3. Biotechnological Importance of MO - Copy
... 1. Nutritional characteristics of the organism when grown on a cheap medium 2. Optimum temp of the organism 3. Reaction of the organism with the equipment and suitability for the type of process 4. Stability of the organism and its amenability for genetic ...
... 1. Nutritional characteristics of the organism when grown on a cheap medium 2. Optimum temp of the organism 3. Reaction of the organism with the equipment and suitability for the type of process 4. Stability of the organism and its amenability for genetic ...
charles darwin theory of evolution and mordern genetic engineering
... the European Union,2001). If genetic material is added to a host, the resulting organism is said to be transgenic. If genetic material is added from same specie or specie that can naturally breed with the host is employed, the resulting organism is said to be cisgenic. Humans have altered the genome ...
... the European Union,2001). If genetic material is added to a host, the resulting organism is said to be transgenic. If genetic material is added from same specie or specie that can naturally breed with the host is employed, the resulting organism is said to be cisgenic. Humans have altered the genome ...
Robots Walking by Using GA
... the process of natural evolution. This heuristic is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems. Genetic algorithms belong to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA), which generate solutions to optimization problems using techniques inspired by natural e ...
... the process of natural evolution. This heuristic is routinely used to generate useful solutions to optimization and search problems. Genetic algorithms belong to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA), which generate solutions to optimization problems using techniques inspired by natural e ...
Independent evolution of overlapping polymerase and surface
... The overall mean Dn and Ds in the overlapping region of the P and S genes, calculated by using the MEGA program, were similar for both genes: for P, respectively 0.035±0.005 and 0.109±0.014 (Dn/Ds ratio of 0.32), and for S, respectively 0.041±0.005 and 0.092±0.015 (Dn/Ds ratio of 0.45). Hence, negat ...
... The overall mean Dn and Ds in the overlapping region of the P and S genes, calculated by using the MEGA program, were similar for both genes: for P, respectively 0.035±0.005 and 0.109±0.014 (Dn/Ds ratio of 0.32), and for S, respectively 0.041±0.005 and 0.092±0.015 (Dn/Ds ratio of 0.45). Hence, negat ...
CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2 -CH 2
... rate of a reaction, the following events must take place. 1. The enzyme must form a temporary association with the substance or substances whose reaction rate it affects. These substances are known as substrates. 2. The association between enzyme and substrate is thought to form a close physical ass ...
... rate of a reaction, the following events must take place. 1. The enzyme must form a temporary association with the substance or substances whose reaction rate it affects. These substances are known as substrates. 2. The association between enzyme and substrate is thought to form a close physical ass ...
Lecture on PROTEIN FOLDING
... Proteins loose their 3-D shape (denature) when the weak bonds that hold together the structure are broken. Weak bonds are broken when the temperature is raised from body temp (37 C) to about 60 C Or by changing the pH Or by using chemical agents ...
... Proteins loose their 3-D shape (denature) when the weak bonds that hold together the structure are broken. Weak bonds are broken when the temperature is raised from body temp (37 C) to about 60 C Or by changing the pH Or by using chemical agents ...
Genetic Mutations SDK Nov 2, 2012
... Types of Mutations according to their effects on the protein (or mRNA). Silent Mutations. Mutation in a codons that produce same amino acid. These mutations affect the DNA but not the protein. Therefore they have no effect on the organism’s phenotype. CUU CUC Missense Mutations. Missense mutations ...
... Types of Mutations according to their effects on the protein (or mRNA). Silent Mutations. Mutation in a codons that produce same amino acid. These mutations affect the DNA but not the protein. Therefore they have no effect on the organism’s phenotype. CUU CUC Missense Mutations. Missense mutations ...
Amino Acid Synthesis Inhibitors-Group 2 Mode of
... -Mechanisms by which a herbicide causes plant death -The suite of plant process interfered with by a herbicide at the tissue or cellular level -How a herbicide kills a plant ...
... -Mechanisms by which a herbicide causes plant death -The suite of plant process interfered with by a herbicide at the tissue or cellular level -How a herbicide kills a plant ...
DOC
... any correlation between the concentrations of free amino acid in whole-body and dietary amino acid composition does not preclude the possibility that amino acid requirements of crustaceans could be estimated by analysis of levels in the hemolymph [14]. The amino acid flux of the lobsters also sugges ...
... any correlation between the concentrations of free amino acid in whole-body and dietary amino acid composition does not preclude the possibility that amino acid requirements of crustaceans could be estimated by analysis of levels in the hemolymph [14]. The amino acid flux of the lobsters also sugges ...
Word
... B) N5, N10-methylene tetrahydrofolate (methylene THF) C) N5-methyl tetrahydrofolate (methyl THF) D) S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) E) methotrexate 21) Identify the direct donor of the one-carbon units in the reaction shown below, catalyzed by phosphatidylethanolamine methyl transferase. ...
... B) N5, N10-methylene tetrahydrofolate (methylene THF) C) N5-methyl tetrahydrofolate (methyl THF) D) S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) E) methotrexate 21) Identify the direct donor of the one-carbon units in the reaction shown below, catalyzed by phosphatidylethanolamine methyl transferase. ...
MGY314H Principles of Genetic Analysis I Bacterial Genetics Sept
... will perform several experiments over the 12-week period. You will carry out a variety of crosses, mutant hunts, and phenotypic characterization in bacteria, and learn to analyze and interpret the genetic data that you obtain. Most of your time will be in the lab, with some tutorials and short lectu ...
... will perform several experiments over the 12-week period. You will carry out a variety of crosses, mutant hunts, and phenotypic characterization in bacteria, and learn to analyze and interpret the genetic data that you obtain. Most of your time will be in the lab, with some tutorials and short lectu ...
Student Overview - 3D Molecular Designs
... The function of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen to your body’s cells. After you have folded the β-globin model, you will see how its structure makes it possible for hemoglobin to transport oxygen to your cells. ...where molecules become real TM ...
... The function of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen to your body’s cells. After you have folded the β-globin model, you will see how its structure makes it possible for hemoglobin to transport oxygen to your cells. ...where molecules become real TM ...
AAlast+nuc
... 2. Which ribosomal amino acid’s biosynthesis is closely associated with the urea cycle? ...
... 2. Which ribosomal amino acid’s biosynthesis is closely associated with the urea cycle? ...
1 - SMIC Nutrition Science
... in sufficient oxygen to support the electron transport chain’s continued generation of ATP. Answer (key points): When endurance athletes cannot take in enough oxygen to meet the body’s demands for the large amounts of oxygen needed to produce ATP via the electron transport chain, pyruvate remains in ...
... in sufficient oxygen to support the electron transport chain’s continued generation of ATP. Answer (key points): When endurance athletes cannot take in enough oxygen to meet the body’s demands for the large amounts of oxygen needed to produce ATP via the electron transport chain, pyruvate remains in ...
For lecture notes click here
... body can synthesize roughly half of the various amino acids needed to build proteins are 10 essential amino acids. You cannot synthesize eight of them (isoleucine, leucine, lysine, threonine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, valine, and methionine); the other two (arginine and histidine) can be synthe ...
... body can synthesize roughly half of the various amino acids needed to build proteins are 10 essential amino acids. You cannot synthesize eight of them (isoleucine, leucine, lysine, threonine, tryptophan, phenylalanine, valine, and methionine); the other two (arginine and histidine) can be synthe ...
Diagnostic Genetic Testing of a Potentially Affected
... Check all that apply to the individual: Individual has symptoms of a genetic disorder Individual is at risk for a late onset genetic disorder or slowly evolving genetic disorder Individual has melanoma (hereditary) Individual has amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig's disease ...
... Check all that apply to the individual: Individual has symptoms of a genetic disorder Individual is at risk for a late onset genetic disorder or slowly evolving genetic disorder Individual has melanoma (hereditary) Individual has amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig's disease ...
FEMS ML 00 CODH cooF
... cally related to the CooS of Methanococcus and Archaeoglobus. cooS genes from other methanogenic archaea, such as M. thermoautotrophicum and M. soehngenii, cluster together and are distinct from the cooS genes from anaerobic bacteria and Methanococcus/Archaeoglobus. A functionally essential cysteine ...
... cally related to the CooS of Methanococcus and Archaeoglobus. cooS genes from other methanogenic archaea, such as M. thermoautotrophicum and M. soehngenii, cluster together and are distinct from the cooS genes from anaerobic bacteria and Methanococcus/Archaeoglobus. A functionally essential cysteine ...
A STUDY OF THE AMINO ACIDS ASSOCIATED WITH OVALBUMIN
... subscripts represent varying amounts of the sugars as the oligosaccharide is usually heterogeneous. Another crystalline form of ovalbumin was discovered by Linderstrom-Lang and Ottesen (1947) in solutions of ovalbumin that had been allowed to stand without an antiseptic. named plakalbumin since it c ...
... subscripts represent varying amounts of the sugars as the oligosaccharide is usually heterogeneous. Another crystalline form of ovalbumin was discovered by Linderstrom-Lang and Ottesen (1947) in solutions of ovalbumin that had been allowed to stand without an antiseptic. named plakalbumin since it c ...
Genetic testing - Science Museum
... whether or not they have inherited the altered gene, but cannot predict when they will start to develop symptoms, which usually happens between the ages of 30 and 50. ...diabetes? There are two main types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes develops when the insulin-producing cells in the body have been de ...
... whether or not they have inherited the altered gene, but cannot predict when they will start to develop symptoms, which usually happens between the ages of 30 and 50. ...diabetes? There are two main types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes develops when the insulin-producing cells in the body have been de ...
Worksheet 1 (isolation)
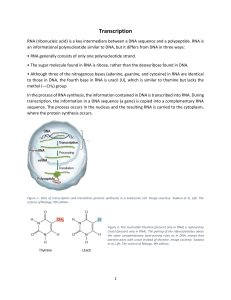
... Besides the coding information (exons), DNA contains a lot of non-coding information (introns). During RNA processing these non-coding parts are removed. Before the synthesis of a protein starts, the corresponding RNA molecule is formed by RNA transcription. One strand of the DNA double helix is use ...
... Besides the coding information (exons), DNA contains a lot of non-coding information (introns). During RNA processing these non-coding parts are removed. Before the synthesis of a protein starts, the corresponding RNA molecule is formed by RNA transcription. One strand of the DNA double helix is use ...
ppt
... Besides the coding information (exons), DNA contains a lot of non-coding information (introns). During RNA processing these non-coding parts are removed. Before the synthesis of a protein starts, the corresponding RNA molecule is formed by RNA transcription. One strand of the DNA double helix is use ...
... Besides the coding information (exons), DNA contains a lot of non-coding information (introns). During RNA processing these non-coding parts are removed. Before the synthesis of a protein starts, the corresponding RNA molecule is formed by RNA transcription. One strand of the DNA double helix is use ...
metabolism in muscle and nerves
... Peroxisomes (X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy) Lysosomes (GM2 gangliosidoses - Tay Sachs disease) ...
... Peroxisomes (X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy) Lysosomes (GM2 gangliosidoses - Tay Sachs disease) ...
Transcription and RNA processing
... In bacterial cells, the holoenzyme (RNA polymerase plus sigma) recognizes and binds directly to sequences in the promoter. In eukaryotic cells, promoter recognition is carried out by accessory proteins (transcription factors) that bind to the promoter and then recruit a specific RNA polymerase (I, II ...
... In bacterial cells, the holoenzyme (RNA polymerase plus sigma) recognizes and binds directly to sequences in the promoter. In eukaryotic cells, promoter recognition is carried out by accessory proteins (transcription factors) that bind to the promoter and then recruit a specific RNA polymerase (I, II ...
The Future of the Gene -
... severe ones, are not determined by genetic defects but by other, environmental pre- and perinatal conditions. The decision to procreate entails the risk to have offspring affected by various kinds of diseases and malformations, of which only very few can be avoided by genetic testing. Once on the wa ...
... severe ones, are not determined by genetic defects but by other, environmental pre- and perinatal conditions. The decision to procreate entails the risk to have offspring affected by various kinds of diseases and malformations, of which only very few can be avoided by genetic testing. Once on the wa ...
Preview Sample 2
... A sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds is known as a polypeptide. Strictly speaking, the term polypeptide refers to a structural unit and does not necessarily suggest that the molecule is functional. By convention, if the number of amino acids in a polypeptide is 50 or fewer and has a kno ...
... A sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds is known as a polypeptide. Strictly speaking, the term polypeptide refers to a structural unit and does not necessarily suggest that the molecule is functional. By convention, if the number of amino acids in a polypeptide is 50 or fewer and has a kno ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.