Spectral Variations of Several RV Tauri Type Stars Patrick Durant
... time. Our group has acquired spectra of these stars during the past 10 years using the coude feed telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO). The set of spectra were examined to determine their effective temperature and other physical properties as a function of time. We present our results ...
... time. Our group has acquired spectra of these stars during the past 10 years using the coude feed telescope at Kitt Peak National Observatory (KPNO). The set of spectra were examined to determine their effective temperature and other physical properties as a function of time. We present our results ...
Resources: - Real Science
... planets in orbit around a star, in the same way as our Earth is in orbit around the sun. Extrasolar planets don't usually have interesting names like Venus or Pluto. This one is called HD 189733b. It orbits a star in the constellation of Vulpecula the Fox. It is 64 light years away from us. HD 18973 ...
... planets in orbit around a star, in the same way as our Earth is in orbit around the sun. Extrasolar planets don't usually have interesting names like Venus or Pluto. This one is called HD 189733b. It orbits a star in the constellation of Vulpecula the Fox. It is 64 light years away from us. HD 18973 ...
Model of Stars—6 Oct Test 1: Average 17 (75%) •
... The luminosity of a star (the energy produced every second) depends on temperature and size. What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? (Without modifying the sun, what can I do to make the sun brighter or fainter?) A. B. ...
... The luminosity of a star (the energy produced every second) depends on temperature and size. What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand and not burn my hand? (Without modifying the sun, what can I do to make the sun brighter or fainter?) A. B. ...
The Cook Memorial Library
... Sky Calendar (telescope.com), or to charts published monthly in Astronomy, Sky & Telescope, or other astronomy magazines and web sites. Venus, Jupiter, and Saturn are the brightest objects in the sky after the Sun and the Moon. Stars: Even powerful telescopes cannot magnify a star to appear as more ...
... Sky Calendar (telescope.com), or to charts published monthly in Astronomy, Sky & Telescope, or other astronomy magazines and web sites. Venus, Jupiter, and Saturn are the brightest objects in the sky after the Sun and the Moon. Stars: Even powerful telescopes cannot magnify a star to appear as more ...
“Other ideas for gamma ray instruments” 1) Preserving the highest energies
... Δr=14% @ 5mV , Δr=3% This is with just one baseline!!! ...
... Δr=14% @ 5mV , Δr=3% This is with just one baseline!!! ...
telescope as time machine - Galaxy Evolution Explorer
... many awesome pictures of the universe, GALEX operates above Earth’s atmosphere, so gathers light that cannot penetrate to telescopes on Earth’s surface. While the Hubble is used by many astronomers around the world to study very particular, tiny regions of the sky, GALEX has its very specific missio ...
... many awesome pictures of the universe, GALEX operates above Earth’s atmosphere, so gathers light that cannot penetrate to telescopes on Earth’s surface. While the Hubble is used by many astronomers around the world to study very particular, tiny regions of the sky, GALEX has its very specific missio ...
Summer 2013, Vol. 2, No. 2 - CAAUL
... nowadays in Portugal. We started with the keynote talk by Jarle Brinchmann on the EUCLID mission legacy science; the telescope is planned to be launched in 2020, and Portugal’s one of the members of the consortium since early 2012. CAAUL participates actively in the Sky Survey Working Group, which h ...
... nowadays in Portugal. We started with the keynote talk by Jarle Brinchmann on the EUCLID mission legacy science; the telescope is planned to be launched in 2020, and Portugal’s one of the members of the consortium since early 2012. CAAUL participates actively in the Sky Survey Working Group, which h ...
Astronomy Glossary Key
... In 1925 Hubble was first to notice that the light from hydrogen starlight was shifted towards the red end of the spectrum. This proves all stars are moving away from each other so the universe must be expanding. The HST was launched in 1990. It was the largest optical telescope in space. As soon as ...
... In 1925 Hubble was first to notice that the light from hydrogen starlight was shifted towards the red end of the spectrum. This proves all stars are moving away from each other so the universe must be expanding. The HST was launched in 1990. It was the largest optical telescope in space. As soon as ...
September - Rose City Astronomers
... Messier must have seen these objects in much the same way, which is a pretty cool insight into what his thoughts may have been while at the eyepiece of his own telescopes (http:// www.seds.org/messier/xtra/history/m-scopes.html). He did most of his observing with scopes that had very close to the sa ...
... Messier must have seen these objects in much the same way, which is a pretty cool insight into what his thoughts may have been while at the eyepiece of his own telescopes (http:// www.seds.org/messier/xtra/history/m-scopes.html). He did most of his observing with scopes that had very close to the sa ...
v A v A
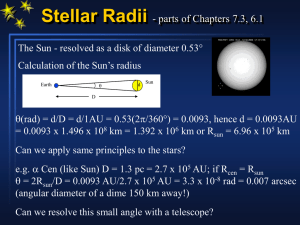
... = 0.0093 x 1.496 x 108 km = 1.392 x 106 km or Rsun = 6.96 x 105 km Can we apply same principles to the stars? e.g. Cen (like Sun) D = 1.3 pc = 2.7 x 105 AU; if Rcen = Rsun = 2Rsun/D = 0.0093 AU/2.7 x 105 AU = 3.3 x 10-8 rad = 0.007 arcsec (angular diameter of a dime 150 km away!) Can we resolve ...
... = 0.0093 x 1.496 x 108 km = 1.392 x 106 km or Rsun = 6.96 x 105 km Can we apply same principles to the stars? e.g. Cen (like Sun) D = 1.3 pc = 2.7 x 105 AU; if Rcen = Rsun = 2Rsun/D = 0.0093 AU/2.7 x 105 AU = 3.3 x 10-8 rad = 0.007 arcsec (angular diameter of a dime 150 km away!) Can we resolve ...
Why does Sirius twinkle?
... It's not just Sirius that twinkles; all stars twinkle. Light travels many light years from stars and right at the end of its journey, it hits Earth's atmosphere, which consists of nitrogen, oxygen and other Sirius is the brightest star in the sky and can easily gasses. be found in the faint constell ...
... It's not just Sirius that twinkles; all stars twinkle. Light travels many light years from stars and right at the end of its journey, it hits Earth's atmosphere, which consists of nitrogen, oxygen and other Sirius is the brightest star in the sky and can easily gasses. be found in the faint constell ...
Telescopes
... A reflector telescope has a mirror as its objective •James Gregory proposed such a telescope in 1663 but no optician could build it. He gave up, but still got a design named after him. ...
... A reflector telescope has a mirror as its objective •James Gregory proposed such a telescope in 1663 but no optician could build it. He gave up, but still got a design named after him. ...
Measuring the Solar Diameter with a Michelson Radio
... 2013) linked off the course website. Make sure to read these ahead of time. 2. Decide when you will conduct your observations. The radio signal from the Sun or the TV satellites is not affected by cloud cover. However, having enough sunlight so that you can see shadows will help greatly with the cal ...
... 2013) linked off the course website. Make sure to read these ahead of time. 2. Decide when you will conduct your observations. The radio signal from the Sun or the TV satellites is not affected by cloud cover. However, having enough sunlight so that you can see shadows will help greatly with the cal ...
astri-design-poster_110x80
... Base and Azimuth Fork Structures Re-Design GEC Consortium was responsible for the manufacturing and the erection of the ASTRI SST, based on ...
... Base and Azimuth Fork Structures Re-Design GEC Consortium was responsible for the manufacturing and the erection of the ASTRI SST, based on ...
2 GCOM-W
... horns and CSM) may exist, this should be corrected in orbit. To avoid the shading to the solar paddles by large AMSR2 antenna and the effect to CSM mentioned above, the paddles were designed to have longer booms. Overview of the GCOM-W1 satellite is shown in Figure 4 and the major characteristics of ...
... horns and CSM) may exist, this should be corrected in orbit. To avoid the shading to the solar paddles by large AMSR2 antenna and the effect to CSM mentioned above, the paddles were designed to have longer booms. Overview of the GCOM-W1 satellite is shown in Figure 4 and the major characteristics of ...
Telescope notes
... Photo (b) was taken with a telescope twice the size of the telescope that took photo (a) ...
... Photo (b) was taken with a telescope twice the size of the telescope that took photo (a) ...
Telescopes
... Major observatories: Hawaii, Chile, Texas, Canary Islands, Arizona, Australia, California, South Africa, China ...
... Major observatories: Hawaii, Chile, Texas, Canary Islands, Arizona, Australia, California, South Africa, China ...
Deep Space Mystery Note Form 3
... Small core of neutrons Spinning neutron star. Neutrons produce radio waves in a steady stream or random bursts. Stars 10 times the sun will leave a black hole. Leave behind a large core. With no energy fuse, it doesn’t have any out ward pressure so it gets engulfed in it’s own gravity an ...
... Small core of neutrons Spinning neutron star. Neutrons produce radio waves in a steady stream or random bursts. Stars 10 times the sun will leave a black hole. Leave behind a large core. With no energy fuse, it doesn’t have any out ward pressure so it gets engulfed in it’s own gravity an ...
Optical and infrared astronomical telescopes and instruments (L16)
... Optical and infrared astronomical telescopes and instruments (L16) Ian Parry Astronomy is an observational science. Our understanding of the universe beyond the Earth comes mostly from interpreting the electromagnetic radiation we see coming from the sky. This course is about the equipment and techn ...
... Optical and infrared astronomical telescopes and instruments (L16) Ian Parry Astronomy is an observational science. Our understanding of the universe beyond the Earth comes mostly from interpreting the electromagnetic radiation we see coming from the sky. This course is about the equipment and techn ...
Goals of the day Clickers Order of Magnitude Astronomy
... the Andromeda galaxy (the other big galaxy in the local group). The remnants from such explosions disperse in about 10,000 years. A. The supernova remnant still exists now, and we will watch it disperse over the next 10,000 Earth years. B. In reality, the supernova remnant has already dispersed, b ...
... the Andromeda galaxy (the other big galaxy in the local group). The remnants from such explosions disperse in about 10,000 years. A. The supernova remnant still exists now, and we will watch it disperse over the next 10,000 Earth years. B. In reality, the supernova remnant has already dispersed, b ...
Observing Galaxies - Denver Astronomical Society
... hindrance. M51, also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy, is an Sc class spiral galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici, 8.5 Mpc (million parsecs) from Earth. The galaxy is approximately 20 kiloparsecs in diameter, with an angular width of 0.21201°. When compared to published images some spiral ...
... hindrance. M51, also known as the Whirlpool Galaxy, is an Sc class spiral galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici, 8.5 Mpc (million parsecs) from Earth. The galaxy is approximately 20 kiloparsecs in diameter, with an angular width of 0.21201°. When compared to published images some spiral ...
NEAR INFRARED CAMERA (NIRCAM) - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... While one of the major themes for NIRCam is “The End of the Dark Ages: First Light and Reionization,” and we are training our leaders with this theme in mind, a major part of our E/PO effort is to allow the leaders to discover the night sky by making naked-eye and telescope observations. However, ma ...
... While one of the major themes for NIRCam is “The End of the Dark Ages: First Light and Reionization,” and we are training our leaders with this theme in mind, a major part of our E/PO effort is to allow the leaders to discover the night sky by making naked-eye and telescope observations. However, ma ...
Spitzer Space Telescope

The Spitzer Space Telescope (SST), formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003. It is the fourth and final of the NASA Great Observatories program.The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments are no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera are still operable with the same sensitivity as before the cryogen was exhausted, and will continue to be used in the Spitzer Warm Mission. All Spitzer data, from both the primary and warm phases, are archived at the Infrared Science Archive (IRSA).In keeping with NASA tradition, the telescope was renamed after its successful demonstration of operation, on 18 December 2003. Unlike most telescopes that are named after famous deceased astronomers by a board of scientists, the new name for SIRTF was obtained from a contest open to the general public.The contest led to the telescope being named in honor of astronomer Lyman Spitzer, who had promoted the concept of space telescopes in the 1940s. Spitzer wrote a 1946 report for RAND Corporation describing the advantages of an extraterrestrial observatory and how it could be realized with available or upcoming technology. He has been cited for his pioneering contributions to rocketry and astronomy, as well as ""his vision and leadership in articulating the advantages and benefits to be realized from the Space Telescope Program.""The US$800 million Spitzer was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on a Delta II 7920H ELV rocket, Monday, 25 August 2003 at 13:35:39 UTC-5 (EDT).It follows a heliocentric instead of geocentric orbit, trailing and drifting away from Earth's orbit at approximately 0.1 astronomical unit per year (a so-called ""earth-trailing"" orbit). The primary mirror is 85 centimeters (33 in) in diameter, f/12, made of beryllium and is cooled to 5.5 K (−449.77 °F). The satellite contains three instruments that allow it to perform astronomical imaging and photometry from 3 to 180 micrometers, spectroscopy from 5 to 40 micrometers, and spectrophotometry from 5 to 100 micrometers.