Chapter 14 The Milky Way Galaxy
... 14.3 Galactic Structure The galactic halo and globular clusters formed very early; the halo is essentially spherical. All the stars in the halo are very old, and there is no gas and dust. The galactic disk is where the youngest stars are, as well as star formation regions – emission nebulae, large ...
... 14.3 Galactic Structure The galactic halo and globular clusters formed very early; the halo is essentially spherical. All the stars in the halo are very old, and there is no gas and dust. The galactic disk is where the youngest stars are, as well as star formation regions – emission nebulae, large ...
Click here to get the file
... will be introduced to pulsars. The flux from pulsars is low at frequencies that can be measured with the 4.6-m radio telescope. So, data from the PARI pulsar timing project, measuring the flux from pulsars at 400 MHz using one of the PARI 26-m radio telescopes, will be made available for students to ...
... will be introduced to pulsars. The flux from pulsars is low at frequencies that can be measured with the 4.6-m radio telescope. So, data from the PARI pulsar timing project, measuring the flux from pulsars at 400 MHz using one of the PARI 26-m radio telescopes, will be made available for students to ...
Astronomy`ssixth annual STAR PRODUCTS
... system, Celestron’s 11-inch “RASA” could be your next purchase. Optical designers Dave Rowe and Mark Ackermann have come up with an update to Celestron’s classic Schmidt Camera that accepts both 42mm T-thread and 48mm camera adapters. This means that dedicated CCD imagers as well as popular DSLR cam ...
... system, Celestron’s 11-inch “RASA” could be your next purchase. Optical designers Dave Rowe and Mark Ackermann have come up with an update to Celestron’s classic Schmidt Camera that accepts both 42mm T-thread and 48mm camera adapters. This means that dedicated CCD imagers as well as popular DSLR cam ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... in 8" telescopes under good seeing conditions. NGC4736 (M94) (8.2) sg. Locate B CVn and move 3o east to locate the tightly wound spiral galaxy which has a very bright core. 16" (40cm) telescopes reveal a hazy ring infilled with dusky mottling surrounding the core. NGC5005 (10.8) sg. Located to the S ...
... in 8" telescopes under good seeing conditions. NGC4736 (M94) (8.2) sg. Locate B CVn and move 3o east to locate the tightly wound spiral galaxy which has a very bright core. 16" (40cm) telescopes reveal a hazy ring infilled with dusky mottling surrounding the core. NGC5005 (10.8) sg. Located to the S ...
script (powerpoint)
... If there is no bright (mag ~ 14-15) nearby star then you must use an artificial star or „laser guide star“. All laser guide AO systems use a sodium laser tuned to Na 5890 Å pointed to the 11.5 km thick layer of enhanced sodium at an altitude of ...
... If there is no bright (mag ~ 14-15) nearby star then you must use an artificial star or „laser guide star“. All laser guide AO systems use a sodium laser tuned to Na 5890 Å pointed to the 11.5 km thick layer of enhanced sodium at an altitude of ...
Nova
... Roche lobe, gas moves into the Roche lobe of the companion star and is pulled in toward that star. This process of mass transfer is referred to as Roche lobe overflow. Binaries in this stage of mass transfer are called semi-detached binaries, because only one of the stars is actually in contact with ...
... Roche lobe, gas moves into the Roche lobe of the companion star and is pulled in toward that star. This process of mass transfer is referred to as Roche lobe overflow. Binaries in this stage of mass transfer are called semi-detached binaries, because only one of the stars is actually in contact with ...
galaxy - 106Thursday130-430
... contains the highest density of stars in the galaxy. Although some hot young stars may be found in the nucleus, the primary population of stars there is similar to the old stars found in the halo. ...
... contains the highest density of stars in the galaxy. Although some hot young stars may be found in the nucleus, the primary population of stars there is similar to the old stars found in the halo. ...
Recurring theme: conservation of energy
... What is the energy source that heats a contracting protostar? A. Friction of the gas molecules rubbing against each ...
... What is the energy source that heats a contracting protostar? A. Friction of the gas molecules rubbing against each ...
Unit 5 – Space Exploration - Buck Mountain Central School
... part of. It is shaped like a only known by an indirect method flattened pinwheel, with arms – when celestial material comes spiraling out from the center. close to a black hole it becomes very hot and very bright (Map of the Milky Way) Birth of Stars (Great site showing an animation of how a star is ...
... part of. It is shaped like a only known by an indirect method flattened pinwheel, with arms – when celestial material comes spiraling out from the center. close to a black hole it becomes very hot and very bright (Map of the Milky Way) Birth of Stars (Great site showing an animation of how a star is ...
COSTAR - STScI
... in a state of disbelief. This was, after all, the most perfect mirror ever made. But, if Chris thought it was spherical aberration, I knew we were in real trouble . ...
... in a state of disbelief. This was, after all, the most perfect mirror ever made. But, if Chris thought it was spherical aberration, I knew we were in real trouble . ...
educational activities for the international Year of astronomy
... Granule: Cells of hot gas circulating in the Sun. Granules are the size of Texas to the size of Alaska! Lane: Cool gas circulating back to interior. Bright point: Tiny area heated by intense magnetic fields. ...
... Granule: Cells of hot gas circulating in the Sun. Granules are the size of Texas to the size of Alaska! Lane: Cool gas circulating back to interior. Bright point: Tiny area heated by intense magnetic fields. ...
An optical/UV space coronagraph concept for the terrestrial planet finder
... Before describing the proposed spacecraft, it helps to review the requirements and potential science to be gained by a visible light coronagraph. We note that in addition to planet finding, a large visible light telescope will provide enormous potential for additional astrophysics in a post-Hubble a ...
... Before describing the proposed spacecraft, it helps to review the requirements and potential science to be gained by a visible light coronagraph. We note that in addition to planet finding, a large visible light telescope will provide enormous potential for additional astrophysics in a post-Hubble a ...
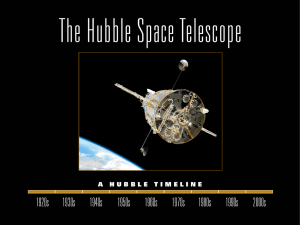
1920s 1930s 1940s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s
... The Butterfly Nebula: This object is a dying star that was once about five times the mass of the Sun. It has ejected its layer of gases and is now unleashing a stream of ultraviolet radiation that is making the ejected material glow, lighting up its delicate-looking butterfly shape. [Credit: NASA, E ...
... The Butterfly Nebula: This object is a dying star that was once about five times the mass of the Sun. It has ejected its layer of gases and is now unleashing a stream of ultraviolet radiation that is making the ejected material glow, lighting up its delicate-looking butterfly shape. [Credit: NASA, E ...
Beyond the Hubble Space Telescope: Early
... Studies in the different wavelength regions nevertheless ran a similar course in that research generally started with survey missions, leading in time to very versatile but complex and costly spacecraft. The pace at which a particular wavelength region reached the stage of what would later be called ...
... Studies in the different wavelength regions nevertheless ran a similar course in that research generally started with survey missions, leading in time to very versatile but complex and costly spacecraft. The pace at which a particular wavelength region reached the stage of what would later be called ...
Pulsars: Astronomical Clocks In The Sky
... The light from the pulsar is blue-shifted and red-shifted because the pulsar is moving around another object ...
... The light from the pulsar is blue-shifted and red-shifted because the pulsar is moving around another object ...
Star Formation
... move as they’re very low mass • Photons will also push on dust, but a dust grain is millions of atoms, like a massive boulder compared to atoms, and much harder to push around. • Therefore, as star clusters age, they push away the “after birth” of gas quickly, and only later the ...
... move as they’re very low mass • Photons will also push on dust, but a dust grain is millions of atoms, like a massive boulder compared to atoms, and much harder to push around. • Therefore, as star clusters age, they push away the “after birth” of gas quickly, and only later the ...
How Cosmic Clocks Tick - Max-Planck
... black holes. The outer shell is blasted into space, lighting up as a supernova. Square Kilometre Array (SKA): The Square Kilometre Array is a radio telescope with a total collection surface of around one square kilometer. Its sensitivity is expected to be many times that of conventional antennas. Fu ...
... black holes. The outer shell is blasted into space, lighting up as a supernova. Square Kilometre Array (SKA): The Square Kilometre Array is a radio telescope with a total collection surface of around one square kilometer. Its sensitivity is expected to be many times that of conventional antennas. Fu ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... ‘The burst of the century’ “This was the burst of the century!” exclaimed James A. Wren, an engineer at Los Alamos National Laboratory and co-author of one of the papers. Indeed, GRB 130427A (as it is now called) was the most powerful gamma-ray burst and the second-brightest optical flash measured i ...
... ‘The burst of the century’ “This was the burst of the century!” exclaimed James A. Wren, an engineer at Los Alamos National Laboratory and co-author of one of the papers. Indeed, GRB 130427A (as it is now called) was the most powerful gamma-ray burst and the second-brightest optical flash measured i ...
X-RAYS AND GRAVITATIONAL WAVES: LIGO AND VIRGO POINT
... the other direction as well, telling astronomers where and when to look for the source of candidate gravitational wave events. A recent publication, written jointly by Swift and LIGO-Virgo scientists, is summarized here. It describes the Swift satellite's first ever search for electromagnetic radiat ...
... the other direction as well, telling astronomers where and when to look for the source of candidate gravitational wave events. A recent publication, written jointly by Swift and LIGO-Virgo scientists, is summarized here. It describes the Swift satellite's first ever search for electromagnetic radiat ...
No. 2 - Society for Astronomical Sciences
... have been published) and unique information about the surface properties of asteroids. Robert Buchheim described his observation and data reduction methods, and presented two phase curves created from his observations of 1130 Skuld and 535 Montague. The very-nearest astronomical targets discussed th ...
... have been published) and unique information about the surface properties of asteroids. Robert Buchheim described his observation and data reduction methods, and presented two phase curves created from his observations of 1130 Skuld and 535 Montague. The very-nearest astronomical targets discussed th ...
Optical Design of Giant Telescopes for Space
... effects of the atmosphere and far from the thermal emission of earth itself The next giant steps in our understanding ofthe universe will require giant telescopes in space. Some basic requirements for a giant telescope come from the physics of light creation and propagation. The wavelength of intere ...
... effects of the atmosphere and far from the thermal emission of earth itself The next giant steps in our understanding ofthe universe will require giant telescopes in space. Some basic requirements for a giant telescope come from the physics of light creation and propagation. The wavelength of intere ...
Telescope
... design considered here to be more than 3 times more sensitive than existing/planned arrays in the regime above 300 GeV for continuously emitting sources; up to 10 times more sensitive for hour-scale emission; significantly more sensitive in the regime above 10 TeV; and possessing a sky coverage whic ...
... design considered here to be more than 3 times more sensitive than existing/planned arrays in the regime above 300 GeV for continuously emitting sources; up to 10 times more sensitive for hour-scale emission; significantly more sensitive in the regime above 10 TeV; and possessing a sky coverage whic ...
The Final Flight of Atlantis - Westchester Amateur Astronomers
... next generation detector 10 times more sensitive than its predecessor. “We’ll be monitoring a volume of space a thousand times greater than before,” says Cavaglia. “This will transform LIGO into a real observational tool.” When Advanced LIGO is completed in 2014 or so, the inner workings of black ho ...
... next generation detector 10 times more sensitive than its predecessor. “We’ll be monitoring a volume of space a thousand times greater than before,” says Cavaglia. “This will transform LIGO into a real observational tool.” When Advanced LIGO is completed in 2014 or so, the inner workings of black ho ...
SPACE Section 8-STARS- OBSERVING CONSTELLATIONS
... results of similar scientific investigations seldom turn out exactly the same because of differences in the things being investigated, methods being used, or uncertainty in the observation. Students will differentiate evidence from opinion and know the scientists do not rely on claims or conclusions ...
... results of similar scientific investigations seldom turn out exactly the same because of differences in the things being investigated, methods being used, or uncertainty in the observation. Students will differentiate evidence from opinion and know the scientists do not rely on claims or conclusions ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.