Planet formation Abstract Megan K Pickett and Andrew J Lim
... is from this disk that the planets somehow coalesced. Close to the forming Sun, where the temperatures were high enough to vaporize most volatiles, the terrestrial planets formed by the accumulation of silicon, iron, nickel and other refractory grains into progressively larger bodies. Far from the S ...
... is from this disk that the planets somehow coalesced. Close to the forming Sun, where the temperatures were high enough to vaporize most volatiles, the terrestrial planets formed by the accumulation of silicon, iron, nickel and other refractory grains into progressively larger bodies. Far from the S ...
Solar system formation by accretion has no observational evidence
... Yet dust and debris fill expanses of the solar system, Milky Way galaxy, and universe. In the Milky Way, this debris is the interstellar medium (ISM); between galaxies, it is the intergalactic medium (IGM). If these dust particles did not form by accretion, what is their origin? Theorists, in line w ...
... Yet dust and debris fill expanses of the solar system, Milky Way galaxy, and universe. In the Milky Way, this debris is the interstellar medium (ISM); between galaxies, it is the intergalactic medium (IGM). If these dust particles did not form by accretion, what is their origin? Theorists, in line w ...
2-star-life-cycle-and-star-classification
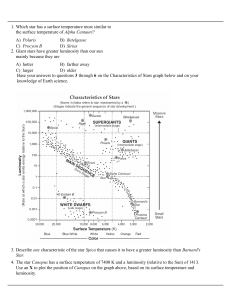
... 38. Compared to other groups of stars, the group that has 44. The schematic below shows the number of stars relatively low luminosities and relatively low formed in each mass range for each star more temperatures is the massive than 10 M Sun . A) Red Dwarfs B) White Dwarfs C) Red Giants D) Blue Supe ...
... 38. Compared to other groups of stars, the group that has 44. The schematic below shows the number of stars relatively low luminosities and relatively low formed in each mass range for each star more temperatures is the massive than 10 M Sun . A) Red Dwarfs B) White Dwarfs C) Red Giants D) Blue Supe ...
The Milky Way Model - University of Chicago
... closely packed stars, was it part of the Earth’s atmosphere or at great astronomical distances? These days, looking up at the sky from even a small city or suburb, the Milky Way isn’t even visible anymore due to light pollution and has lost its hold on imagination of most people on Earth. Yet at the ...
... closely packed stars, was it part of the Earth’s atmosphere or at great astronomical distances? These days, looking up at the sky from even a small city or suburb, the Milky Way isn’t even visible anymore due to light pollution and has lost its hold on imagination of most people on Earth. Yet at the ...
Powerpoint slides - Earth & Planetary Sciences
... • Which elements actually condense will depend on the local nebular conditions (temperature) • E.g. volatile species will only be stable beyond a “snow line”. This is why the inner planets are rock-rich and the outer planets gas- and ice-rich • The compounds formed from the elements will be determin ...
... • Which elements actually condense will depend on the local nebular conditions (temperature) • E.g. volatile species will only be stable beyond a “snow line”. This is why the inner planets are rock-rich and the outer planets gas- and ice-rich • The compounds formed from the elements will be determin ...
12_Testbank
... Answer: The brightness of an asteroid depends on its size, distance, and reflectivity. The brightness can be measured using a telescope, the distance is known from its orbit, and the reflectivity can be measured by comparing how bright the asteroid is at visible and infrared wavelengths. A highly re ...
... Answer: The brightness of an asteroid depends on its size, distance, and reflectivity. The brightness can be measured using a telescope, the distance is known from its orbit, and the reflectivity can be measured by comparing how bright the asteroid is at visible and infrared wavelengths. A highly re ...
2Discovering the Universe for Yourself
... across the sky from east to west. Many ancient people took this appearance at face value, concluding that we lie in the center of a universe that rotates around us each day. Today we know that the ancients had it backward: It is Earth that rotates daily, not the rest of the universe. We can picture ...
... across the sky from east to west. Many ancient people took this appearance at face value, concluding that we lie in the center of a universe that rotates around us each day. Today we know that the ancients had it backward: It is Earth that rotates daily, not the rest of the universe. We can picture ...
Practice Exam for 3 rd Astronomy Exam
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
Copernican Revolution
... Why does Venus exhibit phases but Mars does not? (Hint: Draw the Sun as well as Venus, Earth and Mars in their orbits. Shade in Venus and Mars. What do they look like from Earth’s view?) State Newton's Universal Law of Gravity. If the mass of one of two objects increases, what happens to the gravita ...
... Why does Venus exhibit phases but Mars does not? (Hint: Draw the Sun as well as Venus, Earth and Mars in their orbits. Shade in Venus and Mars. What do they look like from Earth’s view?) State Newton's Universal Law of Gravity. If the mass of one of two objects increases, what happens to the gravita ...
The Solar System
... Just what is a planet anyway? Well, according to The International Astronomical Union The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other bodies in our Solar System, except satellites be defined into three distinct categories in the following way: (1) A "planet“ 1 is a celestial body that (a) is in o ...
... Just what is a planet anyway? Well, according to The International Astronomical Union The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other bodies in our Solar System, except satellites be defined into three distinct categories in the following way: (1) A "planet“ 1 is a celestial body that (a) is in o ...
Variable star information
... periodic manner. These pulsations translate into a periodic variation of the light they emit. The most well known stars of this kind are Cepheid variables that have very stable pulsation periods. The changes in the observed brightness of an extrinsic variable star are either due to some process that ...
... periodic manner. These pulsations translate into a periodic variation of the light they emit. The most well known stars of this kind are Cepheid variables that have very stable pulsation periods. The changes in the observed brightness of an extrinsic variable star are either due to some process that ...
Sky-High 2015 - Irish Astronomical Society
... Star maps You will need at least one star map. This could be a set of monthly charts such as are included in many books on astronomy. A Planisphere is very useful. They come in various sizes at equivalent cost. It allows you to show the constellations visible at any time of the night, any time in th ...
... Star maps You will need at least one star map. This could be a set of monthly charts such as are included in many books on astronomy. A Planisphere is very useful. They come in various sizes at equivalent cost. It allows you to show the constellations visible at any time of the night, any time in th ...
Venus and Maya - Academic Program Pages at Evergreen
... results. By plotting Venus against the background stars, and calculating its speed, I was able to predict the time that Venus will spend in transit across the Solar disk. In order to fully understand the importance of Venus to the Ancient Mayans, I attempted to witness their most important celestial ...
... results. By plotting Venus against the background stars, and calculating its speed, I was able to predict the time that Venus will spend in transit across the Solar disk. In order to fully understand the importance of Venus to the Ancient Mayans, I attempted to witness their most important celestial ...
Earth Science: GEU Standardized Test Practice SE
... Large, well-formed minerals are the result of a slow rate of cooling. A fast rate of cooling results in the formation of very large crystals. ...
... Large, well-formed minerals are the result of a slow rate of cooling. A fast rate of cooling results in the formation of very large crystals. ...
Astronomy - Glen Ridge Public Schools
... scientifically literate life-long learners. Our program fosters a spirit of intellectual curiosity and collaborative problem solving that is authentic, hands-on, inquiry based and developmentally appropriate. This is done through the study of Life, Physical, Earth and Environmental Science. Our stud ...
... scientifically literate life-long learners. Our program fosters a spirit of intellectual curiosity and collaborative problem solving that is authentic, hands-on, inquiry based and developmentally appropriate. This is done through the study of Life, Physical, Earth and Environmental Science. Our stud ...
Planetary Radii Across Five Orders of Magnitude in Mass and Stellar
... To aid in the physical interpretation of planetary radii constrained through observations of transiting planets, or eventually direct detections, we compute model radii of pure hydrogen-helium, water, rock, and iron planets, along with various mixtures. Masses ranging from 0.01 Earth masses to 10 Ju ...
... To aid in the physical interpretation of planetary radii constrained through observations of transiting planets, or eventually direct detections, we compute model radii of pure hydrogen-helium, water, rock, and iron planets, along with various mixtures. Masses ranging from 0.01 Earth masses to 10 Ju ...
A cloaking device for transiting planets
... A related concept using mirrors was recently proposed by Korpela, Sallmen & Leystra (2015), but both ideas require the construction of Earth-sized masks, which is far beyond our current capabilities. In this work, we argue that artificial transit profiles can be feasibly generated using laser emissi ...
... A related concept using mirrors was recently proposed by Korpela, Sallmen & Leystra (2015), but both ideas require the construction of Earth-sized masks, which is far beyond our current capabilities. In this work, we argue that artificial transit profiles can be feasibly generated using laser emissi ...
Teachers Edition Sample Chapter (1.2MB PDF)
... Hold the ball slightly above your head, at arm’s length from your face. Stand about 1 m from the flashlight, which is held at the same level as the ball. Observe the Moon in each of the positions shown in Figure 2. Face the ball at each position. For each position, indicate how much of the ball is d ...
... Hold the ball slightly above your head, at arm’s length from your face. Stand about 1 m from the flashlight, which is held at the same level as the ball. Observe the Moon in each of the positions shown in Figure 2. Face the ball at each position. For each position, indicate how much of the ball is d ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.