The First Stars - Amazon Web Services
... see no relic stars totally lacking in heavier elements such as iron, as would be the case if there was a component of low mass objects in the first generation of stars. We infer that during their short but brilliant lives, aided by large numbers of star-forming dwarf galaxies, also teeming with mass ...
... see no relic stars totally lacking in heavier elements such as iron, as would be the case if there was a component of low mass objects in the first generation of stars. We infer that during their short but brilliant lives, aided by large numbers of star-forming dwarf galaxies, also teeming with mass ...
6th Grade Great Barrier Reef
... Beyond the Milky Way, there are billions more stars in the galaxies that are our closest neighbors. One of our close neighbors is the Andromeda galaxy, but don’t expect to travel there soon. Even though Andromeda is closer to us than most other galaxies, it is almost 2 million light years away ...
... Beyond the Milky Way, there are billions more stars in the galaxies that are our closest neighbors. One of our close neighbors is the Andromeda galaxy, but don’t expect to travel there soon. Even though Andromeda is closer to us than most other galaxies, it is almost 2 million light years away ...
Beyond the Solar System Homework for Geology 8
... 20. A collection or cluster of stars and solar systems such as the Milky Way or Andromeda. 21. This type of nebula is a cloud of glowing gas excited by ultraviolet radiation from hot stars. ...
... 20. A collection or cluster of stars and solar systems such as the Milky Way or Andromeda. 21. This type of nebula is a cloud of glowing gas excited by ultraviolet radiation from hot stars. ...
ASTR-100 - Jiri Brezina Teaching
... Dynamics, Tab. A.4, p. 531). The revolution (orbiting) is ccw when seen from north on all planets and most of their satellites; the axial rotation is ccw when seen from north only on 6 from 9 planets and on several of their 131 satellites. Since the stars seem to make 366 revolutions in a year (365 ...
... Dynamics, Tab. A.4, p. 531). The revolution (orbiting) is ccw when seen from north on all planets and most of their satellites; the axial rotation is ccw when seen from north only on 6 from 9 planets and on several of their 131 satellites. Since the stars seem to make 366 revolutions in a year (365 ...
Transiting exoplanets from the CoRoT space mission
... either too far away or too faint to be of concern. Observations to identify whether any of the concerned stars show such amplitudes were then done on two telescopes: the 1m OGS on Izaa, Tenerife, and the CFHT, Hawaii. The observations on OGS were taken during a transit on 13 Aug. 2010, and the off-t ...
... either too far away or too faint to be of concern. Observations to identify whether any of the concerned stars show such amplitudes were then done on two telescopes: the 1m OGS on Izaa, Tenerife, and the CFHT, Hawaii. The observations on OGS were taken during a transit on 13 Aug. 2010, and the off-t ...
Outline of Lecture on Copernican Revolution: 5b: So, what was
... Modern scientists are now familiar with this, but in Ptolemy’s time the clue might have been more easily missed. But the fact that the Greek’s were aware that a heliocentric model could naturally produce the observations suggests that the coincidences had indeed caused people to question and to thin ...
... Modern scientists are now familiar with this, but in Ptolemy’s time the clue might have been more easily missed. But the fact that the Greek’s were aware that a heliocentric model could naturally produce the observations suggests that the coincidences had indeed caused people to question and to thin ...
The Sky Tonight - Northern Stars Planetarium
... space. It’s the result of the death of an average star (like the Sun). The nebulosity you see is the outer layers of the star that have been blown out into space. Planetary nebula actually have no relationship to planets. They’re called planetary because of their appearance only, which led early ast ...
... space. It’s the result of the death of an average star (like the Sun). The nebulosity you see is the outer layers of the star that have been blown out into space. Planetary nebula actually have no relationship to planets. They’re called planetary because of their appearance only, which led early ast ...
Beyond the Solar System Homework for Geology 8
... 20. A collection or cluster of stars and solar systems such as the Milky Way or Andromeda. 21. This type of nebula is a cloud of glowing gas excited by ultraviolet radiation from hot stars. ...
... 20. A collection or cluster of stars and solar systems such as the Milky Way or Andromeda. 21. This type of nebula is a cloud of glowing gas excited by ultraviolet radiation from hot stars. ...
The Scientific Method
... i.e., to within 1 arc minute. (Comment‐‐A simple thing which Tycho did which greatly improved his accuracy was to make several measurements of quantities and to then average his results in order to arrive at his final answer. This is standard practice today, but was highly unusual during Tycho's tim ...
... i.e., to within 1 arc minute. (Comment‐‐A simple thing which Tycho did which greatly improved his accuracy was to make several measurements of quantities and to then average his results in order to arrive at his final answer. This is standard practice today, but was highly unusual during Tycho's tim ...
Script
... selected cases. We will look at these exciting new developments in Chapter 3 when we discuss planetary atmospheres. Up to date information on detection of exoplanets: The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia (http://exoplanet.eu/) Orbital radius of extrasolar planets: ...
... selected cases. We will look at these exciting new developments in Chapter 3 when we discuss planetary atmospheres. Up to date information on detection of exoplanets: The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia (http://exoplanet.eu/) Orbital radius of extrasolar planets: ...
Searching for Baby Planets in a Star`s Dusty Rings
... which emits over a broad continuum of wavelengths, can be summed to obtain a good signal, the same cannot be done for the gas emission, which occurs in narrow spectral lines. The resulting images of the continuum emission reveal three clear gaps, but the images of the line emission show a much smoot ...
... which emits over a broad continuum of wavelengths, can be summed to obtain a good signal, the same cannot be done for the gas emission, which occurs in narrow spectral lines. The resulting images of the continuum emission reveal three clear gaps, but the images of the line emission show a much smoot ...
2 - 1
... {Abstract – In this segment of our video book, we cover distances inside our Solar System. We start out with a brief history beginning with how Nicolas Copernicus used planetary retrograde motion to help move us from the Earth-centric view to the Sun-centric view of our Solar System. We work our way ...
... {Abstract – In this segment of our video book, we cover distances inside our Solar System. We start out with a brief history beginning with how Nicolas Copernicus used planetary retrograde motion to help move us from the Earth-centric view to the Sun-centric view of our Solar System. We work our way ...
A Jupiter-mass companion to a solar-type star
... The presence of a Jupiter-mass companion to the star 51 Pegasi is inferred from observations of periodic variations in the star's radial velocity. The companion lies only about eight million kilometres from the star, which would be well inside the orbit of Mercury in our Solar System. This object mi ...
... The presence of a Jupiter-mass companion to the star 51 Pegasi is inferred from observations of periodic variations in the star's radial velocity. The companion lies only about eight million kilometres from the star, which would be well inside the orbit of Mercury in our Solar System. This object mi ...
ASTR100 Class 01 - University of Maryland Department of
... measurements of main-sequence stars show that the hot, blue stars are much more massive than the cool, red ones. ...
... measurements of main-sequence stars show that the hot, blue stars are much more massive than the cool, red ones. ...
Nucleus hydrogen helium Relative Mass 1.007825 4.0037 Helium
... One theory of the origin of the Universe was that billions of years ago all matter was in one place, then it exploded (‘big bang’). Describe, in as much detail as you can, how our star (the Sun) formed from the time when there was just dust and gas (mostly hydrogen) up to now when it is in its main ...
... One theory of the origin of the Universe was that billions of years ago all matter was in one place, then it exploded (‘big bang’). Describe, in as much detail as you can, how our star (the Sun) formed from the time when there was just dust and gas (mostly hydrogen) up to now when it is in its main ...
thefixedstarsinnatal.. - Saptarishis Astrology
... inclined to disagree with him about the squares having effect - Anne Wright]. In the case of the trines and sextiles very little effect, if any, is to be discovered, but in all probability this is due to the fact that, with the exception of the square and opposition, the aspects to the body of a sta ...
... inclined to disagree with him about the squares having effect - Anne Wright]. In the case of the trines and sextiles very little effect, if any, is to be discovered, but in all probability this is due to the fact that, with the exception of the square and opposition, the aspects to the body of a sta ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... very high actual brightness (100,000 times that of our sun) and yet has a temperature that is quite cool (3500 Kelvins). How can this be? A. B. C. D. ...
... very high actual brightness (100,000 times that of our sun) and yet has a temperature that is quite cool (3500 Kelvins). How can this be? A. B. C. D. ...
Lecture #5 Copernicus, Kepler, Galileo, and Newton 11 June 2012
... time, it was thought that changes only occurred in the sublunar regions; the idea that there could be a change among the fixed stars was revolutionary. His observations of the Great Comet of 1577 showed that it was farther away than the orbit of the Moon. At the time, comets were thought to be atmos ...
... time, it was thought that changes only occurred in the sublunar regions; the idea that there could be a change among the fixed stars was revolutionary. His observations of the Great Comet of 1577 showed that it was farther away than the orbit of the Moon. At the time, comets were thought to be atmos ...
Nature of Stars 2
... Kepler 3rd Law gives us a relationship between the average distance of a planet from the Sun and the amount of time it takes a planet to orbit the Sun once. For objects orbiting the Sun, P2 = a3 (P in years, a in AUs). Kepler’s relation does not work for objects that are not orbiting the Sun, for ex ...
... Kepler 3rd Law gives us a relationship between the average distance of a planet from the Sun and the amount of time it takes a planet to orbit the Sun once. For objects orbiting the Sun, P2 = a3 (P in years, a in AUs). Kepler’s relation does not work for objects that are not orbiting the Sun, for ex ...
How far away are the Stars?
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age old question’: How far away are the stars? ...
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age old question’: How far away are the stars? ...
2014-2015 SCIENCE Instructional Curriculum Plan Grade: K
... SC.4.E.5.In.4: Recognize that the Sun appears to rise and set because of Earth’s rotation in a 24hour day. SC.4.E.5.Su.4: Recognize that the side of Earth facing the Sun has daylight. SC.4.E.5.Pa.3: Identify morning, noon, and night. SC.4.E.5.In.5: Identify objects and people related to the space pr ...
... SC.4.E.5.In.4: Recognize that the Sun appears to rise and set because of Earth’s rotation in a 24hour day. SC.4.E.5.Su.4: Recognize that the side of Earth facing the Sun has daylight. SC.4.E.5.Pa.3: Identify morning, noon, and night. SC.4.E.5.In.5: Identify objects and people related to the space pr ...
what`s up this month – march 2016
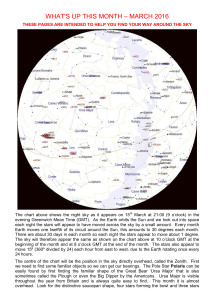
... The night sky looking south on 15th March The chart above shows the night sky looking south at about 21:00 on 15th March. West is to the right and east to the left. The point in the sky directly overhead is known as the Zenith or Nadir and is shown on the chart at the upper centre of the chart. The ...
... The night sky looking south on 15th March The chart above shows the night sky looking south at about 21:00 on 15th March. West is to the right and east to the left. The point in the sky directly overhead is known as the Zenith or Nadir and is shown on the chart at the upper centre of the chart. The ...
Catching Planets in Formation with GMT
... • Substantial mismatch between predicted and observed distribution of exoplanets. • Major uncertainties: • How do gas-giant planets form. • How much do planets migrate. • Are there many habitable (water, etc) planets. ...
... • Substantial mismatch between predicted and observed distribution of exoplanets. • Major uncertainties: • How do gas-giant planets form. • How much do planets migrate. • Are there many habitable (water, etc) planets. ...
Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) - Sunshine Coast Centre RASC
... ► It was quickly realised that this bright reflection nebula was from a star that had flared during the last few months ...
... ► It was quickly realised that this bright reflection nebula was from a star that had flared during the last few months ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.