G) cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Adenine and guanine are classi ed as purines. The primary structure of a purine is two carbon-nitrogen rings. Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are classi ed as pyrimidines which have a single carbon-nitrogen ring as their primary structure (Figure ...
The DNA sequence of the gene and genetic control sites for the
... sequences of an increasing number of Bacillus genes it will become possible to assess codon usage across the genome and investigate differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms (24). (c) Transcriptional and translational signals. There are several different forms of RNA polymerase i ...
... sequences of an increasing number of Bacillus genes it will become possible to assess codon usage across the genome and investigate differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms (24). (c) Transcriptional and translational signals. There are several different forms of RNA polymerase i ...
- Biological Sciences
... intergenic sequence contains an open reading frame of 24 codons, insertions and deletions in the other monotremes suggest that the sequence does not encode a polypeptide. No significant similarity to sequences in data banks exists and the sequence cannot be folded into any stable secondary structure ...
... intergenic sequence contains an open reading frame of 24 codons, insertions and deletions in the other monotremes suggest that the sequence does not encode a polypeptide. No significant similarity to sequences in data banks exists and the sequence cannot be folded into any stable secondary structure ...
Bell Activity
... E. Uses of Acids Acids are used in many areas of industry and in homes. Sulfuric acid is the most widely made industrial chemical in the world. It is used to make many products, including paper, paint, detergents, and fertilizers. ...
... E. Uses of Acids Acids are used in many areas of industry and in homes. Sulfuric acid is the most widely made industrial chemical in the world. It is used to make many products, including paper, paint, detergents, and fertilizers. ...
Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Transposition
... nucleotides that is not a multiple of three, this will cause frameshift mutations o Insertions or deletions consisting of nucleotides that are multiples of three are called in-frame insertions or deletions Based on the type of nucleotide substitution o Frequency of spontaneous mutations o Insertio ...
... nucleotides that is not a multiple of three, this will cause frameshift mutations o Insertions or deletions consisting of nucleotides that are multiples of three are called in-frame insertions or deletions Based on the type of nucleotide substitution o Frequency of spontaneous mutations o Insertio ...
Biochemistry of neurotransmitters
... Glutamate is released (1) and acts on NMDA receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron (2) Ca2+ enters the postsynaptic neuron and binds with calmodulin activating NOS (3) resulting in formation of NO and citrulline from L-arginine (4). ...
... Glutamate is released (1) and acts on NMDA receptors located on the postsynaptic neuron (2) Ca2+ enters the postsynaptic neuron and binds with calmodulin activating NOS (3) resulting in formation of NO and citrulline from L-arginine (4). ...
Protein: Amino Acids
... – The liver can produce nonessential amino acids. – Cells must dismantle to produce essential amino acids if they are not provided in the diet. – Limiting amino acids are those essential amino acids that are supplied in less than the amount needed to support protein synthesis. ...
... – The liver can produce nonessential amino acids. – Cells must dismantle to produce essential amino acids if they are not provided in the diet. – Limiting amino acids are those essential amino acids that are supplied in less than the amount needed to support protein synthesis. ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Nucleotide sequence of mRNA transcript is translated into an amino acid sequence in the polypeptide. - rRNA molecule within ribosome recognizes and binds to start sequence on mRNA. Moves along three nucleotides at a ...
... Nucleotide sequence of mRNA transcript is translated into an amino acid sequence in the polypeptide. - rRNA molecule within ribosome recognizes and binds to start sequence on mRNA. Moves along three nucleotides at a ...
From DNA to Protein WS
... Match codons of the mRNA strand you’ve created with their corresponding amino acids written on the line below them. Use the 1st 3 letters of the amino acid as abbreviations. The genetic code is found on page 207 of your text and on page 3 of accompanying WS. _________________________________________ ...
... Match codons of the mRNA strand you’ve created with their corresponding amino acids written on the line below them. Use the 1st 3 letters of the amino acid as abbreviations. The genetic code is found on page 207 of your text and on page 3 of accompanying WS. _________________________________________ ...
Monohybrid Crosses
... These nitrogen bases link together in three’s to form a codon and many codons link together to form a person’s genetic code. Codons, DNA triplets, code for one amino acid. Amino acids link together to form polypeptides-chain containing 2 or more amino acids Polypeptides make up proteins. Genes code ...
... These nitrogen bases link together in three’s to form a codon and many codons link together to form a person’s genetic code. Codons, DNA triplets, code for one amino acid. Amino acids link together to form polypeptides-chain containing 2 or more amino acids Polypeptides make up proteins. Genes code ...
Genetic variation
... Codominance – where both alleles present in the genotype of a heterozygous individual contribute to the individuals phenotype Multiple alleles – characteristic for which there are 3 or more alleles in the populations gene pool Sex-linked – genes present on one of the sex chromosomes Autosomal linkag ...
... Codominance – where both alleles present in the genotype of a heterozygous individual contribute to the individuals phenotype Multiple alleles – characteristic for which there are 3 or more alleles in the populations gene pool Sex-linked – genes present on one of the sex chromosomes Autosomal linkag ...
1. Ribonucleic acid is not normally associated with the (1) cytoplasm
... 10. Which nucleic acid carries instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm? (3) Transfer RNA, only (1) DNA, only (4) DNA, messenger RNA, and transfer RNA (2) Messenger RNA, only 11. Which of the following nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides? (3) Transfer RNA, only (1) DNA, only (2) Messenge ...
... 10. Which nucleic acid carries instructions from the nucleus to the cytoplasm? (3) Transfer RNA, only (1) DNA, only (4) DNA, messenger RNA, and transfer RNA (2) Messenger RNA, only 11. Which of the following nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides? (3) Transfer RNA, only (1) DNA, only (2) Messenge ...
Chapter 3: DNA and the Genetic Code
... constantly dying and being replenished with new cells. For example, the average life span of some skin cells is on the order of one to two days, so the skin that you and I had last month is not the same skin that we have today. By living into our eighties, we will have experienced well over 10,000 g ...
... constantly dying and being replenished with new cells. For example, the average life span of some skin cells is on the order of one to two days, so the skin that you and I had last month is not the same skin that we have today. By living into our eighties, we will have experienced well over 10,000 g ...
Full-Text PDF
... code evolution field since Crick’s hypothesis. Conceivably, frozen accident and the requirement of HGT were major, complementary factors that have kept the code universal. 3. The Three Principal Scenarios of the Code Origin and Evolution: Achievements, Limitations, and Compatibility The structure of ...
... code evolution field since Crick’s hypothesis. Conceivably, frozen accident and the requirement of HGT were major, complementary factors that have kept the code universal. 3. The Three Principal Scenarios of the Code Origin and Evolution: Achievements, Limitations, and Compatibility The structure of ...
EE 400: Practice using NCBI, Blast and Clustal
... B. You will see a big box for “Input sequences.” Go to your Word document with all the sequences, and copy them all from the first > to the last amino acid. Paste this into the box. The format we have been using is called fastA, which is accepted by this program. Make sure you are not putting any bl ...
... B. You will see a big box for “Input sequences.” Go to your Word document with all the sequences, and copy them all from the first > to the last amino acid. Paste this into the box. The format we have been using is called fastA, which is accepted by this program. Make sure you are not putting any bl ...
General Biology I Test V
... and what was labeled P32 and S35? • The Hershey-Chase experiment took a T2 bacteriophage which was composed only of DNA and protein, separately labeled the DNA with P32 and the proteins with S35 to see which was passed on to bacteria in infection. The radioactive phages were mixed with bacteria and ...
... and what was labeled P32 and S35? • The Hershey-Chase experiment took a T2 bacteriophage which was composed only of DNA and protein, separately labeled the DNA with P32 and the proteins with S35 to see which was passed on to bacteria in infection. The radioactive phages were mixed with bacteria and ...
Intermolecular interaction studies in some amino acids with aqueous
... Thermodynamic properties of amino acids i.e. proteins in electrolyte solution provide information about solute- solvent interactions, those are important in understanding the stability of Proteins. Some of these interactions are found applicable in several biochemical and physiological processses in ...
... Thermodynamic properties of amino acids i.e. proteins in electrolyte solution provide information about solute- solvent interactions, those are important in understanding the stability of Proteins. Some of these interactions are found applicable in several biochemical and physiological processses in ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.