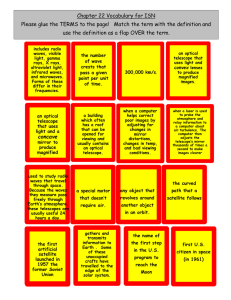
25 light years from Earth, there`s a planet about the size of our own
... The star is a pulsar, PSR 1257+12, the seething-hot core of a supernova that exploded millions of years ago. Its planets are bathed not in gentle, life-giving sunshine but instead a blistering torrent of X-rays and high-energy particles. "It would be like trying to live next to Chernobyl," says Char ...
... The star is a pulsar, PSR 1257+12, the seething-hot core of a supernova that exploded millions of years ago. Its planets are bathed not in gentle, life-giving sunshine but instead a blistering torrent of X-rays and high-energy particles. "It would be like trying to live next to Chernobyl," says Char ...
How Technology is Used to Observe Objects in Outer Space
... Some space probes fly out of our solar system and never come back. Other space probes, like the Hubble Space Telescope, stay in orbit around the same planet their ...
... Some space probes fly out of our solar system and never come back. Other space probes, like the Hubble Space Telescope, stay in orbit around the same planet their ...
Modern Day astronomical tools
... Combine the views of a group of antennas spread over a large area to operate together as one gigantic telescope. Many astronomical objects are not only observable in visible light but also emit radiation at radio wavelengths. Besides observing energetic objects such as pulsars and quasars, radio tel ...
... Combine the views of a group of antennas spread over a large area to operate together as one gigantic telescope. Many astronomical objects are not only observable in visible light but also emit radiation at radio wavelengths. Besides observing energetic objects such as pulsars and quasars, radio tel ...
Ch 22 Voc - Flushing Community Schools
... twin, reflecting telescopes located on Mauna Kea in Hawaii that can be used together to more than double their ability to distinguish objects. ...
... twin, reflecting telescopes located on Mauna Kea in Hawaii that can be used together to more than double their ability to distinguish objects. ...
Chapter 17 study guide
... 35. Explain how Voyager 2 could be used to flyby other planets that are further away from Earth? ...
... 35. Explain how Voyager 2 could be used to flyby other planets that are further away from Earth? ...
Supplemental Educational Support Materials
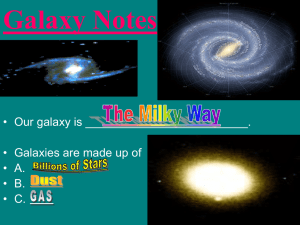
... A spiral galaxy that is the home of Earth. The Milky Way contains more than 100 billion stars and has a diameter of 100,000 light-years. ...
... A spiral galaxy that is the home of Earth. The Milky Way contains more than 100 billion stars and has a diameter of 100,000 light-years. ...
Starshade - Northrop Grumman Corporation
... model occulters to prove that the Starshade functions as expected. Component hardware has been built to determine the state-of-the-art capability to produce the required structure. ...
... model occulters to prove that the Starshade functions as expected. Component hardware has been built to determine the state-of-the-art capability to produce the required structure. ...
The Great Observatories - Center for STEM Education
... billions of years before the Sun and Earth formed. These represent the mission's first direct distance, or redshift, measurements, its latest milestone since being launched in November 2004. The distances were attained with Swift's Ultraviolet/OpticalTelescope (UVOT). ...
... billions of years before the Sun and Earth formed. These represent the mission's first direct distance, or redshift, measurements, its latest milestone since being launched in November 2004. The distances were attained with Swift's Ultraviolet/OpticalTelescope (UVOT). ...
science chapter 5 checkup
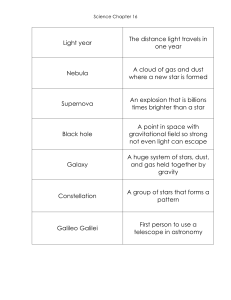
... SCIENCE CHAPTER 5 CHECKUP A. DEFINE EACH TERM. 1. VISIBLE SPECTRUM 2. MAGNETIC FIELD 3. ELECTRIC FIELD 4. WAVE 5. OSCILLATION 6. CREST 7. TROUGH 8. MEDIUM 9. ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE 10. SPEED OF LIGHT 11. FREQUENCY 12. WAVELENGTH 13. ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM 14. PULSARS 15. ASTRONAUT 16. SATELLITE 17. ...
... SCIENCE CHAPTER 5 CHECKUP A. DEFINE EACH TERM. 1. VISIBLE SPECTRUM 2. MAGNETIC FIELD 3. ELECTRIC FIELD 4. WAVE 5. OSCILLATION 6. CREST 7. TROUGH 8. MEDIUM 9. ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE 10. SPEED OF LIGHT 11. FREQUENCY 12. WAVELENGTH 13. ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM 14. PULSARS 15. ASTRONAUT 16. SATELLITE 17. ...
Using the Electromagnetic Spectrum
... On right: IC 410, IC 405 (Flaming Star Nebula), and environs. This image is a composite from B&W images. The images were recorded on 2 types of photographic plates, one sensitive to red light and the other to blue, and then digitized. Credit: David De Martin ...
... On right: IC 410, IC 405 (Flaming Star Nebula), and environs. This image is a composite from B&W images. The images were recorded on 2 types of photographic plates, one sensitive to red light and the other to blue, and then digitized. Credit: David De Martin ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
Slide 1
... • An AU stands for ________________ The avg. distance between the Earth and the Sun . (Used to measure distances inside the Solar System.) 1 AU= 150,000,000 km ...
... • An AU stands for ________________ The avg. distance between the Earth and the Sun . (Used to measure distances inside the Solar System.) 1 AU= 150,000,000 km ...
Name Class ______ Earth Science Study Guide: Introduction to
... 11. What was the name of the first Russian satellite? 12. What was the name of the United States’ satellite? ...
... 11. What was the name of the first Russian satellite? 12. What was the name of the United States’ satellite? ...
Infrared Telescopes
... year mission. It operates at far-IR wavelengths. Because it has a larger mirror than Spitzer (3.5 m vs. 0.85 m), it produces sharper images. ...
... year mission. It operates at far-IR wavelengths. Because it has a larger mirror than Spitzer (3.5 m vs. 0.85 m), it produces sharper images. ...
Space Explorations - Holy Cross Collegiate
... actually invisible to telescopes. Their existence is only known by an indirect method – when celestial material comes close to a black hole it becomes very hot and bright. ...
... actually invisible to telescopes. Their existence is only known by an indirect method – when celestial material comes close to a black hole it becomes very hot and bright. ...
Because the Hubble telescope is located in space
... Because the Hubble telescope is located in space, Earth’s atmosphere does not interfere with light from objects the telescope is aimed at. This lack of interference allows it to obtain clearer images than ground-based telescopes with much larger mirrors. In addition to collecting visible light, the ...
... Because the Hubble telescope is located in space, Earth’s atmosphere does not interfere with light from objects the telescope is aimed at. This lack of interference allows it to obtain clearer images than ground-based telescopes with much larger mirrors. In addition to collecting visible light, the ...
problems
... Q1. List three advantages of reflecting telescopes over refracting telescopes. Q3. How does Earth’s atmosphere affect what is seen through an optical telescope? Q9. What is interferometry, and what problem in radio astronomy does it address? Q14. What are the main advantages of studying objects at m ...
... Q1. List three advantages of reflecting telescopes over refracting telescopes. Q3. How does Earth’s atmosphere affect what is seen through an optical telescope? Q9. What is interferometry, and what problem in radio astronomy does it address? Q14. What are the main advantages of studying objects at m ...
Telescopes & Dead Guys Review Game
... If the area of sector A of a planet around the sun is 3947 m^2, according to Kepler’s second law the area of another sector (sector B) that represents the same amount of time should be? ...
... If the area of sector A of a planet around the sun is 3947 m^2, according to Kepler’s second law the area of another sector (sector B) that represents the same amount of time should be? ...
The Search for Extra-Terrestrial Unintelligence
... Hydrogen cyanide HCN On HD189733b with more to come ...
... Hydrogen cyanide HCN On HD189733b with more to come ...
Using the Electromagnetic Spectrum
... On right: IC 410, IC 405 (Flaming Star Nebula), and environs. This image is a composite from B&W images. The images were recorded on 2 types of photographic plates, one sensitive to red light and the other to blue, and then digitized. Credit: David De Martin ...
... On right: IC 410, IC 405 (Flaming Star Nebula), and environs. This image is a composite from B&W images. The images were recorded on 2 types of photographic plates, one sensitive to red light and the other to blue, and then digitized. Credit: David De Martin ...
Mission update
... Spitzer, XMM-Newton, FUSE and Swift, but it’s not all good news for space missions. ...
... Spitzer, XMM-Newton, FUSE and Swift, but it’s not all good news for space missions. ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.