Nucleotides - Mrs Miller's Blog | Science Revision
... producing a complementary strand. As base pairing rules apply, this lining up will be the same as it appears on the coding strand- apart from U in RNA replacing T in DNA If a DNA template strand code reads ATTCGCGTTAAT, what would the complementary MRNA strand read? UAAGCGCAAUUA Suggest why MRNA is ...
... producing a complementary strand. As base pairing rules apply, this lining up will be the same as it appears on the coding strand- apart from U in RNA replacing T in DNA If a DNA template strand code reads ATTCGCGTTAAT, what would the complementary MRNA strand read? UAAGCGCAAUUA Suggest why MRNA is ...
Modeling biological data and structure with probabilistic networks
... relative frequency of each amino acid in position i independently of other position. • The joint probability of X1, …, XL is defined by – P(X1,…,XL) = P(X1)P(X2)…P(XL) ...
... relative frequency of each amino acid in position i independently of other position. • The joint probability of X1, …, XL is defined by – P(X1,…,XL) = P(X1)P(X2)…P(XL) ...
Inheritance of biological information
... all within a group of species that are so similar to one another that most people cannot tell them apart.7 The chromosomes have been grossly scrambled, yet the cell is still able to extract the information it needs for survival. If the genes had been in control during such a scrambling process, Darw ...
... all within a group of species that are so similar to one another that most people cannot tell them apart.7 The chromosomes have been grossly scrambled, yet the cell is still able to extract the information it needs for survival. If the genes had been in control during such a scrambling process, Darw ...
DNA
... • The relationship between genes and their effects is complex • Despite the neatness of the genetic code, every gene cannot be simply lined to a single outcome • Some genes are expressed only at certain times or under some specific condition • Some traits result from the expression of multiple genes ...
... • The relationship between genes and their effects is complex • Despite the neatness of the genetic code, every gene cannot be simply lined to a single outcome • Some genes are expressed only at certain times or under some specific condition • Some traits result from the expression of multiple genes ...
Chapter 15
... • Francis Crick and Sydney Brenner determined how the order of nucleotides in DNA encoded amino acid order • Codon – block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid • Introduced single nulcleotide insertions or deletions and looked for mutations – Frameshift mutations ...
... • Francis Crick and Sydney Brenner determined how the order of nucleotides in DNA encoded amino acid order • Codon – block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid • Introduced single nulcleotide insertions or deletions and looked for mutations – Frameshift mutations ...
Functional dissection of the baculovirus late expression factor
... digestion. Mutations within the RNA polymerase homologous motif were created using the Transformer Site-Directed Mutagenesis kit (Clontech), whereas the remaining mutations were introduced using the Quik-Change Mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). Oligonucleotides used for mutagenesis are shown in Table 1, ...
... digestion. Mutations within the RNA polymerase homologous motif were created using the Transformer Site-Directed Mutagenesis kit (Clontech), whereas the remaining mutations were introduced using the Quik-Change Mutagenesis kit (Stratagene). Oligonucleotides used for mutagenesis are shown in Table 1, ...
A General Model of Codon Bias Due to GC Mutational Bias
... we find additional mysteries. For many codons, usage is well modeled as a linear function of GC bias. For example, Figure 1B ...
... we find additional mysteries. For many codons, usage is well modeled as a linear function of GC bias. For example, Figure 1B ...
Amino acidopathies: defects in amino acid metabolism
... 1. To distinguish between phenylketonuria (PKU) caused by phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) defect and PKU caused by defect in dihydropterin synthesis or regeneration. 2. To describe clinical symptoms and metabolic intermediates indicative of PKU. 3. To explain the cause and symptoms of albinism and a ...
... 1. To distinguish between phenylketonuria (PKU) caused by phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) defect and PKU caused by defect in dihydropterin synthesis or regeneration. 2. To describe clinical symptoms and metabolic intermediates indicative of PKU. 3. To explain the cause and symptoms of albinism and a ...
Introduction to amino acid metabolism Overview - Rose
... usable nitrogen. Nitrate is formed by microorganisms that can use ammonium as an energy source, and is thus the lowest energy form of nitrogen. On the other hand, nitrate and other nitrogen oxides are major components in explosives, which is why fertilizer can be dangerous. The explosive potential o ...
... usable nitrogen. Nitrate is formed by microorganisms that can use ammonium as an energy source, and is thus the lowest energy form of nitrogen. On the other hand, nitrate and other nitrogen oxides are major components in explosives, which is why fertilizer can be dangerous. The explosive potential o ...
Human fertility gene found - Carole Ober
... which reduces both genetic and environmental noise that can confound studies of inheritance. Carole Ober, a geneticist at the University of Chicago who has been studying fertility in a population of Hutterites in South Dakota for more than 20 years, showed two years ago that reproductive success had ...
... which reduces both genetic and environmental noise that can confound studies of inheritance. Carole Ober, a geneticist at the University of Chicago who has been studying fertility in a population of Hutterites in South Dakota for more than 20 years, showed two years ago that reproductive success had ...
Oxyntomodulin - Pacific Biomarkers
... remain unclear. Its importance as a biologically active peptide would be greatly strengthened by the identification of a separate oxyntomodulin receptor, or by studies employing specific oxyntomodulin antagonists or immunoneutralizing antisera that blocked actions of oxyntomodulin but not glucagon o ...
... remain unclear. Its importance as a biologically active peptide would be greatly strengthened by the identification of a separate oxyntomodulin receptor, or by studies employing specific oxyntomodulin antagonists or immunoneutralizing antisera that blocked actions of oxyntomodulin but not glucagon o ...
Ethical Issues in Genetic Testing: the Duty to Warn At
... • MG more likely to disclose than GC, but both GC & MG less likely to disclose than non-genetics MD* • More recent studies focus on cancer and sudden death risks, still theoretical ...
... • MG more likely to disclose than GC, but both GC & MG less likely to disclose than non-genetics MD* • More recent studies focus on cancer and sudden death risks, still theoretical ...
Metabolism
... Metabolic Rate and Body Heat Production • Basic metabolic rate (BMR) reflects the amount of energy spent per unit of time by a body at rest ...
... Metabolic Rate and Body Heat Production • Basic metabolic rate (BMR) reflects the amount of energy spent per unit of time by a body at rest ...
PPCMatrix: a PowerPC dotmatrix program to compare large
... software GeneJockey II. The 3-frame nested translation dotmatrix is especially useful in those cases, when open reading frames in the genomic sequence are interrupted by introns or frameshifts (sequencing errors) and coding regions are found in different frames. The new feature of the 3-frame nested ...
... software GeneJockey II. The 3-frame nested translation dotmatrix is especially useful in those cases, when open reading frames in the genomic sequence are interrupted by introns or frameshifts (sequencing errors) and coding regions are found in different frames. The new feature of the 3-frame nested ...
8-30-16 Macomolecule Foldable Instructions
... 3. Sketch and label the parts of a NUCLEOTIDE 4. List the base pairs (what base pairs with what other base) BACK SIDE OF TABS: Tab A 1. Give 4 FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS and EXPLAIN what is meant by that function 2. List 2 EXAMPLES OF PROTEINS and WHERE you would find that protein 3. Describe each level ...
... 3. Sketch and label the parts of a NUCLEOTIDE 4. List the base pairs (what base pairs with what other base) BACK SIDE OF TABS: Tab A 1. Give 4 FUNCTIONS OF PROTEINS and EXPLAIN what is meant by that function 2. List 2 EXAMPLES OF PROTEINS and WHERE you would find that protein 3. Describe each level ...
CHAPTER 6 Molecular Genetics: From DNA to Proteins
... nucleic acid, is made from nucleotide monomers, and the DNA double helix consists of two polynucleotide chains. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing base (A, C, G, or T). The sugar-phosphate backbone of the double helix was discussed in the ...
... nucleic acid, is made from nucleotide monomers, and the DNA double helix consists of two polynucleotide chains. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing base (A, C, G, or T). The sugar-phosphate backbone of the double helix was discussed in the ...
Protein Synthesis - Sonoma Valley High School
... 2) DNA must replicate itself exactly prior to each cell ...
... 2) DNA must replicate itself exactly prior to each cell ...
Nitrogen Metabolism - Oregon State University
... Can Be Reduced to Nitric Oxide in Hypoxic Conditions In Human Diet 80-90% from Reduction of Nitrates in Vegetables Nitrates in Vegetables From Fertilizers or Plant Stresses Nitrite Readily Forms Cancer-Causing Nitrosamines in Stomach Acid Nitrites Oxidize Hemoglobin’s Iron From Ferrous (II) to Ferri ...
... Can Be Reduced to Nitric Oxide in Hypoxic Conditions In Human Diet 80-90% from Reduction of Nitrates in Vegetables Nitrates in Vegetables From Fertilizers or Plant Stresses Nitrite Readily Forms Cancer-Causing Nitrosamines in Stomach Acid Nitrites Oxidize Hemoglobin’s Iron From Ferrous (II) to Ferri ...
Lect 9: BioMacromolecular Visualization I: Principles - BIDD
... Knowledge of their structure useful for drug design ...
... Knowledge of their structure useful for drug design ...
Minimum Essential Medium Eagle (MEM)
... User must ensure suitability of the product(s) in their application prior to use. Products conform solely to the information contained in this and other related HiMedia™ publications. The information contained in this publication is based on our research and development work and is to the best of ou ...
... User must ensure suitability of the product(s) in their application prior to use. Products conform solely to the information contained in this and other related HiMedia™ publications. The information contained in this publication is based on our research and development work and is to the best of ou ...
Role of insulin
... -HLA complex contains genes for the class II MHC molecules which present antigen to helper T cells and are thus involved in initiating the immune response -ability of class II MHC molecules to present antigen is dependent on the amino acid composition of their antigen binding sites ...
... -HLA complex contains genes for the class II MHC molecules which present antigen to helper T cells and are thus involved in initiating the immune response -ability of class II MHC molecules to present antigen is dependent on the amino acid composition of their antigen binding sites ...
Towards a Phylogeny of Bacteriophage via Protein Importance
... two proteins. The value of the function at the optimized t is a transition probability matrix for the amino acid transition probability. Note that the same amino acid transition rate matrix, Q, is determined for an entire family of proteins, but there is a different transition probability matrix, P, ...
... two proteins. The value of the function at the optimized t is a transition probability matrix for the amino acid transition probability. Note that the same amino acid transition rate matrix, Q, is determined for an entire family of proteins, but there is a different transition probability matrix, P, ...
ORIGIN OF LIFE ON EARTH
... reactions at that time. Cairns & Smith (1971), however, believe that the earliest genes were minerals associated with proteins, capable of self-replicating and coding for useful proteins. Nucleic acids as coding material came later and being more efficient were selected out against minerals. It is n ...
... reactions at that time. Cairns & Smith (1971), however, believe that the earliest genes were minerals associated with proteins, capable of self-replicating and coding for useful proteins. Nucleic acids as coding material came later and being more efficient were selected out against minerals. It is n ...
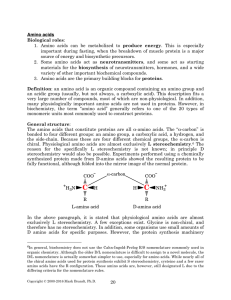
Amino Acids - Rose
... chiral. Physiological amino acids are almost exclusively L stereochemistry.6 The reason for the specifically L stereochemistry is not known; in principle D stereochemistry would also be possible. Experiments performed using a chemically synthesized protein made from D-amino acids showed the resultin ...
... chiral. Physiological amino acids are almost exclusively L stereochemistry.6 The reason for the specifically L stereochemistry is not known; in principle D stereochemistry would also be possible. Experiments performed using a chemically synthesized protein made from D-amino acids showed the resultin ...
The Spandrels of San Marco Adaptation or Drift?
... • Organisms are more than collections of traits. ...
... • Organisms are more than collections of traits. ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.