Name_________KEY 282 WAYS TO PASS THE EARTH SCIENCE
... The following is in _____ decreasing _____ size and age order: Universe, Galaxy, Solar system, Earth. _____ Geocentric _______ model is earth centered. Everything revolves around the earth. ______ Heliocentric ______________ model is sun centered. Planets revolve around the sun. All planets orbit in ...
... The following is in _____ decreasing _____ size and age order: Universe, Galaxy, Solar system, Earth. _____ Geocentric _______ model is earth centered. Everything revolves around the earth. ______ Heliocentric ______________ model is sun centered. Planets revolve around the sun. All planets orbit in ...
01-Syllabus
... be followed. You are responsible for knowing these, see the university website. Students are welcome to work together, exchange ideas, etc. But for the Observational Project you must do your own measurements and calculations. Exam procedures: Room assignments for the exams will be announced beforeha ...
... be followed. You are responsible for knowing these, see the university website. Students are welcome to work together, exchange ideas, etc. But for the Observational Project you must do your own measurements and calculations. Exam procedures: Room assignments for the exams will be announced beforeha ...
03_Testbank - Lick Observatory
... A) recording the seasonal changes in average temperature. B) observing the path of the planets across the sky. C) observing the length of the lunar cycle. D) observing the orientation of the crescent Moon relative to the horizon. E) observing the location of the Moon relative to the Sun in the sky. ...
... A) recording the seasonal changes in average temperature. B) observing the path of the planets across the sky. C) observing the length of the lunar cycle. D) observing the orientation of the crescent Moon relative to the horizon. E) observing the location of the Moon relative to the Sun in the sky. ...
FCAT 2.0 Science Review Big Idea 1: The Practice of Science THE
... • Most small objects are found in three areas: • Asteroid belt- region of the solar system between Jupiter and Mars. • Kuiper belt- extends to about 100 times Earth’s distance from the sun. • Oort cloud- stretches out more than 1,000 times the distance between the sun and Neptune. DWARF PLANETS • Th ...
... • Most small objects are found in three areas: • Asteroid belt- region of the solar system between Jupiter and Mars. • Kuiper belt- extends to about 100 times Earth’s distance from the sun. • Oort cloud- stretches out more than 1,000 times the distance between the sun and Neptune. DWARF PLANETS • Th ...
Earth Science
... The following is in _____ decreasing _____ size and age order: Universe, Galaxy, Solar system, Earth. _____ Geocentric _______ model is earth centered. Everything revolves around the earth. ______ Heliocentric ______________ model is sun centered. Planets revolve around the sun. All planets orbit in ...
... The following is in _____ decreasing _____ size and age order: Universe, Galaxy, Solar system, Earth. _____ Geocentric _______ model is earth centered. Everything revolves around the earth. ______ Heliocentric ______________ model is sun centered. Planets revolve around the sun. All planets orbit in ...
Uranus - Our Lady of Consolation National School
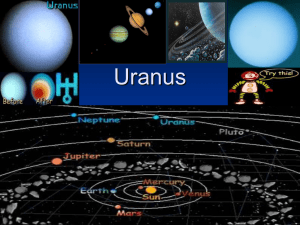
... The giant planets have diameters greater than 48000kg. The giant planets are sometimes also referred to as gas giants. Uranus has been visited by only one spacecraft, Voyager 2 on Jan 24 1986. Uranus is a giant gas planet which is made up of mostly rock and various ices. Uranus spins differently fro ...
... The giant planets have diameters greater than 48000kg. The giant planets are sometimes also referred to as gas giants. Uranus has been visited by only one spacecraft, Voyager 2 on Jan 24 1986. Uranus is a giant gas planet which is made up of mostly rock and various ices. Uranus spins differently fro ...
Taylor Samantha Taylor Professor Gennifer Marconette English 102
... The discussions of the general assembly resulted in the establishment of a new criteria for identification of a planet; a planet is a celestial body that is in orbit around the sun, has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (n ...
... The discussions of the general assembly resulted in the establishment of a new criteria for identification of a planet; a planet is a celestial body that is in orbit around the sun, has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (n ...
Star Formation, HR Diagram, and the Main Sequence (Professor
... (“EGGs”): Newly forming stars exposed by the ionizing radiation from nearby massive stars ...
... (“EGGs”): Newly forming stars exposed by the ionizing radiation from nearby massive stars ...
2016 Spring, VAS Newsletter
... like the Orion Nebula, containing thousands of new stars with light so bright it's visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectacular sights in the night sky, and the vast majority of the light from galaxies originates from nebulae like this o ...
... like the Orion Nebula, containing thousands of new stars with light so bright it's visible to the naked eye. At over 400 parsecs (1,300 light years) distant, it's one of the most spectacular sights in the night sky, and the vast majority of the light from galaxies originates from nebulae like this o ...
Stellar variability and microvariability II. Spot maps and modelling
... solar-like activity in late-type MS stars; For at least 40-50 solar analogues and a few hundreds F5V-M0V stars/field, we expect to obtain: • AR evolution time scales and contrast properties; • preferential longitude for AR formation (if any); • surface differential rotation (SDR); • possible short-t ...
... solar-like activity in late-type MS stars; For at least 40-50 solar analogues and a few hundreds F5V-M0V stars/field, we expect to obtain: • AR evolution time scales and contrast properties; • preferential longitude for AR formation (if any); • surface differential rotation (SDR); • possible short-t ...
Helioseismology - University of Warwick
... “At first sight it would seem that the deep interior of the Sun and stars is less accessible to scientific investigation than any other region of the universe. Our telescopes may probe farther and farther into the depths of space; but how can we ever obtain certain knowledge of that which is hidden ...
... “At first sight it would seem that the deep interior of the Sun and stars is less accessible to scientific investigation than any other region of the universe. Our telescopes may probe farther and farther into the depths of space; but how can we ever obtain certain knowledge of that which is hidden ...
Astronomy Talk July 2016 - Unitarian Universalist Church of
... Years away. That means that any kind of electromagnetic radiation (light, X-rays, radio waves) would take 12 years to san the distance one-way. So right about now they should be catching the last season of “Friends” and the first season of “House.” If our solar system is not that unusual, there ough ...
... Years away. That means that any kind of electromagnetic radiation (light, X-rays, radio waves) would take 12 years to san the distance one-way. So right about now they should be catching the last season of “Friends” and the first season of “House.” If our solar system is not that unusual, there ough ...
that provides the scientific rationale for sample return from asteroids
... plex (Joswiak et al. 2000). Although their provenance is unknown, the unique characteristics of IDPs indicate that meteorites are a limited sampling of the most primitive asteroids. Sample return from asteroids Returning samples from an asteroid would have a strong impact on scientific issues that ...
... plex (Joswiak et al. 2000). Although their provenance is unknown, the unique characteristics of IDPs indicate that meteorites are a limited sampling of the most primitive asteroids. Sample return from asteroids Returning samples from an asteroid would have a strong impact on scientific issues that ...
Hubble observations of Ceres and Pluto:
... will take another 8 years – yes, the Solar System is really, really big. The New Horizons science team wants to reach Pluto and Charon as soon as possible. Pluto is swinging further out on it’s eccentric orbit, getting less sunlight all the time, and less of its surface can be mapped. As Pluto gets ...
... will take another 8 years – yes, the Solar System is really, really big. The New Horizons science team wants to reach Pluto and Charon as soon as possible. Pluto is swinging further out on it’s eccentric orbit, getting less sunlight all the time, and less of its surface can be mapped. As Pluto gets ...
The Cosmic Perspective Asteroids, Comets, and Dwarf Planets
... Why do some comets come from far out in space and from all different directions (i.e., not in the plane of the solar system)? a) They come from other solar systems. b) They come from nebulae in interstellar space. c) They come from a giant spherical cloud called the Oort cloud. d) They come from ...
... Why do some comets come from far out in space and from all different directions (i.e., not in the plane of the solar system)? a) They come from other solar systems. b) They come from nebulae in interstellar space. c) They come from a giant spherical cloud called the Oort cloud. d) They come from ...
Scientific Justification
... correlations of auroral emissions with Saturn Kilometric Radiation (SKR), the nonthermal radio emissions associated with Saturn’s aurora [Kurth et al. 2005]. SKR measurements will be made continuously by Cassini over the period of proposed HST observations. The combination of Cassini field and plasm ...
... correlations of auroral emissions with Saturn Kilometric Radiation (SKR), the nonthermal radio emissions associated with Saturn’s aurora [Kurth et al. 2005]. SKR measurements will be made continuously by Cassini over the period of proposed HST observations. The combination of Cassini field and plasm ...
Talk - Otterbein University
... • We now know how far away stars are, so we know how big they are, and we can understand how they work. • We understand how big our galaxy is (100,000 ly) and that some “nebulae” are galaxies like our own ...
... • We now know how far away stars are, so we know how big they are, and we can understand how they work. • We understand how big our galaxy is (100,000 ly) and that some “nebulae” are galaxies like our own ...
main sequence
... nuclear reactions in its core. In the collapsed stars known as white dwarfs or neutron stars, other forces prevent the ultimate collapse. If there is too much mass in a given volume, though, the object reaches a critical density where nothing can prevent its ultimate collapse to form a black hole. B ...
... nuclear reactions in its core. In the collapsed stars known as white dwarfs or neutron stars, other forces prevent the ultimate collapse. If there is too much mass in a given volume, though, the object reaches a critical density where nothing can prevent its ultimate collapse to form a black hole. B ...
The Case against Copernicus
... This new “geoheliocentric” cosmology had two major advantages going for it: it squared with deep intuitions about how the world appeared to behave, and it fit the available data better than Copernicus’s system did. Brahe was a towering figure. He ran a huge research program with a castlelike observa ...
... This new “geoheliocentric” cosmology had two major advantages going for it: it squared with deep intuitions about how the world appeared to behave, and it fit the available data better than Copernicus’s system did. Brahe was a towering figure. He ran a huge research program with a castlelike observa ...
a to z of astronomy
... A relatively dense cloud of interstellar material containing dust particles. The dust particles absorb light from the more distant stars etc, so that the region appears dark compared with its surroundings. The clouds are often of low temperature and contain many molecules. DARK MATTER Material in th ...
... A relatively dense cloud of interstellar material containing dust particles. The dust particles absorb light from the more distant stars etc, so that the region appears dark compared with its surroundings. The clouds are often of low temperature and contain many molecules. DARK MATTER Material in th ...
astronomy - Jiri Brezina Teaching
... PHYSICS (Greek: physis = nature), NCE: branch of science traditionally defined as the study of matter, energy, and the relation between them; it was called natural philosophy until the late 19th century, and is still known by this name at a few universities. Physics is in some senses the oldest and ...
... PHYSICS (Greek: physis = nature), NCE: branch of science traditionally defined as the study of matter, energy, and the relation between them; it was called natural philosophy until the late 19th century, and is still known by this name at a few universities. Physics is in some senses the oldest and ...
Formation and evolution of the Solar System

The formation of the Solar System began 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed.This widely accepted model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, physics, geology, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations.The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets, while other moons are thought to have formed independently and later been captured by their planets. Still others, such as the Moon, may be the result of giant collisions. Collisions between bodies have occurred continually up to the present day and have been central to the evolution of the Solar System. The positions of the planets often shifted due to gravitational interactions. This planetary migration is now thought to have been responsible for much of the Solar System's early evolution.In roughly 5 billion years, the Sun will cool and expand outward many times its current diameter (becoming a red giant), before casting off its outer layers as a planetary nebula and leaving behind a stellar remnant known as a white dwarf. In the far distant future, the gravity of passing stars will gradually reduce the Sun's retinue of planets. Some planets will be destroyed, others ejected into interstellar space. Ultimately, over the course of tens of billions of years, it is likely that the Sun will be left with none of the original bodies in orbit around it.