Developments for coating, testing, and aligning Cherenkov
... the Controller Area Network (CAN) interface [8] has been developed and employed. For each mirror there is a electronic control board, composed of a driver for each motor and a micro-controller (Atmel AT90CANxx), which is placed in one of the two actuator boxes. The other actuator is connected to the ...
... the Controller Area Network (CAN) interface [8] has been developed and employed. For each mirror there is a electronic control board, composed of a driver for each motor and a micro-controller (Atmel AT90CANxx), which is placed in one of the two actuator boxes. The other actuator is connected to the ...
ISA_lecture02
... from across the EM spectrum, but we still sometimes talk about different ‘astronomies’ (optical astronomy, radio astronomy, X-ray astronomy) because Atmospheric transmission varies Telescopes and detector vary Different parts of the spectrum reveal different objects and different kinds of info ...
... from across the EM spectrum, but we still sometimes talk about different ‘astronomies’ (optical astronomy, radio astronomy, X-ray astronomy) because Atmospheric transmission varies Telescopes and detector vary Different parts of the spectrum reveal different objects and different kinds of info ...
8 m Club Meeting - Adaptive optics
... Measurement of zodiacal dust around nearby stars using nulling (TPF) ...
... Measurement of zodiacal dust around nearby stars using nulling (TPF) ...
Constituents of the Milky Way
... Measuring Ages of Individual Stars For individual stars that aren’t in clusters (like the Sun), we can’t use the cluster turnoff method to measure an age. For instance, a lone G star might be young, or it might be 10 billion years old. How do we measure its age? The universe contained only hydrogen ...
... Measuring Ages of Individual Stars For individual stars that aren’t in clusters (like the Sun), we can’t use the cluster turnoff method to measure an age. For instance, a lone G star might be young, or it might be 10 billion years old. How do we measure its age? The universe contained only hydrogen ...
A sound nebula: the origin of the Solar System in the field of a
... It consists of trillions of small objects composed of dust and water, ammonia and methane ice and it is believed that these objects were scattered outwards by the gas giants at the planetary formation stage and then acquired distant circular orbits (out to about one light year) as a result of gravi ...
... It consists of trillions of small objects composed of dust and water, ammonia and methane ice and it is believed that these objects were scattered outwards by the gas giants at the planetary formation stage and then acquired distant circular orbits (out to about one light year) as a result of gravi ...
October, 2006 - The Astronomical Society of Las Cruces
... the Sun will next align also with Pluto at aphelion. But this is not an exact condition, only approximate. Suppose that due to some disturbance, such as a gravitational perturbation by Jupiter, Saturn, or Uranus, Pluto had already passed aphelion and was starting inward when Neptune overtook the slo ...
... the Sun will next align also with Pluto at aphelion. But this is not an exact condition, only approximate. Suppose that due to some disturbance, such as a gravitational perturbation by Jupiter, Saturn, or Uranus, Pluto had already passed aphelion and was starting inward when Neptune overtook the slo ...
Concepts discussed Jargon and conventions
... • Photometric calibration & VO • In other words: physics of interaction over light path; calibration: quantifying interactions; sharing your photometry ...
... • Photometric calibration & VO • In other words: physics of interaction over light path; calibration: quantifying interactions; sharing your photometry ...
Copyright 1995 Scientific American, Inc.
... the sun) and showed that obsecond supernova contains servations agreed with his themost of the mass of the binary (since rather than out into the void. The sec- ory. Arthur Eddington detected the the remaining neutron star contains a ond supernova also may be less disrup- bending of light rays durin ...
... the sun) and showed that obsecond supernova contains servations agreed with his themost of the mass of the binary (since rather than out into the void. The sec- ory. Arthur Eddington detected the the remaining neutron star contains a ond supernova also may be less disrup- bending of light rays durin ...
My Planets
... moon? That’s because it has that curved shape. We call that curved shape a crescent. In the bright part, it’s daytime on Venus. In the dark part, it’s nighttime on Venus. The other planets have day and night just as we do on Earth. Whoa…the sky is getting bright in the telescope…we’re pointing the t ...
... moon? That’s because it has that curved shape. We call that curved shape a crescent. In the bright part, it’s daytime on Venus. In the dark part, it’s nighttime on Venus. The other planets have day and night just as we do on Earth. Whoa…the sky is getting bright in the telescope…we’re pointing the t ...
Introduction
... which stars die depends on their original mass. In low and intermediate mass stars (∼18 M ) death is preceded by the so-called planetary nebula phase. Our Sun will become a Planetary Nebula in some 5 billion years. Because by far most stars have masses below 8 M , the planetary nebula phase must b ...
... which stars die depends on their original mass. In low and intermediate mass stars (∼18 M ) death is preceded by the so-called planetary nebula phase. Our Sun will become a Planetary Nebula in some 5 billion years. Because by far most stars have masses below 8 M , the planetary nebula phase must b ...
Section 7 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
... passes through it. Light does not seem to be absorbed by a shiny metallic material either. Instead, it appears to be reflected. But there objects that do not reflect or let any radiation pass through them. Scientists refer to such objects as black bodies. A black body is an object that absorbs all r ...
... passes through it. Light does not seem to be absorbed by a shiny metallic material either. Instead, it appears to be reflected. But there objects that do not reflect or let any radiation pass through them. Scientists refer to such objects as black bodies. A black body is an object that absorbs all r ...
The Magellan 20 Telescope Science Goals
... in the plane of the sky. A 3D tomographic reconstruction of the mass distribution and kinematics of the IGM becomes possible, mapping tenuous structures with densities down to the mean density of the universe. A combination with a traditional galaxy redshift survey of the same volume sampled by the ...
... in the plane of the sky. A 3D tomographic reconstruction of the mass distribution and kinematics of the IGM becomes possible, mapping tenuous structures with densities down to the mean density of the universe. A combination with a traditional galaxy redshift survey of the same volume sampled by the ...
The Intricate Role of Cold Gas and Dust in Galaxy Evolution at Early
... Credits: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/D.Patnaude et al, Optical: ESO/VLT, Infrared: NASA/JPL/Caltech ...
... Credits: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/D.Patnaude et al, Optical: ESO/VLT, Infrared: NASA/JPL/Caltech ...
orion® starBlast™ 4.5 EQ
... The EZ Finder II works by projecting a tiny red dot (it’s not a laser beam) onto a lens mounted in the front of the unit. When you look through the EZ Finder II, the red dot will appear to float in space, helping you locate even the faintest of deepsky objects. The red dot is produced by a light-emi ...
... The EZ Finder II works by projecting a tiny red dot (it’s not a laser beam) onto a lens mounted in the front of the unit. When you look through the EZ Finder II, the red dot will appear to float in space, helping you locate even the faintest of deepsky objects. The red dot is produced by a light-emi ...
To Measure the Sky: An Introduction to Observational Astronomy.
... indeed, are we? Astronomers have always needed to locate objects and events in space. As our science evolves, it demands ever more exact locations. Suppose, for example, an astronomer observes with an X-ray telescope and discovers a source that flashes on and off with a curious rhythm. Is this source ...
... indeed, are we? Astronomers have always needed to locate objects and events in space. As our science evolves, it demands ever more exact locations. Suppose, for example, an astronomer observes with an X-ray telescope and discovers a source that flashes on and off with a curious rhythm. Is this source ...
public_lector_10
... The dark halo was built up from mergers of smaller sub-halos Saw spiral structure developing in the gas Merging of galaxies is still going on now ...
... The dark halo was built up from mergers of smaller sub-halos Saw spiral structure developing in the gas Merging of galaxies is still going on now ...
ATA2010
... Galaxies like the Milky Way are believed to form by • the infall of gas which then turns gradually to stars (most of which form in the disk of the Galaxy, in open star clusters which quickly dissolve), and also by • the accretion of smaller galaxies which become absorbed in the larger system. A majo ...
... Galaxies like the Milky Way are believed to form by • the infall of gas which then turns gradually to stars (most of which form in the disk of the Galaxy, in open star clusters which quickly dissolve), and also by • the accretion of smaller galaxies which become absorbed in the larger system. A majo ...
special - Carl Zeiss
... center of the galaxy. Spectroscopy of the light of stars and the study of the Doppler effect can be used to measure the kinematics of a galaxy. However, most galaxies outside the Milky Way are so remote that the stars cannot be seen individually. They instead blur into a diffuse luminous distributio ...
... center of the galaxy. Spectroscopy of the light of stars and the study of the Doppler effect can be used to measure the kinematics of a galaxy. However, most galaxies outside the Milky Way are so remote that the stars cannot be seen individually. They instead blur into a diffuse luminous distributio ...
The Optical Design of the Background Emission Anisotropy Scanning Telescope
... gs: cosmic microwave background — cosmology: observations — telescopes 1. INTRODUCTION ...
... gs: cosmic microwave background — cosmology: observations — telescopes 1. INTRODUCTION ...
Core-collapse supernovae and their massive progenitors
... core-collapse supernovae. Direct detection of massive stars via the UV continua and indirectly via ionized H ii regions provides some of the most stringent constraints upon the physical properties of galaxies at high-redshift. Within the past few years a direct connection has been established betwee ...
... core-collapse supernovae. Direct detection of massive stars via the UV continua and indirectly via ionized H ii regions provides some of the most stringent constraints upon the physical properties of galaxies at high-redshift. Within the past few years a direct connection has been established betwee ...
1. Chapter 10
... days at a time. We have learned through experiments and observations that the stars are like our Sun, giving off light and heat, but are very far away. Thousands of years ago, what must people have thought when they looked up at the sky? Many people in early civilizations were farmers. They needed t ...
... days at a time. We have learned through experiments and observations that the stars are like our Sun, giving off light and heat, but are very far away. Thousands of years ago, what must people have thought when they looked up at the sky? Many people in early civilizations were farmers. They needed t ...
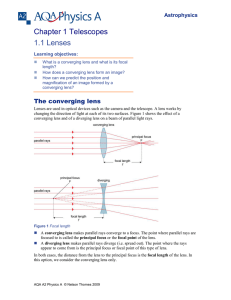
Chapter 1 Telescopes 1.1 Lenses
... the diameter of the objective of a telescope, the greater the number of stars that can be seen. Planets and other astronomical objects in the solar system are magnified using a telescope (unlike stars which are point objects and are seen through telescopes as point images no matter how large the mag ...
... the diameter of the objective of a telescope, the greater the number of stars that can be seen. Planets and other astronomical objects in the solar system are magnified using a telescope (unlike stars which are point objects and are seen through telescopes as point images no matter how large the mag ...
orion® starBlast™ - Spectrum Scientifics
... are twinkling noticeably, the seeing is bad and you will be limited to viewing with low powers (bad seeing affects images at high powers more severely). Planetary observing may also be poor. In conditions of good seeing, star twinkling is minimal and images appear steady in the eyepiece. Seeing is b ...
... are twinkling noticeably, the seeing is bad and you will be limited to viewing with low powers (bad seeing affects images at high powers more severely). Planetary observing may also be poor. In conditions of good seeing, star twinkling is minimal and images appear steady in the eyepiece. Seeing is b ...
Is Protostellar Jet Spinning? Chin
... Top) The two-sided (red for receding and blue for approaching sides) SiO (J=87) jet observed with the SMA (Lee et al. 2007). Gray image shows the shocked H2 emission produced by the jet (Hirano et al. 2006). The jet is knotty, consisting of a chain of knots on each side of the protostar, with an int ...
... Top) The two-sided (red for receding and blue for approaching sides) SiO (J=87) jet observed with the SMA (Lee et al. 2007). Gray image shows the shocked H2 emission produced by the jet (Hirano et al. 2006). The jet is knotty, consisting of a chain of knots on each side of the protostar, with an int ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.