an introduction to alpha-fetoprotein and the growth inhibitory peptide
... Proteins are classified into several broad classes based on the functional role played by them within the body. • Structural proteins- which provide structural rigidity to the cell. • Transport proteins- those which control the flow of materials across the body and cellular membranes e.g. albumin an ...
... Proteins are classified into several broad classes based on the functional role played by them within the body. • Structural proteins- which provide structural rigidity to the cell. • Transport proteins- those which control the flow of materials across the body and cellular membranes e.g. albumin an ...
Study Guide for Transcription.
... into protein. Exons are the sequences in the primary transcript that become part of the messenger RNA that is transported into the cytoplasm. --most but not all eukaryotic genes have introns. --introns are spliced out by spliceosomes, which are assembled from several snRNPs, which are protein/RNA hy ...
... into protein. Exons are the sequences in the primary transcript that become part of the messenger RNA that is transported into the cytoplasm. --most but not all eukaryotic genes have introns. --introns are spliced out by spliceosomes, which are assembled from several snRNPs, which are protein/RNA hy ...
2491456_Gajda JChildNeurol_pre
... electron-dense, rod-shaped structures appearing as thickened Z-disks.1-3 Muscle imaging by MR can be helpful to visualize the pattern of selective muscle involvement and guide in localizing the site of the biopsy.7,8 The work up of a case with nemaline myopathy is further complicated by its heteroge ...
... electron-dense, rod-shaped structures appearing as thickened Z-disks.1-3 Muscle imaging by MR can be helpful to visualize the pattern of selective muscle involvement and guide in localizing the site of the biopsy.7,8 The work up of a case with nemaline myopathy is further complicated by its heteroge ...
Test 1
... iii. Double helix with bases forming hydrogen bonds. iv. Watson/Crick 1953 solved structure. Rosalind Franklin provided key evidence ( b. Replication (Fig. 4.11) i. Replication occurs during S phase of the cell cycle. ii. Free nucleotides are linked by the enzyme DNA polymerase iii. Replication begi ...
... iii. Double helix with bases forming hydrogen bonds. iv. Watson/Crick 1953 solved structure. Rosalind Franklin provided key evidence ( b. Replication (Fig. 4.11) i. Replication occurs during S phase of the cell cycle. ii. Free nucleotides are linked by the enzyme DNA polymerase iii. Replication begi ...
File
... • Protein Adaptation and Evolution – Adaptations are traits that improve the chance of survival of an organism in a specific environment. – Proteins are subject to natural selection. – Members of a protein family are thought to have evolved from a single ancestor gene. – A particular protein may hav ...
... • Protein Adaptation and Evolution – Adaptations are traits that improve the chance of survival of an organism in a specific environment. – Proteins are subject to natural selection. – Members of a protein family are thought to have evolved from a single ancestor gene. – A particular protein may hav ...
L16-Enzyme Structure
... lowest-energy conformation which, owing to the uniqueness of the primary structure, is very precise. The polarity of the amino acid functional groups dictates the affinity of particular peptide sequences for water. Hydrophilic sequences favour positions on the surface of the enzyme, while hydrophobi ...
... lowest-energy conformation which, owing to the uniqueness of the primary structure, is very precise. The polarity of the amino acid functional groups dictates the affinity of particular peptide sequences for water. Hydrophilic sequences favour positions on the surface of the enzyme, while hydrophobi ...
Nuclear and mitochondrial forms of human uracil
... synthesised in the cytoplasm, and imported into their respective • To whom correspondence should be addressed ...
... synthesised in the cytoplasm, and imported into their respective • To whom correspondence should be addressed ...
RNA Structure
... mature RNA and that will be translated into protein so that’s the main purpose of mRNA, which is encoding the genetic information into protein. f. There is RNA that helps in the translation of RNA. There are two that are important to help the translation of mRNA. One is rRNA. XXVII. Ribosomal RNA (r ...
... mature RNA and that will be translated into protein so that’s the main purpose of mRNA, which is encoding the genetic information into protein. f. There is RNA that helps in the translation of RNA. There are two that are important to help the translation of mRNA. One is rRNA. XXVII. Ribosomal RNA (r ...
Evaluation of volatile compounds produced by Lactobacillus
... (5 min). Hydrogen was used as carrier gas at a flow rate of 2.0 mL.min−1. The FID detector temperature was setup at 290 °C. Volatile compounds were identified by matching their retention time with those of standard compounds (when available) and by calculating linear retention indexes (LRI) accordin ...
... (5 min). Hydrogen was used as carrier gas at a flow rate of 2.0 mL.min−1. The FID detector temperature was setup at 290 °C. Volatile compounds were identified by matching their retention time with those of standard compounds (when available) and by calculating linear retention indexes (LRI) accordin ...
Document
... – Partitioning of the alignment (variant - various rates, invariant sites, secondary structure, protein domains…) – Amino acid groupings (6 categories - GTR like) – LogDet for proteins - rare/absent changes? For long alignments? – DNA based LogDet or the protein alignment…? ...
... – Partitioning of the alignment (variant - various rates, invariant sites, secondary structure, protein domains…) – Amino acid groupings (6 categories - GTR like) – LogDet for proteins - rare/absent changes? For long alignments? – DNA based LogDet or the protein alignment…? ...
The Two Major Membrane Skeletal Proteins (Articulins) of Euglena
... The most abundant proteins of the Euglena membrane skeleton are the equimolar articulins (Mr = 80 and 86; Dubreuil and Bouck, 1985). The articulins appear to form hetero-oligomers that when solubilized by urea or NaOH can reassemble on NaOH stripped membranes (Dubreuil and Bouck, 1988). Articulins i ...
... The most abundant proteins of the Euglena membrane skeleton are the equimolar articulins (Mr = 80 and 86; Dubreuil and Bouck, 1985). The articulins appear to form hetero-oligomers that when solubilized by urea or NaOH can reassemble on NaOH stripped membranes (Dubreuil and Bouck, 1988). Articulins i ...
Conformational Analysis Protein Folding Protein Structure
... The underlying principle that can be deduced from Anfisen's experiment is that the energetically favored state of a protein coincides with its correctly folded one. However, Levinthal demonstrated that a systematic random search of all possible conformations of the protein would take almost infinite ...
... The underlying principle that can be deduced from Anfisen's experiment is that the energetically favored state of a protein coincides with its correctly folded one. However, Levinthal demonstrated that a systematic random search of all possible conformations of the protein would take almost infinite ...
Genetic Counseling in the Prenatal Settting
... Concern by advocates for persons with disabilities, feminists, and bioethicists – At the core of the medical model view is that “disability must be prevented, because disabled people cannot function within existing society” ...
... Concern by advocates for persons with disabilities, feminists, and bioethicists – At the core of the medical model view is that “disability must be prevented, because disabled people cannot function within existing society” ...
Conversion of amino acids to specialized products
... 5) Type III porphyrines (e.g. uroporphyrin III) which contain an asymmetric substitution on ring D are physiologically important in humans. Porphyrinogens: porphyrin precursors, intermediate between porphobilinogen and the oxidized colored protoporphyrins in heme biosyhthesis. ...
... 5) Type III porphyrines (e.g. uroporphyrin III) which contain an asymmetric substitution on ring D are physiologically important in humans. Porphyrinogens: porphyrin precursors, intermediate between porphobilinogen and the oxidized colored protoporphyrins in heme biosyhthesis. ...
Asymptotic Genetic Improvement Programming via Type Functors
... Genetic Improvement Programming (GIP) is an increasingly important technique for software maintenance. It employs Genetic Programming (GP) to optimize human-generated source code for a variety of functional and non-functional properties [1]. For example, it has been successfully used to improve runt ...
... Genetic Improvement Programming (GIP) is an increasingly important technique for software maintenance. It employs Genetic Programming (GP) to optimize human-generated source code for a variety of functional and non-functional properties [1]. For example, it has been successfully used to improve runt ...
Gentile, Margaret: Computational Methods for the Design of PCR Primers for the Amplification of functional Markers from Environmental Samples
... Challenges of primer design for unknown, diverse sequences The design of a primer to amplify a gene of interest from all species present differs from the applications described above, because the sequence to be amplified is not actually known and can be quite different from known sequences of the ge ...
... Challenges of primer design for unknown, diverse sequences The design of a primer to amplify a gene of interest from all species present differs from the applications described above, because the sequence to be amplified is not actually known and can be quite different from known sequences of the ge ...
A SOLUBLE RIBONUCLEIC ACID INTERMEDIATE IN PROTEIN
... to effect a dilution in the absence of added ATP would be anticipated since, due to the high ATPase activity of the preparation and the absence of a generating system, the ATP concentration would be effectively zero and the reaction would proceed rapidly to the left. It is of interest in this connec ...
... to effect a dilution in the absence of added ATP would be anticipated since, due to the high ATPase activity of the preparation and the absence of a generating system, the ATP concentration would be effectively zero and the reaction would proceed rapidly to the left. It is of interest in this connec ...
Unique Human Subjects Concerns for j Genetic Research
... Shift of focus from specific mutation associated with a rare disease to pattern of more common variations (genetic signature) g ) associated with more common conditions genome has Possible because entire human g been sequenced: alternate versions of single nucleotides (SNPs) have been id tifi d (3 m ...
... Shift of focus from specific mutation associated with a rare disease to pattern of more common variations (genetic signature) g ) associated with more common conditions genome has Possible because entire human g been sequenced: alternate versions of single nucleotides (SNPs) have been id tifi d (3 m ...
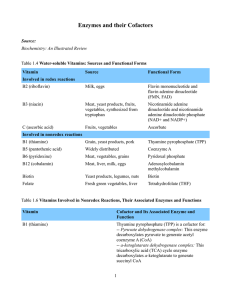
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... cofactors for: -- Methylmalonyl CoA mutase: This enzyme isomerizes methylmalonyl CoA into succinyl CoA in a reaction that is part of the pathway that degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrof ...
... cofactors for: -- Methylmalonyl CoA mutase: This enzyme isomerizes methylmalonyl CoA into succinyl CoA in a reaction that is part of the pathway that degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrof ...
2011_InstructorSlidesR
... about themselves or the surrounding microbial environment • Run 2-3 different projects, to keep group number to a manageable size and so different groups can present to and learn from each other • Select genes for study that have easily-identifiable differences in DNA sequence in the test population ...
... about themselves or the surrounding microbial environment • Run 2-3 different projects, to keep group number to a manageable size and so different groups can present to and learn from each other • Select genes for study that have easily-identifiable differences in DNA sequence in the test population ...
Sickle Cell Handout
... (mRNA) sequences that corresponds to the DNA sequences that you examined in Part B. One member of the group should determine the mRNA sequence that results from the DNA sequence that represents the allele for Normal Hemoglobin. The other group member should transcribe the mRNA from the DNA sequence ...
... (mRNA) sequences that corresponds to the DNA sequences that you examined in Part B. One member of the group should determine the mRNA sequence that results from the DNA sequence that represents the allele for Normal Hemoglobin. The other group member should transcribe the mRNA from the DNA sequence ...
LecturesPart07
... A.J. Gibbs & G.A. McIntyre. The diagram, a method for comparing sequences. Its use with amino acid and nucleotide sequences. Eur. J. Biochem. 16:1-11 (1970) A.D. McLachlan. Test for comparing related amino acid sequences: cytochrome c and cytochrome c551. J. Mol. Biol. 61:409-424 ...
... A.J. Gibbs & G.A. McIntyre. The diagram, a method for comparing sequences. Its use with amino acid and nucleotide sequences. Eur. J. Biochem. 16:1-11 (1970) A.D. McLachlan. Test for comparing related amino acid sequences: cytochrome c and cytochrome c551. J. Mol. Biol. 61:409-424 ...
Green Dew Natural HGH Releaser
... Take 16 grams (one table spoon) with water or juice per 150 pounds of body weight before sleep or between meals on an empty stomach. This products would be taken for 6 days in a row. The seventh day is a day off in process called "cycling". ...
... Take 16 grams (one table spoon) with water or juice per 150 pounds of body weight before sleep or between meals on an empty stomach. This products would be taken for 6 days in a row. The seventh day is a day off in process called "cycling". ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.