Characteristics of Main Sequence Stars
... • In high mass stars, the CNO nuclear reactions are highly concentrated in the center of the star. As a result, the molecular weight is unchanged over most of the star, and only the core contracts. The star therefore becomes redder, as the increase in the radius overwhelms that of the luminosity. Fo ...
... • In high mass stars, the CNO nuclear reactions are highly concentrated in the center of the star. As a result, the molecular weight is unchanged over most of the star, and only the core contracts. The star therefore becomes redder, as the increase in the radius overwhelms that of the luminosity. Fo ...
w 2012-01-13 Stellar Life Cycle
... Emission nebulae are clouds of high temperature gas. The atoms in the cloud are energized by ultraviolet light from a nearby star and emit radiation as they fall back into lower energy states (in much the same way as a neon light). These nebulae are usually red because the predominant emission line ...
... Emission nebulae are clouds of high temperature gas. The atoms in the cloud are energized by ultraviolet light from a nearby star and emit radiation as they fall back into lower energy states (in much the same way as a neon light). These nebulae are usually red because the predominant emission line ...
70 Thousand Million, Million, Million Stars in Space
... A comet is not a star. It is formed by bits of dust and gas that collect into an icy form. Comets take their name from the Greek aster kometes, which means “long-haired stars.” Comets have come as close to Earth as 31,068,560 miles (50 million km). Asteroids are not stars. They are bits of rock that ...
... A comet is not a star. It is formed by bits of dust and gas that collect into an icy form. Comets take their name from the Greek aster kometes, which means “long-haired stars.” Comets have come as close to Earth as 31,068,560 miles (50 million km). Asteroids are not stars. They are bits of rock that ...
latest Edition - ExoPlanet News
... samples of planet and non-planet hosts. Whether these chemical differences are indeed related to the presence of planets is still strongly debated. Aims. We aim to test whether solar-type stars with debris discs show any chemical peculiarity that could be related to the planet formation process. Met ...
... samples of planet and non-planet hosts. Whether these chemical differences are indeed related to the presence of planets is still strongly debated. Aims. We aim to test whether solar-type stars with debris discs show any chemical peculiarity that could be related to the planet formation process. Met ...
Unit 5 -
... Conduction cannot travel through a vacuum because in a vacuum there are no atoms or molecules…something made of atoms or molecules has to touch something else made of atoms or molecules in order for there to be conduction. ◦ Ex: If you touch a hot object the heat is conducted by physical contact wit ...
... Conduction cannot travel through a vacuum because in a vacuum there are no atoms or molecules…something made of atoms or molecules has to touch something else made of atoms or molecules in order for there to be conduction. ◦ Ex: If you touch a hot object the heat is conducted by physical contact wit ...
Astrophysics
... • From these figures it was calculated that if the Sun was made of coal, it could burn for about 10,000 years given a lot of oxygen! As life on the Earth seemed to be millions of years old this appeared to be a problem! • Lord Kelvin and Hermann von Helmholtz suggested that the collapsing matter for ...
... • From these figures it was calculated that if the Sun was made of coal, it could burn for about 10,000 years given a lot of oxygen! As life on the Earth seemed to be millions of years old this appeared to be a problem! • Lord Kelvin and Hermann von Helmholtz suggested that the collapsing matter for ...
Chapter 12
... • The black hole (Located by the star symbol in the animation) is located in the center of the Milky Way, in the constellation Sagittarius, at a distance of about 26,000 ly. • The mass is about 4.3 million ...
... • The black hole (Located by the star symbol in the animation) is located in the center of the Milky Way, in the constellation Sagittarius, at a distance of about 26,000 ly. • The mass is about 4.3 million ...
Powerpoint for today
... - billions of years old Clusters are crucial for stellar evolution studies because: 1) All stars in a cluster formed at about same time (so all have same age) 2) All stars are at about the same distance 3) All stars have same chemical composition ...
... - billions of years old Clusters are crucial for stellar evolution studies because: 1) All stars in a cluster formed at about same time (so all have same age) 2) All stars are at about the same distance 3) All stars have same chemical composition ...
Teacher`s Guide - Discovery Education
... What evidence do scientists have that comets and asteroids have collided with Earth? ...
... What evidence do scientists have that comets and asteroids have collided with Earth? ...
Astronomy 103
... identical to patterns of spectral lines from particular elements found on the Earth. (One set of lines failed to match the spectrum of any known element. The conclusion was that we were seeing an element on the Sun that had not been seen on Earth, and it was given the name helium after the Greek Sun ...
... identical to patterns of spectral lines from particular elements found on the Earth. (One set of lines failed to match the spectrum of any known element. The conclusion was that we were seeing an element on the Sun that had not been seen on Earth, and it was given the name helium after the Greek Sun ...
24_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... material in these systems to form many planets, and, theoretically, that planet growth should be common in these disks. Observationally, we have detected Jupiter- (and even Saturn-) mass planets around nearby stars. 4) Why might the presence of a giant planet be both good and bad news for life on a ...
... material in these systems to form many planets, and, theoretically, that planet growth should be common in these disks. Observationally, we have detected Jupiter- (and even Saturn-) mass planets around nearby stars. 4) Why might the presence of a giant planet be both good and bad news for life on a ...
Slide 1
... Nothing left (that we know of) from before the Big Bang…so don’t ask what happened before…no one knows! The idea begins with Hubble’s Discovery, 1939 – the Universe is moving away…expanding in all directions taking galaxies with it = Hubble’s Law Thus, in reverse thought, the Universe must have be ...
... Nothing left (that we know of) from before the Big Bang…so don’t ask what happened before…no one knows! The idea begins with Hubble’s Discovery, 1939 – the Universe is moving away…expanding in all directions taking galaxies with it = Hubble’s Law Thus, in reverse thought, the Universe must have be ...
the earth in space - North Salem Schools Teachers Module
... 4. Stars rise in the east, set in the west, circle around Polaris in the north, and move in large, arc shaped paths in the south B. The movements of planets across the nighttime sky is not uniform 1. The reason planets have non-uniform motion is that they really are moving in space - stars only loo ...
... 4. Stars rise in the east, set in the west, circle around Polaris in the north, and move in large, arc shaped paths in the south B. The movements of planets across the nighttime sky is not uniform 1. The reason planets have non-uniform motion is that they really are moving in space - stars only loo ...
Earth in Space and Time (SC.5.E.5.1)
... actually larger than the Sun. If this is true, why do these stars appear like points of light in the sky? A. These stars are hotter than the Sun. B. These stars have less mass than the Sun. C. These stars are farther away from Earth than the Sun is. D. These stars are made of different chemicals tha ...
... actually larger than the Sun. If this is true, why do these stars appear like points of light in the sky? A. These stars are hotter than the Sun. B. These stars have less mass than the Sun. C. These stars are farther away from Earth than the Sun is. D. These stars are made of different chemicals tha ...
Stellar aberration
... located in any other direction its apparent displacement traces elliptical/circular figures in space. As distance travelled by solar system, in a solar year, is considerable, difference this makes in relative direction of distant star (various types of parallaxes) also has to be accounted for. In or ...
... located in any other direction its apparent displacement traces elliptical/circular figures in space. As distance travelled by solar system, in a solar year, is considerable, difference this makes in relative direction of distant star (various types of parallaxes) also has to be accounted for. In or ...
Star formation - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... keeps the star a stable size until late in its life. During this time, the star is on the Main Sequence of the H-R Diagram. ...
... keeps the star a stable size until late in its life. During this time, the star is on the Main Sequence of the H-R Diagram. ...
The Planets
... large area but is preferable to the second activity as it allows students to compare the sizes of the planets to the space between them and better demonstrates the hugeness of space. The second activity, “Scaling the Solar System with Toilet Paper,” has the advantage of requiring less room. On its s ...
... large area but is preferable to the second activity as it allows students to compare the sizes of the planets to the space between them and better demonstrates the hugeness of space. The second activity, “Scaling the Solar System with Toilet Paper,” has the advantage of requiring less room. On its s ...
File - Zemali Salem
... mass of the entire solar system. It is a huge ball of hydrogen and helium gas that is 1,392,000 kilometers in diameter. It has a temperature, at its core, of more than 15,600,000° C. The intense radiation emitted by the sun provides almost all the energy to heat the planets, and, in the case of Eart ...
... mass of the entire solar system. It is a huge ball of hydrogen and helium gas that is 1,392,000 kilometers in diameter. It has a temperature, at its core, of more than 15,600,000° C. The intense radiation emitted by the sun provides almost all the energy to heat the planets, and, in the case of Eart ...
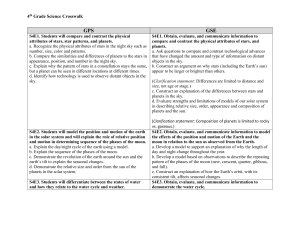
GPS-GSE Science Crosswalk 4th Grade
... compare and contrast the physical attributes of stars, and planets. a. Ask questions to compare and contrast technological advances that have changed the amount and type of information on distant objects in the sky. b. Construct an argument on why stars (including the Earth’s sun) appear to be large ...
... compare and contrast the physical attributes of stars, and planets. a. Ask questions to compare and contrast technological advances that have changed the amount and type of information on distant objects in the sky. b. Construct an argument on why stars (including the Earth’s sun) appear to be large ...
Star Classification and its Connection to Exoplanets.
... already been collected, and now this data will be interpreted. Based on the data, a star’s spectral classification influences its capability to host planets. More specifically, through hypothesis testing, stars similar to the sun tend to host planets more often than other stars: a conclusion that is ...
... already been collected, and now this data will be interpreted. Based on the data, a star’s spectral classification influences its capability to host planets. More specifically, through hypothesis testing, stars similar to the sun tend to host planets more often than other stars: a conclusion that is ...
6th Grade Winter - Partnership for Effective Science Teaching and
... Objective 2: Describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky relative to Earth and how various cultures have understood and used them. a. Locate and identify stars that are grouped in patterns in the night sky. b. Identify ways people have historically grouped stars i ...
... Objective 2: Describe the appearance and apparent motion of groups of stars in the night sky relative to Earth and how various cultures have understood and used them. a. Locate and identify stars that are grouped in patterns in the night sky. b. Identify ways people have historically grouped stars i ...
Chapter 25 Our Solar System - Information Technology Florida Wing
... Venus is covered with an opaque layer that has a highly reflective atmosphere with clouds of sulfuric acid and sulfur dioxide. This keeps its surface from being seen from space in normal visible light. The Venusian atmosphere also has a pressure that is about 90 times greater than that of Earth. The ...
... Venus is covered with an opaque layer that has a highly reflective atmosphere with clouds of sulfuric acid and sulfur dioxide. This keeps its surface from being seen from space in normal visible light. The Venusian atmosphere also has a pressure that is about 90 times greater than that of Earth. The ...
Earth Space EOC Review Test #2 NAME
... have not been overturned. Letters A though E identify different rock layers. Fossils found in the rock layers are shown. Which fossil could be classified as an index fossil? ...
... have not been overturned. Letters A though E identify different rock layers. Fossils found in the rock layers are shown. Which fossil could be classified as an index fossil? ...
Astronomical and Physical Sciences
... This is a composite photograph (not-to-scale) of all planets in the solar system, except Pluto. They are, from top to bottom: Mercury, Venus, Earth (with the Moon to the right), Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The photos were taken by Mariner 10 (Mercury), Pioneer Venus Orbiter (Venus), ...
... This is a composite photograph (not-to-scale) of all planets in the solar system, except Pluto. They are, from top to bottom: Mercury, Venus, Earth (with the Moon to the right), Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. The photos were taken by Mariner 10 (Mercury), Pioneer Venus Orbiter (Venus), ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.