PDF file of Lab 5
... Introduction: This lab is about “models” for reality and what they predict. We would like to compare the predictions for various models to our observations made over the past few weeks. For our solar observations, we used a transparent half-dome to mark the location of the sun in the sky for several ...
... Introduction: This lab is about “models” for reality and what they predict. We would like to compare the predictions for various models to our observations made over the past few weeks. For our solar observations, we used a transparent half-dome to mark the location of the sun in the sky for several ...
program - Accretion and Early Differentiation of the Earth
... Consequences of the Moon-forming collision on Earth (Chair: D. O’Brien) 14.30-15.00 – Marty: (invited) Origin and early evolution of the terrestrial atmosphere: implications for the age of the Moon, the rate of continental crust growth, and the evolution of the young Sun 15.00-15.15 – Nakajima: The ...
... Consequences of the Moon-forming collision on Earth (Chair: D. O’Brien) 14.30-15.00 – Marty: (invited) Origin and early evolution of the terrestrial atmosphere: implications for the age of the Moon, the rate of continental crust growth, and the evolution of the young Sun 15.00-15.15 – Nakajima: The ...
ASTR 1010 – Astronomy of the Solar System – Professor Caillault
... (d) time over which the Moon completes one orbit around Earth, relative to the stars. 43. During a lunar eclipse the (b) Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon. 44. During a total lunar eclipse (as viewed from Earth) you are standing on the Moon looking back at Earth. What do you see? (d) Earth ap ...
... (d) time over which the Moon completes one orbit around Earth, relative to the stars. 43. During a lunar eclipse the (b) Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon. 44. During a total lunar eclipse (as viewed from Earth) you are standing on the Moon looking back at Earth. What do you see? (d) Earth ap ...
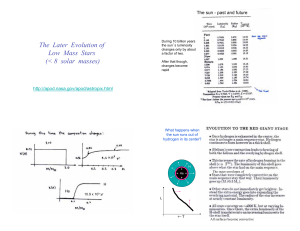
The Later Evolution of Low Mass Stars (< 8 solar masses)
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_Nebula AGB stars are known to lose mass at a prodigious rate during their final stages, around 10-5 - 10-4 solar masses per year. This obviously cannot persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin he ...
... http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_Nebula AGB stars are known to lose mass at a prodigious rate during their final stages, around 10-5 - 10-4 solar masses per year. This obviously cannot persist for much over 100,000 years. The mass loss is driven in part by the pulsational instability of the thin he ...
Exoplanets - An ESO/OPTICON/IAU summer school on modern
... Brown dwarfs: between 13-80 Jupiter-masses (only deuterium-fusion) Planetary bodies: below 13 Jupiter-masses (no natural fusion) These mass limits depend slightly on the chemical composition. But: (i) no definition from giant planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, meteors etc. in this astrophysical defi ...
... Brown dwarfs: between 13-80 Jupiter-masses (only deuterium-fusion) Planetary bodies: below 13 Jupiter-masses (no natural fusion) These mass limits depend slightly on the chemical composition. But: (i) no definition from giant planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, meteors etc. in this astrophysical defi ...
ph507lecnote06
... • Planet formation • Explaining the properties of exoplanets Rapidly developing subject - first extrasolar planet around an ordinary star only discovered in 1995 by Mayor & Queloz. Observations thought to be secure, but theory still preliminary... Resources. For observations, a good starting point i ...
... • Planet formation • Explaining the properties of exoplanets Rapidly developing subject - first extrasolar planet around an ordinary star only discovered in 1995 by Mayor & Queloz. Observations thought to be secure, but theory still preliminary... Resources. For observations, a good starting point i ...
CML_DPS_PressBriefing_10Oct2006
... 9P/Tempel 1 or C/Hale-Bopp 1995 O1 and comet-dominated YSO HD100546. It lacks carbonaceous and ferrous materials but includes small icy grains. - The composition of the HD 69830 dust resembles that of a disrupted P or D-type asteroid. The amount of mass responsible for the observed emission is the e ...
... 9P/Tempel 1 or C/Hale-Bopp 1995 O1 and comet-dominated YSO HD100546. It lacks carbonaceous and ferrous materials but includes small icy grains. - The composition of the HD 69830 dust resembles that of a disrupted P or D-type asteroid. The amount of mass responsible for the observed emission is the e ...
1 - Humble ISD
... ___________________: semimajor axes greater than 1.0 AU and perihelion distances less than 1.017 AU ___________________: perihelion distances between 1.017 and 1.3 AU; ___________________: located near Jupiter's Lagrange points (60 degrees ahead and behind Jupiter in its orbit). Several hundred such ...
... ___________________: semimajor axes greater than 1.0 AU and perihelion distances less than 1.017 AU ___________________: perihelion distances between 1.017 and 1.3 AU; ___________________: located near Jupiter's Lagrange points (60 degrees ahead and behind Jupiter in its orbit). Several hundred such ...
this article as a PDF
... Visible towards the southern horizon from winter through spring in the northern hemisphere, Orion is one of the most easily recognizable and beloved constellations. By far, the most popular celestial gem in the constellation of Orion is M42, The Great Orion Nebula. Although it is 1500 light-years aw ...
... Visible towards the southern horizon from winter through spring in the northern hemisphere, Orion is one of the most easily recognizable and beloved constellations. By far, the most popular celestial gem in the constellation of Orion is M42, The Great Orion Nebula. Although it is 1500 light-years aw ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... • Remaining core of a supergiant that was more than 40 times the size of our Sun • The core of the supergiant, after a supernova, is so dense that its gravitational pull sucks in space, time, light and matter • Thought to be at the centre of all galaxies ...
... • Remaining core of a supergiant that was more than 40 times the size of our Sun • The core of the supergiant, after a supernova, is so dense that its gravitational pull sucks in space, time, light and matter • Thought to be at the centre of all galaxies ...
Clicker Frequency Setting Lecture 2 Outline
... • stars, sun, planets appear to move WESTWARD (rise E, set W) • constellations normally “fixed” in the sky • Earth’s motion causes constellations to “rise”, “set” ...
... • stars, sun, planets appear to move WESTWARD (rise E, set W) • constellations normally “fixed” in the sky • Earth’s motion causes constellations to “rise”, “set” ...
Lecture 09
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of “hot Jupiters” has forced a reexamination of nebular theory. • “Planetary migration” or gravitational encounters may explain “hot Jupiters.” ...
... Jupiter-like planets should not form inside the frost line (at << 5 AU). • The discovery of “hot Jupiters” has forced a reexamination of nebular theory. • “Planetary migration” or gravitational encounters may explain “hot Jupiters.” ...
Winter solstice, 2016 - NRC Publications Archive
... constellation of Draco, “The Dragon”. Precession has caused the Zodiac to slip. The first sign was once Aries. It has slipped back one sign and it now starts with Pisces. In astronomy, we describe the positions of stars using analogues of the Earth’s latitude and longitude system, referred to the Ea ...
... constellation of Draco, “The Dragon”. Precession has caused the Zodiac to slip. The first sign was once Aries. It has slipped back one sign and it now starts with Pisces. In astronomy, we describe the positions of stars using analogues of the Earth’s latitude and longitude system, referred to the Ea ...
A Triple Conjunction
... triple conjunction whereby, instead of a single pass, the planets meet and separate three times over a period of a few months. The more exterior a pair of planets are, the more frequent are triple conjunctions relative to normal conjunctions, although the more infrequently a conjunction of any kind ...
... triple conjunction whereby, instead of a single pass, the planets meet and separate three times over a period of a few months. The more exterior a pair of planets are, the more frequent are triple conjunctions relative to normal conjunctions, although the more infrequently a conjunction of any kind ...
Orbital Instabilities in Triaxial Mass Distributions and
... Clusters have a moderate effect on the solar systems forming within them -- environmental effects are neither dominant nor negligible: Closest approaches of order 1000 AU Disks truncated dynamically to 300 AU Disks truncated via radiation to 40 AU Lifetimes have environmental upper limit Planetary o ...
... Clusters have a moderate effect on the solar systems forming within them -- environmental effects are neither dominant nor negligible: Closest approaches of order 1000 AU Disks truncated dynamically to 300 AU Disks truncated via radiation to 40 AU Lifetimes have environmental upper limit Planetary o ...
Why do excited at - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... A synchronous orbit means that the time for the Moon to complete one rotation around it’s own spin axis is exactly equal to the time it takes for the Moon to complete one revolution (orbit) around Earth. The Moon came into this configuration (called tidally locked) due to gravitational interactions ...
... A synchronous orbit means that the time for the Moon to complete one rotation around it’s own spin axis is exactly equal to the time it takes for the Moon to complete one revolution (orbit) around Earth. The Moon came into this configuration (called tidally locked) due to gravitational interactions ...
HomeWork #2
... 2. he placed the planets on epicycles, the centers of which followed orbits around the Sun. ...
... 2. he placed the planets on epicycles, the centers of which followed orbits around the Sun. ...
Exploring the Solar System Jeopardy!
... Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun (closest to furthest). ...
... Name the eight planets in order by increasing distance from the sun (closest to furthest). ...
titel - Maastricht University
... The line connecting a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal amounts of time. 3. Kepler's law of periods: The time required for a planet to orbit the sun, called its period, is proportional to the long axis of the ellipse raised to the 3/2 power. The constant of proportionality is the sam ...
... The line connecting a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal amounts of time. 3. Kepler's law of periods: The time required for a planet to orbit the sun, called its period, is proportional to the long axis of the ellipse raised to the 3/2 power. The constant of proportionality is the sam ...
The Big Picture: A hypothesis
... creating an alternative branch of their own timeline, so that particular events – about to happen to us in our very near future – would not actually occur. The Roswell visitors were on a purely altruistic mission. They did not have to do this, but chose to... out of compassion. But the mission went ...
... creating an alternative branch of their own timeline, so that particular events – about to happen to us in our very near future – would not actually occur. The Roswell visitors were on a purely altruistic mission. They did not have to do this, but chose to... out of compassion. But the mission went ...
Andrej Cadez - UCLA Physics & Astronomy
... • If flares are produced by magnetized disk oscillations, the magnetic field must be high enough to essentially influence dynamics, i.e. ½ m0B2~rc2. For example, a conservatively high field B=100gauss requires r to be lower then 4.5 10-16g/cm3 and has to fill the volume 4p/3(13 rg)3 to contain a mas ...
... • If flares are produced by magnetized disk oscillations, the magnetic field must be high enough to essentially influence dynamics, i.e. ½ m0B2~rc2. For example, a conservatively high field B=100gauss requires r to be lower then 4.5 10-16g/cm3 and has to fill the volume 4p/3(13 rg)3 to contain a mas ...
Button Text
... remember that is not miles, that is light years. So take 2,538,000 times ten trillion and you get the amount of miles. This distance in space, while a number we cannot possibly fathom, is minuscule. The furthest objects in space are the objects at the farthest reaches of the known universe, some 13 ...
... remember that is not miles, that is light years. So take 2,538,000 times ten trillion and you get the amount of miles. This distance in space, while a number we cannot possibly fathom, is minuscule. The furthest objects in space are the objects at the farthest reaches of the known universe, some 13 ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.