Time runs out for Herschel
... eye of the storm is about 2000 km across – ten times the typical size on Earth – and clouds at the outer edge of the hurricane on Saturn are moving at more than 500 kph – rather faster than on Earth! One difference from terrestrial hurricanes is that this storm is locked into the weather system at t ...
... eye of the storm is about 2000 km across – ten times the typical size on Earth – and clouds at the outer edge of the hurricane on Saturn are moving at more than 500 kph – rather faster than on Earth! One difference from terrestrial hurricanes is that this storm is locked into the weather system at t ...
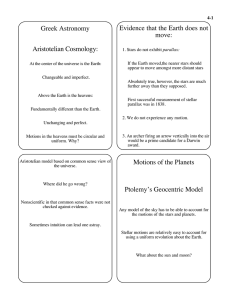
A Short History of the Origin of Modern Astronomy What is a “Theory
... The universe is governed by two sets of rules to “...save the appearances of symmetry and perfection.” – objects on Earth naturally seek the downward direction. – Heavenly objects naturally move in circles. ...
... The universe is governed by two sets of rules to “...save the appearances of symmetry and perfection.” – objects on Earth naturally seek the downward direction. – Heavenly objects naturally move in circles. ...
Science 1 (MillinerSci1)
... 6. A) the Moon. 7. D) the Sun. 8. C) planet. 9. D) star. 10. C) a telescope 11. B) The Moon is closer to Earth. 12. D) telescope 13. B) The brown rabbits inherited different coat colors than the white rabbits. 14. A) satellites 15. C) telescope 16. D) telescope 17. B) a desert 18. D) too many to cou ...
... 6. A) the Moon. 7. D) the Sun. 8. C) planet. 9. D) star. 10. C) a telescope 11. B) The Moon is closer to Earth. 12. D) telescope 13. B) The brown rabbits inherited different coat colors than the white rabbits. 14. A) satellites 15. C) telescope 16. D) telescope 17. B) a desert 18. D) too many to cou ...
History of Astronomy
... same speed? No. A planet’s speed depends on its average distance from the Sun. The closest planet moves fastest, the most ...
... same speed? No. A planet’s speed depends on its average distance from the Sun. The closest planet moves fastest, the most ...
Time
... Time • What Time Is It? Before 1884, almost every town in the world kept its own local time. There were no national or international conventions which set how time should be measured, or when the day would begin and end, or what length an hour might be. However, with the vast expansion of the railwa ...
... Time • What Time Is It? Before 1884, almost every town in the world kept its own local time. There were no national or international conventions which set how time should be measured, or when the day would begin and end, or what length an hour might be. However, with the vast expansion of the railwa ...
KS1 Astronomy Centre trail
... say that it landed safely so astronomers did not know what happened to it until January 2015 when a satellite orbiting Mars took a picture of it. ...
... say that it landed safely so astronomers did not know what happened to it until January 2015 when a satellite orbiting Mars took a picture of it. ...
Chapter 23 Section 4 Minor Members of the Solar System
... (1) Interplanetary debris that was not gravitationally swept up by the planets during the formation of the solar system (2) Material from the asteroid belt (3) The solid remains of comets that once traveled near Earth’s orbit. A few meteoroids are believed to be fragments of the moon, or possibly Ma ...
... (1) Interplanetary debris that was not gravitationally swept up by the planets during the formation of the solar system (2) Material from the asteroid belt (3) The solid remains of comets that once traveled near Earth’s orbit. A few meteoroids are believed to be fragments of the moon, or possibly Ma ...
Chapter 39
... 39.5 The Sun • Sun’s surface = 5800 K (10,000 degrees Fahrenheit!!), made of plasma – Photosphere – transparent solar surface – Sunspots created by cooler areas – About the size of earth ...
... 39.5 The Sun • Sun’s surface = 5800 K (10,000 degrees Fahrenheit!!), made of plasma – Photosphere – transparent solar surface – Sunspots created by cooler areas – About the size of earth ...
Kepler*s laws of planetary motion
... and the planet’s orbital period • Orbital period- time required for planet to complete one orbit • Helps astronomers find out how far away planets are from the sun ...
... and the planet’s orbital period • Orbital period- time required for planet to complete one orbit • Helps astronomers find out how far away planets are from the sun ...
23.3 Note Guide The Outer Planets In 2004, the space probe
... The _____________________________ probe, carried into space by the Cassini orbiter, will descend to Titan’s surface for further studies In this section, we’ll take a clue from Cassini and explore the outer planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, Uranus, and Pluto ...
... The _____________________________ probe, carried into space by the Cassini orbiter, will descend to Titan’s surface for further studies In this section, we’ll take a clue from Cassini and explore the outer planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Neptune, Uranus, and Pluto ...
To learn how the shape and period of... To learn how the shape of the orbit... Gravity, Orbits and Kepler’s Laws
... 3. Imagine another solar system with a star of the same mass as the Sun. In this solar system there is a planet with a mass twice that of Earth orbiting at a distance of 1 AU from the star. What is the orbital period of that planet? Explain your answer based on what you observed in this activity. 4. ...
... 3. Imagine another solar system with a star of the same mass as the Sun. In this solar system there is a planet with a mass twice that of Earth orbiting at a distance of 1 AU from the star. What is the orbital period of that planet? Explain your answer based on what you observed in this activity. 4. ...
Astronomy Library wk 4 .cwk (WP)
... The Copernican revolution was not just the birth of modern astronomy but modern science in general. ...
... The Copernican revolution was not just the birth of modern astronomy but modern science in general. ...
geol0810 homework 1: early solar system history
... Isotopic analyses. Certain isotopic ratios in samples from asteroids, comets, and meteorites reveal a wealth of information about the sequence of events in early Solar System history. A variety of isotopic systems can be used, but we will focus on only two of them: the hafnium-tungsten and aluminum- ...
... Isotopic analyses. Certain isotopic ratios in samples from asteroids, comets, and meteorites reveal a wealth of information about the sequence of events in early Solar System history. A variety of isotopic systems can be used, but we will focus on only two of them: the hafnium-tungsten and aluminum- ...
Asteroids4 Feb Asteroids, Comets, Minor Planets • Understanding composition of solar system
... – Read for next week: Chapter 8, Formation of the solar system ...
... – Read for next week: Chapter 8, Formation of the solar system ...
a light year is
... 3. The astronomical unit is defined as a) the time between astronomical observations , b) the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun c) a unit for measuring the amount of work astronomers do , d) not well defined 4. The observed changing positions of the stars during a night is the result of th ...
... 3. The astronomical unit is defined as a) the time between astronomical observations , b) the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun c) a unit for measuring the amount of work astronomers do , d) not well defined 4. The observed changing positions of the stars during a night is the result of th ...
Name
... 22. Jupiter is a very large planet in our solar system, but it failed to become a star due to: a. It’s mass b. It’s energy c. It’s chemical makeup d. It’s being cooled off because it is so far away from the sun. 23. Scientists believe Mars might have had running water at one time in the past because ...
... 22. Jupiter is a very large planet in our solar system, but it failed to become a star due to: a. It’s mass b. It’s energy c. It’s chemical makeup d. It’s being cooled off because it is so far away from the sun. 23. Scientists believe Mars might have had running water at one time in the past because ...
Shashanka R. Gurumath1, Hiremath KM2, and
... of a star belongs to spectral type of M stars. It is to be noted that, nearly 70% of stars in our galaxy are belongs to M stars. Hence, this study suggests that, M stars are more likely to harbor an Earth’s twin. ...
... of a star belongs to spectral type of M stars. It is to be noted that, nearly 70% of stars in our galaxy are belongs to M stars. Hence, this study suggests that, M stars are more likely to harbor an Earth’s twin. ...
Terrestrial Planet (and Life) Finder
... Now estimate number of planets with life in our Galaxy (not number with intelligent, communicating life) If we leave out fi and fc (i.e. assume they are unity—all life forms develop our kind of intelligence and technology and try to communicate), we are calculating the number of life-bearing planet ...
... Now estimate number of planets with life in our Galaxy (not number with intelligent, communicating life) If we leave out fi and fc (i.e. assume they are unity—all life forms develop our kind of intelligence and technology and try to communicate), we are calculating the number of life-bearing planet ...
Topic Nine - Science - Miami
... information about the Universe, but not specific technology. 1. Gravity Forms Stars, Solar Systems, and (as in telescopes and probes) ...
... information about the Universe, but not specific technology. 1. Gravity Forms Stars, Solar Systems, and (as in telescopes and probes) ...
Lecture 5 Astronomy
... 24. Pluto is so cold compounds which are gasses on Earth are solids like nitrogen. What major difficulty would impede human exploration of this planet? A. Body temperature of astronauts would cause them to melt through Pluto’s crust B. Lack of solar radiation would limit using of solar panels to pro ...
... 24. Pluto is so cold compounds which are gasses on Earth are solids like nitrogen. What major difficulty would impede human exploration of this planet? A. Body temperature of astronauts would cause them to melt through Pluto’s crust B. Lack of solar radiation would limit using of solar panels to pro ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.




![Macmillan Natural and Social Science 1 [bold PB font]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006552150_1-744c96fecd477a0d4dbe6606035b9c8f-300x300.png)