Life Histories Of Some Stars
... mass before igniting. In cold nebulae, these “baby stars” can collect this mass very quickly since there is little else to compete with the gravitational forces. This explains why massive stars spend less time in the “conception” phase compared to smaller stars. Large stars also exhaust their reserv ...
... mass before igniting. In cold nebulae, these “baby stars” can collect this mass very quickly since there is little else to compete with the gravitational forces. This explains why massive stars spend less time in the “conception” phase compared to smaller stars. Large stars also exhaust their reserv ...
solarsystemformation..
... Moons of jovian planets form in miniature disks. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Moons of jovian planets form in miniature disks. © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Life Histories Stars
... mass before igniting. In cold nebulae, these “baby stars” can collect this mass very quickly since there is little else to compete with the gravitational forces. This explains why massive stars spend less time in the “conception” phase compared to smaller stars. Large stars also exhaust their reserv ...
... mass before igniting. In cold nebulae, these “baby stars” can collect this mass very quickly since there is little else to compete with the gravitational forces. This explains why massive stars spend less time in the “conception” phase compared to smaller stars. Large stars also exhaust their reserv ...
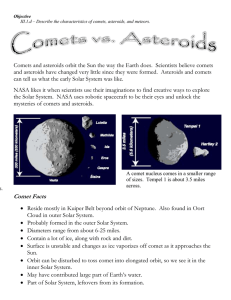
Comets vs. Asteroids
... Asteroids are small, rocky objects, left over from the formation of our Solar System. They range from the size of small rocks to the size of asteroid Ceres, which is more than 600 miles across. Ceres is so large, it is a dwarf planet, rather than an asteroid. ...
... Asteroids are small, rocky objects, left over from the formation of our Solar System. They range from the size of small rocks to the size of asteroid Ceres, which is more than 600 miles across. Ceres is so large, it is a dwarf planet, rather than an asteroid. ...
Chapter 20
... Over 160 extrasolar planets have already been found (see our discussion in Chapter 9). ...
... Over 160 extrasolar planets have already been found (see our discussion in Chapter 9). ...
AST-103L Spring 2001 - University of Texas Astronomy Home Page
... known feature is the sunspot. Typically moving in groups, these dark, planet-sized features have been known to humankind for centuries. As sunspots form and disappear over periods of days or weeks, they also appear to move across the Sun’s surface because the Sun rotates. Caused by strong magnetic f ...
... known feature is the sunspot. Typically moving in groups, these dark, planet-sized features have been known to humankind for centuries. As sunspots form and disappear over periods of days or weeks, they also appear to move across the Sun’s surface because the Sun rotates. Caused by strong magnetic f ...
AChapter 7 notes2017
... There's still a little bit of atmosphere even at the height at which the ISS orbits, and that causes some drag. Every now and then they have to re-boost the station, using rockets. During a re-boost, the station isn't in free fall. The result is, in effect, a very small "gravitational" pull inside t ...
... There's still a little bit of atmosphere even at the height at which the ISS orbits, and that causes some drag. Every now and then they have to re-boost the station, using rockets. During a re-boost, the station isn't in free fall. The result is, in effect, a very small "gravitational" pull inside t ...
Why is it so difficult to detect planets around other stars? Planet
... • A young planet’s motion can create waves in a young star’s disk • Models show that matter in these waves can tug on a planet, causing its orbit to migrate inward ...
... • A young planet’s motion can create waves in a young star’s disk • Models show that matter in these waves can tug on a planet, causing its orbit to migrate inward ...
Unit Name or Identification
... 1.8 Recognize that gravity is a force that pulls all things on and near the earth toward the center of the earth. Gravity plays a major role in the formation of the planets, stars, and solar system and in determining their motions. 1.9 Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and ...
... 1.8 Recognize that gravity is a force that pulls all things on and near the earth toward the center of the earth. Gravity plays a major role in the formation of the planets, stars, and solar system and in determining their motions. 1.9 Describe lunar and solar eclipses, the observed moon phases, and ...
in SATURN`S RINGS
... photos defied belief (see next slide, and also the slide presentation after this). T should have been expected, after star occultation photos had revealed in 1977 existence of filamentary rings around Uranus- but it was not. ...
... photos defied belief (see next slide, and also the slide presentation after this). T should have been expected, after star occultation photos had revealed in 1977 existence of filamentary rings around Uranus- but it was not. ...
Solar System Astronomy Notes
... In fact, many of our basic time divisions (days, months, and years for example) are based on this apparent motion of celestial objects as seen from a fixed point on the earth. • Notice that this means that we can define at least two different time systems using the apparent position of different typ ...
... In fact, many of our basic time divisions (days, months, and years for example) are based on this apparent motion of celestial objects as seen from a fixed point on the earth. • Notice that this means that we can define at least two different time systems using the apparent position of different typ ...
Procedure
... 3. Shift each Saturn image so that the spectrum to be extracted will only cover the background These spectra will be subtracted from the extracted object spectra to remove the background effect This is done manually because the “apall” algorithm would take part of the rings or Saturn to be the ...
... 3. Shift each Saturn image so that the spectrum to be extracted will only cover the background These spectra will be subtracted from the extracted object spectra to remove the background effect This is done manually because the “apall” algorithm would take part of the rings or Saturn to be the ...
Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6
... 1 A galaxy is a collection of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter. A galaxy is held together by gravitational attraction. 2 The Milky Way. 3 Spiral galaxies are a rotating spin wheel of stars. Elliptical galaxies have an elliptical shape. 4 The big bang theory proposes that the universe began as a ...
... 1 A galaxy is a collection of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter. A galaxy is held together by gravitational attraction. 2 The Milky Way. 3 Spiral galaxies are a rotating spin wheel of stars. Elliptical galaxies have an elliptical shape. 4 The big bang theory proposes that the universe began as a ...
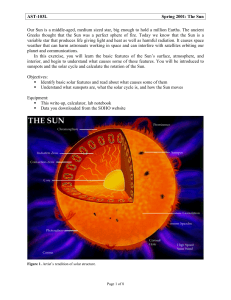
The%Sun - Learn@Illinois
... The Sun’s surface is called the “photosphere” - where the Sun’s gas becomes opaque. It is a layer of gas about 500 km deep. The photosphere has a temperature of about 5,800 K (over 10,000℉), and it is the source of most of the sunlight received by Earth Although the photosphere appears to be substan ...
... The Sun’s surface is called the “photosphere” - where the Sun’s gas becomes opaque. It is a layer of gas about 500 km deep. The photosphere has a temperature of about 5,800 K (over 10,000℉), and it is the source of most of the sunlight received by Earth Although the photosphere appears to be substan ...
Unpublished draft available in format
... Nevertheless, the areas of imperfect understanding remains vast and many. This is reflected in the vocabulary to be organized. It was noted in 3.12 that a major principle of classification in this subject is inevitably that of Whole-part, giving a hierarchy of galactic groups (the most comprehensive ...
... Nevertheless, the areas of imperfect understanding remains vast and many. This is reflected in the vocabulary to be organized. It was noted in 3.12 that a major principle of classification in this subject is inevitably that of Whole-part, giving a hierarchy of galactic groups (the most comprehensive ...
Stellar Evolution
... neighborhood of our Sun, within our Milky Way. No, not in other galaxies, but throughout our Milky ...
... neighborhood of our Sun, within our Milky Way. No, not in other galaxies, but throughout our Milky ...
Export To Word
... article describes scientists' discovery of the oldest habitable exoplanet that has been discovered. This planet formed outside our Milky Way and is about 11.5 billion years old. The planet looks like it could support water, has a rocky terrain, and is about five times bigger than Earth. Its proximit ...
... article describes scientists' discovery of the oldest habitable exoplanet that has been discovered. This planet formed outside our Milky Way and is about 11.5 billion years old. The planet looks like it could support water, has a rocky terrain, and is about five times bigger than Earth. Its proximit ...
Life of the Sun—15 Oct 10/15/2010
... Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Suppose a particle is allowed to move within a region of length x. ...
... Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. Suppose a particle is allowed to move within a region of length x. ...
Lecture 10 - Concord University
... Fusing light elements together results in more nuclear binding energy and less mass per nucleon. When the mass disappears, it is converted to energy so light-element fusion produces energy. But, when fusing any element to Fe, you now need to PROVIDE some energy to be converted into mass and Natu ...
... Fusing light elements together results in more nuclear binding energy and less mass per nucleon. When the mass disappears, it is converted to energy so light-element fusion produces energy. But, when fusing any element to Fe, you now need to PROVIDE some energy to be converted into mass and Natu ...
Rosette Nebula - Westchester Amateur Astronomers
... Mars is getting larger all the time as we near closest approach at the end of May. That’s not surprising, since Mars is the closest planet to Earth through the end of summer. (Mercury, briefly, is nearly as close as Mars when it transits in the sun in May.) While Mars is still very small, even in a ...
... Mars is getting larger all the time as we near closest approach at the end of May. That’s not surprising, since Mars is the closest planet to Earth through the end of summer. (Mercury, briefly, is nearly as close as Mars when it transits in the sun in May.) While Mars is still very small, even in a ...
Stars: from Adolescence to Old Age
... As a star becomes a red giant, its (helium) core continues to shrink, causing its temperature to continue increasing When the core temperature reaches 100 million K, the helium nuclei can fuse to form carbon nuclei through a process called the triple-alpha process In this reaction, three helium nucl ...
... As a star becomes a red giant, its (helium) core continues to shrink, causing its temperature to continue increasing When the core temperature reaches 100 million K, the helium nuclei can fuse to form carbon nuclei through a process called the triple-alpha process In this reaction, three helium nucl ...
Assignment 8 - utoledo.edu
... ____ 21. In a planetary nebula, the shell of expelled material is glowing intensely. What is the main source of energy for this glow? a. friction, as the atoms of the expelled shell rub against each other b. the explosion of the dying star c. ultraviolet radiation from the hot star at the center d ...
... ____ 21. In a planetary nebula, the shell of expelled material is glowing intensely. What is the main source of energy for this glow? a. friction, as the atoms of the expelled shell rub against each other b. the explosion of the dying star c. ultraviolet radiation from the hot star at the center d ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.