Slide 1
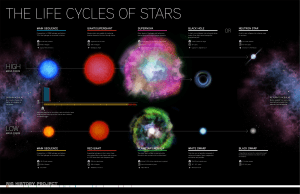
... low mass stars • Red giants continue to eject outer layers and evolve along the Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) • AGB stars are left with the stellar core surrounded by a relatively thin sphere of hot gas which looks like planetary disk, and called Planetary Nebulae (PNe) (nothing to do with planets p ...
... low mass stars • Red giants continue to eject outer layers and evolve along the Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) • AGB stars are left with the stellar core surrounded by a relatively thin sphere of hot gas which looks like planetary disk, and called Planetary Nebulae (PNe) (nothing to do with planets p ...
14 The Planets
... Blue color due to methane gas (like Uranus) Fastest winds in solar system (1,500 mi/hour, windier than ...
... Blue color due to methane gas (like Uranus) Fastest winds in solar system (1,500 mi/hour, windier than ...
The Solar System Worksheet - Laureate International College
... < to see how large the Sun is compared to this planet < boundary between the inside & outside of the Sun < yellow part we see from Earth (coolest layer ~ 5500°C) < large, often curved, bright stream of particles < extends outward from the photosphere into the corona < layer outside the core (plasma ...
... < to see how large the Sun is compared to this planet < boundary between the inside & outside of the Sun < yellow part we see from Earth (coolest layer ~ 5500°C) < large, often curved, bright stream of particles < extends outward from the photosphere into the corona < layer outside the core (plasma ...
NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS
... degrees Celsius (about 18,000 degrees F) and hydrogen fusion begins, a STAR is born. ...
... degrees Celsius (about 18,000 degrees F) and hydrogen fusion begins, a STAR is born. ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... Composition is > 98% hydrogen and helium. 1/3 of the hydrogen is converted to helium. ...
... Composition is > 98% hydrogen and helium. 1/3 of the hydrogen is converted to helium. ...
our planet - section 1
... The universe is massive and is continuing to expand. Our minds cannot fathom the enormous scope and size of the universe. The size for some of the objects in the universe is so large that they are measured in light years. A light year is the distance light will travel in one year. The speed of light ...
... The universe is massive and is continuing to expand. Our minds cannot fathom the enormous scope and size of the universe. The size for some of the objects in the universe is so large that they are measured in light years. A light year is the distance light will travel in one year. The speed of light ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... The Heavens Are Not Changeless • The Stars Move – Most of our constellations would have been unrecognizable to Neanderthal Man ...
... The Heavens Are Not Changeless • The Stars Move – Most of our constellations would have been unrecognizable to Neanderthal Man ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What force causes particles of stellar dust to become attracted to each other ? ____gravity_____ The most widely held astronomical theory about the origin of the universe is the ...
... What force causes particles of stellar dust to become attracted to each other ? ____gravity_____ The most widely held astronomical theory about the origin of the universe is the ...
Introduction Notes - Sunflower Astronomy
... unit is the distance from the Earth to the Sun, 1.48x108 km) or 4.3 light years. This distance is typical of distances between stars in our galaxy. Stars are formed from interstellar clouds of dust and gas and evolve at rates that depend on their mass (massive stars evolve fast, less massive stars e ...
... unit is the distance from the Earth to the Sun, 1.48x108 km) or 4.3 light years. This distance is typical of distances between stars in our galaxy. Stars are formed from interstellar clouds of dust and gas and evolve at rates that depend on their mass (massive stars evolve fast, less massive stars e ...
stars concept review
... b. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born c. a shrinking, spinning region in space with a central concentration of matter d. a large explosion on a star that makes it brighter e. an object so dense that even light cannot escape its gravity ...
... b. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born c. a shrinking, spinning region in space with a central concentration of matter d. a large explosion on a star that makes it brighter e. an object so dense that even light cannot escape its gravity ...
Coursework 2 File
... (ii). Define what is meant by the synodic period for two planets – the Earth and a superior planet. (iii). By assuming that the planets in the Solar System are on circular orbits, Copernicus devised a method for calculating the sidereal period for either an inferior or superior planet based on know ...
... (ii). Define what is meant by the synodic period for two planets – the Earth and a superior planet. (iii). By assuming that the planets in the Solar System are on circular orbits, Copernicus devised a method for calculating the sidereal period for either an inferior or superior planet based on know ...
a 03 Scale and Comparing Planets to Stars ppt
... • This Means that the light we see from Andromeda Galaxy left there 2.2 million years ago. • It is therefore very possible that some of the stars in Andromeda have exploded as a supernova or gone out long ago. The message of these star finishing events just has not gotten to us yet! ...
... • This Means that the light we see from Andromeda Galaxy left there 2.2 million years ago. • It is therefore very possible that some of the stars in Andromeda have exploded as a supernova or gone out long ago. The message of these star finishing events just has not gotten to us yet! ...
GEARS Workshop Monday - Georgia Southern University
... own. (despite the fact we keep assigning them as homework) ...
... own. (despite the fact we keep assigning them as homework) ...
Astronomy
... - a galaxy is a large collection of billions of stars - our solar system is in the Milky Way galaxy. ...
... - a galaxy is a large collection of billions of stars - our solar system is in the Milky Way galaxy. ...
Sample Exam 1
... 16. Which one of the following is NOT true of Jupiter? a. largest and most massive planet b. a rotational speed slower than Mercury c. dominantly composed of hydrogen d. a very dense atmosphere 17. Micrometeorites are found on the surface of the Earth, what are they called prior to impact? a. meteor ...
... 16. Which one of the following is NOT true of Jupiter? a. largest and most massive planet b. a rotational speed slower than Mercury c. dominantly composed of hydrogen d. a very dense atmosphere 17. Micrometeorites are found on the surface of the Earth, what are they called prior to impact? a. meteor ...
E8B4_CRT_CR_MSTIPS_FinalS
... 6. Earth is considered to be a unique plant, different from all the others within the Solar System. Which of the following characteristics makes Earth unique? A. Life B. Water C. Orbital Path D. Rotational Period 7. The Solar System consists of the Sun, asteroids, comets, and A. six planets and the ...
... 6. Earth is considered to be a unique plant, different from all the others within the Solar System. Which of the following characteristics makes Earth unique? A. Life B. Water C. Orbital Path D. Rotational Period 7. The Solar System consists of the Sun, asteroids, comets, and A. six planets and the ...
Kepler`s Law - New Mexico Tech
... The Sun’s Lifecycle • The Sun was formed about 4.57 billion years ago when a hydrogen molecular cloud collapsed. • It is about halfway through its main-sequence evolution, during this time, nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium. • It will spend approx. 10 billion years as a ...
... The Sun’s Lifecycle • The Sun was formed about 4.57 billion years ago when a hydrogen molecular cloud collapsed. • It is about halfway through its main-sequence evolution, during this time, nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium. • It will spend approx. 10 billion years as a ...
File
... Where to Look for Life? • Many scientists are convinced that habitable conditions exist beyond Earth and that the solar system offers several possible places that may be, or have been, able to support life. • Sending spacecraft out to look for life is expensive and can take a long time • Scientists ...
... Where to Look for Life? • Many scientists are convinced that habitable conditions exist beyond Earth and that the solar system offers several possible places that may be, or have been, able to support life. • Sending spacecraft out to look for life is expensive and can take a long time • Scientists ...
STARS
... A high mass will form a neutron star An extremely high mass will have a density so high it creates an extreme gravity field, where nothing can escape. This is known as a black hole ...
... A high mass will form a neutron star An extremely high mass will have a density so high it creates an extreme gravity field, where nothing can escape. This is known as a black hole ...
Solar System from Web
... The Sun’s Lifecycle • The Sun was formed about 4.57 billion years ago when a hydrogen molecular cloud collapsed. • It is about halfway through its main-sequence evolution, during this time, nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium. • It will spend approx. 10 billion years as a ...
... The Sun’s Lifecycle • The Sun was formed about 4.57 billion years ago when a hydrogen molecular cloud collapsed. • It is about halfway through its main-sequence evolution, during this time, nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium. • It will spend approx. 10 billion years as a ...
Ch 22 The Sun & It’s Solar System
... related to the distance between the objects & the masses of the two objects b. Calculated the mass of planets from dimensions of orbit c. Thought tides were caused by force of moon as it revolves around Earth d. Used gravity to explain the long orbit of comets & proved they are a part of the solar s ...
... related to the distance between the objects & the masses of the two objects b. Calculated the mass of planets from dimensions of orbit c. Thought tides were caused by force of moon as it revolves around Earth d. Used gravity to explain the long orbit of comets & proved they are a part of the solar s ...
The Sun-Earth-Moon System
... • Composition can be determined through spectral analysis. • Different elements emit different wavelengths of light. • Spectral types are assigned letters (O, B, A, F, G, K, and M). ...
... • Composition can be determined through spectral analysis. • Different elements emit different wavelengths of light. • Spectral types are assigned letters (O, B, A, F, G, K, and M). ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... o The Doppler effect, where objects moving further away produce light that is shifted to the red end of the spectrum, while objects moving closer produce light that is shifted to the blue end of the spectrum. o Light from distant galaxies is red-shifted, proving that they are moving away from Earth. ...
... o The Doppler effect, where objects moving further away produce light that is shifted to the red end of the spectrum, while objects moving closer produce light that is shifted to the blue end of the spectrum. o Light from distant galaxies is red-shifted, proving that they are moving away from Earth. ...
lecture9 Solar System1
... grew larger gravity captured hydrogen & helium composition similar to Sun gaseous accretion disk forms around planet Moons form in disk around planet ...
... grew larger gravity captured hydrogen & helium composition similar to Sun gaseous accretion disk forms around planet Moons form in disk around planet ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.