THE EARTH
... I. IDENTIFY ADULT CONTENT KNOWLEDGE Science For All Americans The Earth (Pages 42 – 43) We live on a fairly small planet, the third from the sun in the only system of planets definitely known to exist (although similar systems are likely to be common in the universe). Like that of all planets and st ...
... I. IDENTIFY ADULT CONTENT KNOWLEDGE Science For All Americans The Earth (Pages 42 – 43) We live on a fairly small planet, the third from the sun in the only system of planets definitely known to exist (although similar systems are likely to be common in the universe). Like that of all planets and st ...
Tuesday, October 28th "The Formation and Evolution of Galaxies"
... "That may sound like a very small angle, but it is in fact significant," says Alexei Pevtsov, RHESSI Program Scientist at NASA Headquarters. Tiny departures from perfect roundness can, for example, affect the Sun's gravitational pull on Mercury and skew tests of Einstein's theory of relativity that ...
... "That may sound like a very small angle, but it is in fact significant," says Alexei Pevtsov, RHESSI Program Scientist at NASA Headquarters. Tiny departures from perfect roundness can, for example, affect the Sun's gravitational pull on Mercury and skew tests of Einstein's theory of relativity that ...
Orbit 13 Yes those famous words, “Class, we have a problem.” once
... & M. to do the actual orbits calculation and some preliminary graphics. Mr Howbackward (on flimsy Hollywood grounds) has chosen to ignore perhaps the greatest scientific discovery of all time and to have all the orbits based on perfect circles rather than the ellipses that Kepler discovered. Run tel ...
... & M. to do the actual orbits calculation and some preliminary graphics. Mr Howbackward (on flimsy Hollywood grounds) has chosen to ignore perhaps the greatest scientific discovery of all time and to have all the orbits based on perfect circles rather than the ellipses that Kepler discovered. Run tel ...
Chapter 2 Basic Chemistry
... releasing it – When fusion requires more energy than it can produce, there is no longer any outward pressure to balance the gravitational force – The core collapses because of its own gravity and then rebounds with a shock wave that violently blow’s the star’s outer layers away from the core – The r ...
... releasing it – When fusion requires more energy than it can produce, there is no longer any outward pressure to balance the gravitational force – The core collapses because of its own gravity and then rebounds with a shock wave that violently blow’s the star’s outer layers away from the core – The r ...
award
... What conclusion can be drawn from the fact that some planets with solid surfaces and satellites have impact craters? Collisions between Solar System bodies and planetesimals were common at one time. The young planets had softer surfaces. Volcanoes were very active in the early stages of planet forma ...
... What conclusion can be drawn from the fact that some planets with solid surfaces and satellites have impact craters? Collisions between Solar System bodies and planetesimals were common at one time. The young planets had softer surfaces. Volcanoes were very active in the early stages of planet forma ...
Telling Time by the Sun - Cornell Astronomy
... The Sun’s Path Throughout the Year • The Sun’s Declination changes throughout the year due to the inclination of the Earth on its axis. • On Sep 20th and Mar 20th, the Sun’s Declination is 0°. • The Sun’s path follows the Celestial Equator. • These are called the autumnal and vernal equinoxes. • On ...
... The Sun’s Path Throughout the Year • The Sun’s Declination changes throughout the year due to the inclination of the Earth on its axis. • On Sep 20th and Mar 20th, the Sun’s Declination is 0°. • The Sun’s path follows the Celestial Equator. • These are called the autumnal and vernal equinoxes. • On ...
Inquiry Activity - Ball State University
... the concept of parallax is to have them hold their index finger out in front of their nose. Tell them to open only one eye and look at their finger, and then have them close that eye and open the other. There finger should appear to be in two different places when viewed from different eyes (The fas ...
... the concept of parallax is to have them hold their index finger out in front of their nose. Tell them to open only one eye and look at their finger, and then have them close that eye and open the other. There finger should appear to be in two different places when viewed from different eyes (The fas ...
Formation of the Solar System
... • 1-2 billion yrs: Milky Way Earliest Stars • 2-8 Gyr: MW Disk supernovae: C,N,O,Fe.. • 9 Gyr: Collapse of solar gas cloud • 13.699 Gyr: People evolve (1 million BP) • 13.699999 Gyr: Astronomy (1000 BP) ...
... • 1-2 billion yrs: Milky Way Earliest Stars • 2-8 Gyr: MW Disk supernovae: C,N,O,Fe.. • 9 Gyr: Collapse of solar gas cloud • 13.699 Gyr: People evolve (1 million BP) • 13.699999 Gyr: Astronomy (1000 BP) ...
Earth in the Universe
... names is not important in itself. When students know that the star patterns stay the same as they move across the sky (and gradually shift with the seasons), they can then observe that the planets change their position against the pattern of stars. Once students have looked directly at the stars, mo ...
... names is not important in itself. When students know that the star patterns stay the same as they move across the sky (and gradually shift with the seasons), they can then observe that the planets change their position against the pattern of stars. Once students have looked directly at the stars, mo ...
15_LectureOutline
... 15.6 Planets Beyond the Solar System Planets orbiting within 0.1 AU of their stars are called “hot Jupiters”; they are not included in the previous figure but are numerous. Stars with composition like our Sun are much more likely to have planets, showing that the “dusty disk” theory is plausible. S ...
... 15.6 Planets Beyond the Solar System Planets orbiting within 0.1 AU of their stars are called “hot Jupiters”; they are not included in the previous figure but are numerous. Stars with composition like our Sun are much more likely to have planets, showing that the “dusty disk” theory is plausible. S ...
Astronomy Through the Ages: 2 Middle ages through Renaissance
... “In the same way that someone in a boat going forward sees an unmoving objects going backward, so someone on earth sees the unmoving stars going uniformly westward…’’ ...
... “In the same way that someone in a boat going forward sees an unmoving objects going backward, so someone on earth sees the unmoving stars going uniformly westward…’’ ...
Galaxy Classification - Starry Night Education
... Milky Way galaxy? a. The plane of the solar system is coincident with the plane of the galaxy. b. The plane of the solar system is perpendicular to that of the Milky Way. c. The plane of the solar system is inclined at a small angle to the plane of the galaxy. d. The angle between the plane of the s ...
... Milky Way galaxy? a. The plane of the solar system is coincident with the plane of the galaxy. b. The plane of the solar system is perpendicular to that of the Milky Way. c. The plane of the solar system is inclined at a small angle to the plane of the galaxy. d. The angle between the plane of the s ...
Sun - Cobb Learning
... sunrise in the east. Venus appears at most ~46° from the sun. It can occasionally be seen for at most a few hours after sunset in the west or before sunrise in the east. ...
... sunrise in the east. Venus appears at most ~46° from the sun. It can occasionally be seen for at most a few hours after sunset in the west or before sunrise in the east. ...
Study Notes Lesson 13 Gravitational Interactions
... iv) The collapse ignites fusion of the nuclear ashes (helium) and fuses them into carbon. v) The star (such as the sun) will expand and extend beyond Earth’s orbit and swallows Earth. (Red Giant) vi) All the helium are burned out and start to collapse and die out. No longer give out heat and light. ...
... iv) The collapse ignites fusion of the nuclear ashes (helium) and fuses them into carbon. v) The star (such as the sun) will expand and extend beyond Earth’s orbit and swallows Earth. (Red Giant) vi) All the helium are burned out and start to collapse and die out. No longer give out heat and light. ...
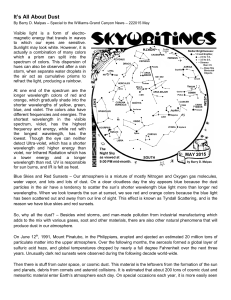
May 2015
... Cosmic Origins – All original matter, including dust, began after the Big Bang when the Universe was created. As everything expanded, gases and dust that were close to each other were attracted, and clumped together by the force of gravity to form galaxies, stars and planetary systems, comets and ot ...
... Cosmic Origins – All original matter, including dust, began after the Big Bang when the Universe was created. As everything expanded, gases and dust that were close to each other were attracted, and clumped together by the force of gravity to form galaxies, stars and planetary systems, comets and ot ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.