Measuring the Stars
... road to the chemist, but that's just peanuts to space…” To be fair though, when confronted by the sheer enormity of the distances between the stars, better minds than the one responsible for the Guide's introduction have faltered. Some invite you to consider for a moment a peanut in Reading and a sm ...
... road to the chemist, but that's just peanuts to space…” To be fair though, when confronted by the sheer enormity of the distances between the stars, better minds than the one responsible for the Guide's introduction have faltered. Some invite you to consider for a moment a peanut in Reading and a sm ...
Name
... planets have three layers a crust, mantle and a core, but thickness of the layers differs between the planets. The inner planets are separated from the outer planets by the asteroid belt that lies between Mars and Jupiter. ...
... planets have three layers a crust, mantle and a core, but thickness of the layers differs between the planets. The inner planets are separated from the outer planets by the asteroid belt that lies between Mars and Jupiter. ...
ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy
... Stars all begin from dust, and the formation of a star will follow a series of events. Nuclear reactions within stars create the radiation emitted and are fueled by hydrogen and/or helium, depending of the life stage of the star. A star’s characteristics, such as parallax, luminosity, apparent and a ...
... Stars all begin from dust, and the formation of a star will follow a series of events. Nuclear reactions within stars create the radiation emitted and are fueled by hydrogen and/or helium, depending of the life stage of the star. A star’s characteristics, such as parallax, luminosity, apparent and a ...
Chapter 1 Section Misconception Truth Distances in the Universe
... The Chromosphere The chromosphere, seen every day by looking straight at the Sun, has emission lines because it is hotter than the photosphere. The chromosphere is too transparent to add emission lines to the solar absorption lines. Only when we see it at the edge of the Sun (known a ...
... The Chromosphere The chromosphere, seen every day by looking straight at the Sun, has emission lines because it is hotter than the photosphere. The chromosphere is too transparent to add emission lines to the solar absorption lines. Only when we see it at the edge of the Sun (known a ...
ASTRONOMY CURRICULUM Unit 1: Introduction to Astronomy
... Stars all begin from dust, and the formation of a star will follow a series of events. Nuclear reactions within stars create the radiation emitted and are fueled by hydrogen and/or helium, depending of the life stage of the star. A star’s characteristics, such as parallax, luminosity, apparent and a ...
... Stars all begin from dust, and the formation of a star will follow a series of events. Nuclear reactions within stars create the radiation emitted and are fueled by hydrogen and/or helium, depending of the life stage of the star. A star’s characteristics, such as parallax, luminosity, apparent and a ...
Unit 4 Space
... Our solar system is full of planets, moons, asteroids and comets, all of which revolve around the Sun at the center. When a star forms from a nebula, gravity pulls most of the material into the new star, but some may also clump together to form objects in a solar system. • A planet is a celestial bo ...
... Our solar system is full of planets, moons, asteroids and comets, all of which revolve around the Sun at the center. When a star forms from a nebula, gravity pulls most of the material into the new star, but some may also clump together to form objects in a solar system. • A planet is a celestial bo ...
B. protostar - University of Maryland Astronomy
... C. We cannot see the entire galaxy due to the presence of interstellar dust. D. They go off when we’re not watching so we miss them. E. No stars are older than the Sun in our galaxy, but other galaxies are older so there are more supernovae. 41. The neutrons and protons in an atom are held together ...
... C. We cannot see the entire galaxy due to the presence of interstellar dust. D. They go off when we’re not watching so we miss them. E. No stars are older than the Sun in our galaxy, but other galaxies are older so there are more supernovae. 41. The neutrons and protons in an atom are held together ...
Space Station One, Grades 4-8 Program Description: Have you ever
... e. when the forces on an object are unbalanced the object will change its motion (that is, it will speed up, slow down, or change direction). f. the greater the mass of an object the more force is needed to achieve the same change in motion. Earth in the Solar System (Earth Science) 4. The structure ...
... e. when the forces on an object are unbalanced the object will change its motion (that is, it will speed up, slow down, or change direction). f. the greater the mass of an object the more force is needed to achieve the same change in motion. Earth in the Solar System (Earth Science) 4. The structure ...
1 Chapter 2 - University of Minnesota
... f. Discovered in 1930. Thought it must exist because of peculiarities in orbit of Uranus, but these were actually measurement errors. g. Pluto may just be one of many large icy bodies in outer ...
... f. Discovered in 1930. Thought it must exist because of peculiarities in orbit of Uranus, but these were actually measurement errors. g. Pluto may just be one of many large icy bodies in outer ...
Digging the Third Grave for Naturalism – No “Dark Matter”
... The Bible says that God created the Heavens and the Earth. It also says that in the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God. This is the Logos which was and is God. The Logos also means Message or Information. It is the totality of Truth. The ancient Chinese also ment ...
... The Bible says that God created the Heavens and the Earth. It also says that in the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with God, and the Word was God. This is the Logos which was and is God. The Logos also means Message or Information. It is the totality of Truth. The ancient Chinese also ment ...
What Makes Up the Solar System?
... the sun at times. Pluto’s moon, Charon, is nearly as big and the planet itself. Scientist claim that Pluto is not a planet because it is unlike the other planets in the solar system. Other scientists claim that Pluto and its moon form a double planet, because they are the same size, and they are mad ...
... the sun at times. Pluto’s moon, Charon, is nearly as big and the planet itself. Scientist claim that Pluto is not a planet because it is unlike the other planets in the solar system. Other scientists claim that Pluto and its moon form a double planet, because they are the same size, and they are mad ...
AstronomyQuotes
... star lost in a galaxy tucked away in some forgotten corner of a universe in which there are far more galaxies than people. ...
... star lost in a galaxy tucked away in some forgotten corner of a universe in which there are far more galaxies than people. ...
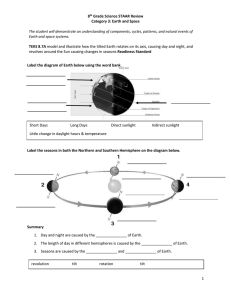
8th Grade Science STAAR Review Category 3: Earth and Space
... and that the Sun is many thousands of times closer to Earth than any other star Supporting Standard 1. If there are stars larger than the sun, why does the sun appear so much larger in Earth’s sky? ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Is the sun considere ...
... and that the Sun is many thousands of times closer to Earth than any other star Supporting Standard 1. If there are stars larger than the sun, why does the sun appear so much larger in Earth’s sky? ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Is the sun considere ...
The Lives of Stars
... Gravity pulls the material togethe Accumulating gas increases temperature At 10,000,000 degrees nuclear fusion begins (transformation of hydrogen into helium) ...
... Gravity pulls the material togethe Accumulating gas increases temperature At 10,000,000 degrees nuclear fusion begins (transformation of hydrogen into helium) ...
The Jovian Planets Sizes of Jovian planets compared to the Earth
... to all of the Jovian planets • Theory 2: they formed from leftover chunks of rocks and ice that condensed into a disk of gas around the planet. Problem: these chunks would been ground down in size by impacts with small dust particles that orbit the Sun. The ground up remains would have lost angular ...
... to all of the Jovian planets • Theory 2: they formed from leftover chunks of rocks and ice that condensed into a disk of gas around the planet. Problem: these chunks would been ground down in size by impacts with small dust particles that orbit the Sun. The ground up remains would have lost angular ...
Unit E Note Pkg
... You can make a rough guess of the number of stars in our galaxy by dividing the Galaxy's total mass by the mass of a typical star (e.g., 1 solar mass). The result is about 200 billion stars! The actual number of stars could be several tens of billions less or more than this approximate value. Recent ...
... You can make a rough guess of the number of stars in our galaxy by dividing the Galaxy's total mass by the mass of a typical star (e.g., 1 solar mass). The result is about 200 billion stars! The actual number of stars could be several tens of billions less or more than this approximate value. Recent ...
Unit 6--Astronomy
... a. Both stars have the same apparent magnitude. b. Star A has the greater apparent magnitude. c. Star B has the greater apparent magnitude. d. Apparent magnitude is not related to distance. 26.The difference in the brightness of two stars with the same surface temperature is attributable to their __ ...
... a. Both stars have the same apparent magnitude. b. Star A has the greater apparent magnitude. c. Star B has the greater apparent magnitude. d. Apparent magnitude is not related to distance. 26.The difference in the brightness of two stars with the same surface temperature is attributable to their __ ...
INSOLATION (INcoming SOLAr radiTION) The Earth receives almost
... The Earth receives almost all of its energy from the sun. Compared with a billion other stars in space, the sun is reasonably typical in size, color and temperature. Stars produce their own energy by the process of nuclear fusion. Deep inside stars, four hydrogen atoms combine to become a single ato ...
... The Earth receives almost all of its energy from the sun. Compared with a billion other stars in space, the sun is reasonably typical in size, color and temperature. Stars produce their own energy by the process of nuclear fusion. Deep inside stars, four hydrogen atoms combine to become a single ato ...
The Universe - The Ohio State University
... anti-leptons of the order of 1 part in 30 million. At approximately 1 second after the Big Bang neutrinos decoupled and begun traveling freely through space. The expansion of the universe had caused the temperature to drop when photons no longer had the energy to create proton anti-proton pairs. Pro ...
... anti-leptons of the order of 1 part in 30 million. At approximately 1 second after the Big Bang neutrinos decoupled and begun traveling freely through space. The expansion of the universe had caused the temperature to drop when photons no longer had the energy to create proton anti-proton pairs. Pro ...
Power Point Link
... • Some 3rd generation Sun-like Stars (with enough heavy elements) are up to two billion years older than the Sun • Imagine the same timeline…intelligent animals could have been around for a billion years rather than ...
... • Some 3rd generation Sun-like Stars (with enough heavy elements) are up to two billion years older than the Sun • Imagine the same timeline…intelligent animals could have been around for a billion years rather than ...
Where are we at within the Universe? Earth
... How many stars are in our solar system? There is only one star, the Sun, in our solar system. Our Milky Way Galaxy has over 200 billion stars, and the Universe has more stars than there are grains of sand on all of the beaches of the entire planet Earth. The Sun, though an average size and temperatu ...
... How many stars are in our solar system? There is only one star, the Sun, in our solar system. Our Milky Way Galaxy has over 200 billion stars, and the Universe has more stars than there are grains of sand on all of the beaches of the entire planet Earth. The Sun, though an average size and temperatu ...
A Proposed Explanation of Dark Matter within General
... quantity that composed of two independent parts : a material part which is the average stress-energy tensor and a geometrical part which represents a non-zero ground state curvature which can be determined from the shape of the universe (as shown in other papers mentioned in the introduction but not ...
... quantity that composed of two independent parts : a material part which is the average stress-energy tensor and a geometrical part which represents a non-zero ground state curvature which can be determined from the shape of the universe (as shown in other papers mentioned in the introduction but not ...
Cosmic Surveyor
... distance to the stars. 5. The rotation of the Earth accounts for the apparent daily rotation of the stars. 6. The apparent annual cycle of movements of the sun is caused by the Earth revolving round it. 7. The apparent retrograde motion of the planets is caused by the motion of the Earth from which ...
... distance to the stars. 5. The rotation of the Earth accounts for the apparent daily rotation of the stars. 6. The apparent annual cycle of movements of the sun is caused by the Earth revolving round it. 7. The apparent retrograde motion of the planets is caused by the motion of the Earth from which ...
Gravity*s Role on Earth
... the body how to act. oFor one thing, it tells muscles and bones how strong they must be. oMuscle mass can vanish at a rate as high as 5% a week. oBlood also feels gravity ...
... the body how to act. oFor one thing, it tells muscles and bones how strong they must be. oMuscle mass can vanish at a rate as high as 5% a week. oBlood also feels gravity ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.