Document
... ❶ In front of the class, explain the steps for assembling the solar system flip book: • Glue the photocopies of the planetary orbit sheets (Appendix 1) onto thick paper. • On each of the illustrations numbered 1 to 24, colour the Sun and four planets (Sun = yellow; Mercury = green; Venus = brown; Ea ...
... ❶ In front of the class, explain the steps for assembling the solar system flip book: • Glue the photocopies of the planetary orbit sheets (Appendix 1) onto thick paper. • On each of the illustrations numbered 1 to 24, colour the Sun and four planets (Sun = yellow; Mercury = green; Venus = brown; Ea ...
CHAPTER 32 1. What is happening inside a star that isn`t happening
... 18. A star somewhat larger than our Sun produces more heat as it contracts. This star will then fuse _____ into heavier elements. ...
... 18. A star somewhat larger than our Sun produces more heat as it contracts. This star will then fuse _____ into heavier elements. ...
Your Birthday on Another Planet
... ❶ In front of the class, explain the steps for assembling the solar system flip book: • Glue the photocopies of the planetary orbit sheets (Appendix 1) onto thick paper. • On each of the illustrations numbered 1 to 24, colour the Sun and four planets (Sun = yellow; Mercury = green; Venus = brown; Ea ...
... ❶ In front of the class, explain the steps for assembling the solar system flip book: • Glue the photocopies of the planetary orbit sheets (Appendix 1) onto thick paper. • On each of the illustrations numbered 1 to 24, colour the Sun and four planets (Sun = yellow; Mercury = green; Venus = brown; Ea ...
Earth Science Facts - Kempsville Middle School
... 8. Constants are factors that are the same. Independent variable is the only thing tested and the dependent variable responds to the independent variable. 9. A scientific theory is based on observations and is proven to be true. 10. Scientific law has proven to be true over time. 11. The altitude of ...
... 8. Constants are factors that are the same. Independent variable is the only thing tested and the dependent variable responds to the independent variable. 9. A scientific theory is based on observations and is proven to be true. 10. Scientific law has proven to be true over time. 11. The altitude of ...
The search for exoplanets
... the research of this subject and nowadays we estimate that there are something like 1011 to 1012 stars in our galaxy and even 1022 to 1024 stars in our universe.(4) A mindboggling number, that isn’t easier to imagine, if you think about the fact, that there are more stars in our universe than there ...
... the research of this subject and nowadays we estimate that there are something like 1011 to 1012 stars in our galaxy and even 1022 to 1024 stars in our universe.(4) A mindboggling number, that isn’t easier to imagine, if you think about the fact, that there are more stars in our universe than there ...
What is the biggest planet in the solar system?
... of a core is also supported by models of planetary Jupiter also has an array of Irregular Satellites, formation that indicate how a rocky or icy core which are substantially smaller and have more would have been necessary at some point in the distant and eccentric orbits than the others. These plane ...
... of a core is also supported by models of planetary Jupiter also has an array of Irregular Satellites, formation that indicate how a rocky or icy core which are substantially smaller and have more would have been necessary at some point in the distant and eccentric orbits than the others. These plane ...
Chapter 13: Earth, Moon, and Beyond
... Sun: star at the center of our universe. rotate: to spin on an axis. axis: An imaginary line that passes through Earth’s center and its North and South poles. revolve: To travel in a closed path. orbit: The path one body takes in space as it revolves around another. equator: An imaginary ...
... Sun: star at the center of our universe. rotate: to spin on an axis. axis: An imaginary line that passes through Earth’s center and its North and South poles. revolve: To travel in a closed path. orbit: The path one body takes in space as it revolves around another. equator: An imaginary ...
File
... One of the storm is called the Great Red Spot Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn, Uranus and Neptune but it is the biggest of the gas giant and Jupiter have stronger winds and storms than Earth . Together, these four planets are sometimes called as the Jovian or outer planets. te ...
... One of the storm is called the Great Red Spot Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn, Uranus and Neptune but it is the biggest of the gas giant and Jupiter have stronger winds and storms than Earth . Together, these four planets are sometimes called as the Jovian or outer planets. te ...
universal gravitation pdf
... • Ellipse is oval with two focal points (foci) • Speed varies in elliptical orbit • Faster speed close to earth, slower when farther away • All planets follow elliptical orbits around sun ...
... • Ellipse is oval with two focal points (foci) • Speed varies in elliptical orbit • Faster speed close to earth, slower when farther away • All planets follow elliptical orbits around sun ...
The fantastic journey of that ring on your finger: From
... where do the other elements—118 in total—come from? And although hydrogen and helium remain the most abundant elements in the universe, accounting for 98.5% of observable matter, why on planets like ours do we live surrounded by residual cosmic elements? Well, let’s start from the beginning of time… ...
... where do the other elements—118 in total—come from? And although hydrogen and helium remain the most abundant elements in the universe, accounting for 98.5% of observable matter, why on planets like ours do we live surrounded by residual cosmic elements? Well, let’s start from the beginning of time… ...
Earth in Space and Beyond - Westmoreland Central School
... – Mass is about 33,000 times Earth’s – Diameter is about 109 times Earth’s – Temp is about 6,000 K at surface and at surface and 12 million K at center – Average star (mass, diameter, and density) – Composed primarily of hydrogen and helium – About 5 billion years old (5 billion years left) – Sunspo ...
... – Mass is about 33,000 times Earth’s – Diameter is about 109 times Earth’s – Temp is about 6,000 K at surface and at surface and 12 million K at center – Average star (mass, diameter, and density) – Composed primarily of hydrogen and helium – About 5 billion years old (5 billion years left) – Sunspo ...
Protostars and planets
... between planets and stars seemed too obvious to require precise formulation when the only planets known were those in the Solar System: the most massive of them is only MJupiter ≈ 10−3 M⊙ , and there are many of them follow approximately circular orbits about the Sun (indeed “planet” comes from Gree ...
... between planets and stars seemed too obvious to require precise formulation when the only planets known were those in the Solar System: the most massive of them is only MJupiter ≈ 10−3 M⊙ , and there are many of them follow approximately circular orbits about the Sun (indeed “planet” comes from Gree ...
quiz 2
... 16. According to a Zodiacal Chart shown in class, the dates listed for “signs” are as follows: If you were born on July 1, which is your true “sun sign?” a) Gemini b)Cancer c)Leo d) Virgo e) Taurus For Questions 17 – 20, complete the following sentences using the letter for the correct terms from th ...
... 16. According to a Zodiacal Chart shown in class, the dates listed for “signs” are as follows: If you were born on July 1, which is your true “sun sign?” a) Gemini b)Cancer c)Leo d) Virgo e) Taurus For Questions 17 – 20, complete the following sentences using the letter for the correct terms from th ...
Midterm 1 Completion What is the official name of the special star
... 1) Planets orbit around the Sun in an ellipse with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse. 2) The line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. Because of this when a planet is closer to the Sun in its orbit, it moves faster than when the planet is farther away from the Sun. ...
... 1) Planets orbit around the Sun in an ellipse with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse. 2) The line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. Because of this when a planet is closer to the Sun in its orbit, it moves faster than when the planet is farther away from the Sun. ...
Quiz 2 material 104
... 2.3 Stars and Planets (page 31): Nuclear fusion creates stars. Stars can be various sizes and go through various stages. Our Sun is an ordinary star (see Hertsprung-Russell figure 2.9 and note where the Sun plots on the diagram) powered by hydrogen fusion. The lifecycle of our Sun is described in th ...
... 2.3 Stars and Planets (page 31): Nuclear fusion creates stars. Stars can be various sizes and go through various stages. Our Sun is an ordinary star (see Hertsprung-Russell figure 2.9 and note where the Sun plots on the diagram) powered by hydrogen fusion. The lifecycle of our Sun is described in th ...
Astronomy Facts
... The sun is 1.4 million km across (110 times the earth), and over 150 million km away (500 light seconds) The largest stars (eg: Betelgeuse, Antares) are over 400 million km across (more than 300 times the diameter of the Sun) The brightest stars are over 10,000 times brighter than the sun. The dista ...
... The sun is 1.4 million km across (110 times the earth), and over 150 million km away (500 light seconds) The largest stars (eg: Betelgeuse, Antares) are over 400 million km across (more than 300 times the diameter of the Sun) The brightest stars are over 10,000 times brighter than the sun. The dista ...
Physics of Astronomy – Week 3 quiz
... space probes, but do not hold for objects orbiting any other object in the universe. apply only to large planets orbiting our Sun, but provide only an approximate description for smaller objects, such as asteroids, etc. and are not applicable at all for other situations such as mutually orbiting bin ...
... space probes, but do not hold for objects orbiting any other object in the universe. apply only to large planets orbiting our Sun, but provide only an approximate description for smaller objects, such as asteroids, etc. and are not applicable at all for other situations such as mutually orbiting bin ...
Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan
... 6.7 How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Edu ...
... 6.7 How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Edu ...
wdtoc1
... radius of 2,403 km (1,493 mi), making it nearly the same size as the planet Mercury. Since Callisto consists mostly of low-density water ice, however, the moon is only onethird as massive as rocky, metallic Mercury. Callisto’s interior is probably not ...
... radius of 2,403 km (1,493 mi), making it nearly the same size as the planet Mercury. Since Callisto consists mostly of low-density water ice, however, the moon is only onethird as massive as rocky, metallic Mercury. Callisto’s interior is probably not ...
Understanding the Outer Planets and Planetary Atmospheres
... thin and composed of dust-like small particles. Saturn’s rings are broad, bright, and opaque. Uranus has narrow, dark rings among broad lanes of dust that are invisible from Earth. Neptune’s rings include incomplete arcs restricted to a small section of their ...
... thin and composed of dust-like small particles. Saturn’s rings are broad, bright, and opaque. Uranus has narrow, dark rings among broad lanes of dust that are invisible from Earth. Neptune’s rings include incomplete arcs restricted to a small section of their ...
Chapter 1 - A Modern View of the Universe
... planets and moons, asteroids, comets Light crossing time: 8 hours (Earth-Sun: 8.3 minutes) ...
... planets and moons, asteroids, comets Light crossing time: 8 hours (Earth-Sun: 8.3 minutes) ...
Chapter 6
... 6.7 How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Edu ...
... 6.7 How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Edu ...
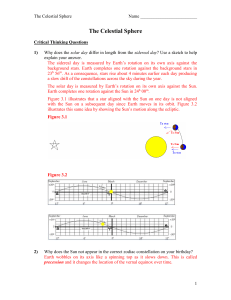
The Celestial Sphere
... October. This is about 6 – 8 weeks later than the normal July – August period when the summer games are held. Why did the International Olympic Committee schedule the 2000 games around the equinox rather than closer to the solstice? ...
... October. This is about 6 – 8 weeks later than the normal July – August period when the summer games are held. Why did the International Olympic Committee schedule the 2000 games around the equinox rather than closer to the solstice? ...
Astronomical Ideas Fall 2012 HW 2 solutions 1. a. Compare the
... planets nearby their parent stars in transit searches, because planets with smaller orbital radii have shorter periods. We need to observe multiple transits to confirm the presence of a planet via this technique. If a planet is very far away from its star, its period will be longer than a year so ob ...
... planets nearby their parent stars in transit searches, because planets with smaller orbital radii have shorter periods. We need to observe multiple transits to confirm the presence of a planet via this technique. If a planet is very far away from its star, its period will be longer than a year so ob ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.