Outline of Lecture on Copernican Revolution: 5b: So, what was
... Modern scientists are now familiar with this, but in Ptolemy’s time the clue might have been more easily missed. But the fact that the Greek’s were aware that a heliocentric model could naturally produce the observations suggests that the coincidences had indeed caused people to question and to thin ...
... Modern scientists are now familiar with this, but in Ptolemy’s time the clue might have been more easily missed. But the fact that the Greek’s were aware that a heliocentric model could naturally produce the observations suggests that the coincidences had indeed caused people to question and to thin ...
Astrobiological Stoichiometry
... hosted at Arizona State University April 11–12, 2013, under the auspices of the NASA Astrobiology Institute. The results focus on the measurement of chemical abundances and the effects of composition on processes from stellar to planetary scales. Of particular interest were the scientific connection ...
... hosted at Arizona State University April 11–12, 2013, under the auspices of the NASA Astrobiology Institute. The results focus on the measurement of chemical abundances and the effects of composition on processes from stellar to planetary scales. Of particular interest were the scientific connection ...
what`s up this month – april 2017
... Polar ice caps have been detected that may be formed by water molecules migrating along the magnetic force lines and being deposited at the poles. There may be a multilayered water and ice surface layer up to 800 km deep. It is suspected that there may be a deep liquid layer of water at the ice / ro ...
... Polar ice caps have been detected that may be formed by water molecules migrating along the magnetic force lines and being deposited at the poles. There may be a multilayered water and ice surface layer up to 800 km deep. It is suspected that there may be a deep liquid layer of water at the ice / ro ...
Debris Belts around Vega - Astronomical Society of the Pacific
... giant planets orbiting in the gap between belts. • Our own solar system also has four giant planets orbiting between the rocky asteroid belt and the icy Kuiper belt. • No planets have yet been detected around Vega, but if the star were eventually found to have several giant planets in orbit, this ...
... giant planets orbiting in the gap between belts. • Our own solar system also has four giant planets orbiting between the rocky asteroid belt and the icy Kuiper belt. • No planets have yet been detected around Vega, but if the star were eventually found to have several giant planets in orbit, this ...
02_LectureOutline
... 6. The apparent movement of the Sun around the Earth is due to the Earth’s rotation. 7. Retrograde motion of planets is due to Earth’s motion around the Sun. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... 6. The apparent movement of the Sun around the Earth is due to the Earth’s rotation. 7. Retrograde motion of planets is due to Earth’s motion around the Sun. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
ppt
... – The Sun and the other bodies orbit around a common center of mass – The Sun is so massive that it is very close to the center of mass and moves very little – Orbits are elliptical, but very slightly so ...
... – The Sun and the other bodies orbit around a common center of mass – The Sun is so massive that it is very close to the center of mass and moves very little – Orbits are elliptical, but very slightly so ...
Chapter 2 The Copernican Revolution
... 6. The apparent movement of the Sun around the Earth is due to the Earth’s rotation. 7. Retrograde motion of planets is due to Earth’s motion around the Sun. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... 6. The apparent movement of the Sun around the Earth is due to the Earth’s rotation. 7. Retrograde motion of planets is due to Earth’s motion around the Sun. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
models
... • Compiled the most accurate (one arcminute) naked eye measurements ever made of planetary positions. Still could not detect stellar parallax, and thus still thought Earth must be at center of solar system (but recognized that other planets go around Sun). ...
... • Compiled the most accurate (one arcminute) naked eye measurements ever made of planetary positions. Still could not detect stellar parallax, and thus still thought Earth must be at center of solar system (but recognized that other planets go around Sun). ...
LIFEPAC® 7th Grade Science Unit 3 Worktext - HomeSchool
... can see a great number of stars. With a telescope you can see many more stars. People in ancient times thought that all stars were part of the Milky Way. Today we know of many other galaxies similar to the Milky Way. To study the Milky Way as a whole is difficult for scientists on the earth because ...
... can see a great number of stars. With a telescope you can see many more stars. People in ancient times thought that all stars were part of the Milky Way. Today we know of many other galaxies similar to the Milky Way. To study the Milky Way as a whole is difficult for scientists on the earth because ...
Chapter 9 Lecture 1
... • Composition differs from the asteroid fragments. • A cheap (but slow) way to acquire moon rocks and Mars rocks. • One Mars meteorite generated a stir when scientists claimed evidence for microscopic life in it. ...
... • Composition differs from the asteroid fragments. • A cheap (but slow) way to acquire moon rocks and Mars rocks. • One Mars meteorite generated a stir when scientists claimed evidence for microscopic life in it. ...
solar system notes
... the MATLAB command line, which will perform Fourier transforms of each sun-planet distance versus time and plot them out. Exercise: Using the zoom function to find the time period that corresponds to the peak in power and write them down for each of the planets. How do these values compare to the or ...
... the MATLAB command line, which will perform Fourier transforms of each sun-planet distance versus time and plot them out. Exercise: Using the zoom function to find the time period that corresponds to the peak in power and write them down for each of the planets. How do these values compare to the or ...
Document
... • How do we even know this happens? – The North star changes from time to time. • See chart pg D90 ...
... • How do we even know this happens? – The North star changes from time to time. • See chart pg D90 ...
study guide
... • Jupiter and Saturn are still “collapsing” and releasing heat • All have moons • Some are large, most are captured asteroids ...
... • Jupiter and Saturn are still “collapsing” and releasing heat • All have moons • Some are large, most are captured asteroids ...
Chapter 2 - personal.kent.edu
... – Waited so long his bladder apparently burst – A long slow painful death ...
... – Waited so long his bladder apparently burst – A long slow painful death ...
Lecture notes - itü | fizik mühendisliği
... What are Moons? • Moons are like little planets that encircle the real planets. • Usually, they are much smaller than planets. • Planets can have no moons (like Mercury and Venus), one moon (like Earth) or up to a very large number of moons (e.g. >63 for Jupiter). • Mars (2), Saturn (>34), Uranus ( ...
... What are Moons? • Moons are like little planets that encircle the real planets. • Usually, they are much smaller than planets. • Planets can have no moons (like Mercury and Venus), one moon (like Earth) or up to a very large number of moons (e.g. >63 for Jupiter). • Mars (2), Saturn (>34), Uranus ( ...
Lecture #33: Solar System Origin I The Main Point What is a
... – Previous generations of stars lived and died before our solar system was formed. The violent death of a previous star or stars contributed material to the present solar system ("cosmic recycling"). ...
... – Previous generations of stars lived and died before our solar system was formed. The violent death of a previous star or stars contributed material to the present solar system ("cosmic recycling"). ...
Chapter 18 - "The Earth in Space"
... • The length of daylight during each season is determined by the relationship of Earth's shadow to the tilt of the axis. At the equinoxes, the shadow is perpendicular to the latitudes, and day and night are of equal length everywhere. At the summer solstice, the North Pole points toward the Sun and ...
... • The length of daylight during each season is determined by the relationship of Earth's shadow to the tilt of the axis. At the equinoxes, the shadow is perpendicular to the latitudes, and day and night are of equal length everywhere. At the summer solstice, the North Pole points toward the Sun and ...
How the Solar System formed
... What are Moons? • Moons are like little planets that encircle the real planets. • Usually, they are much smaller than planets. • Planets can have no moons (like Mercury and Venus), one moon (like Earth) or up to a very large number of moons (e.g. >63 for Jupiter). • Mars (2), Saturn (>34), Uranus ( ...
... What are Moons? • Moons are like little planets that encircle the real planets. • Usually, they are much smaller than planets. • Planets can have no moons (like Mercury and Venus), one moon (like Earth) or up to a very large number of moons (e.g. >63 for Jupiter). • Mars (2), Saturn (>34), Uranus ( ...
How the Solar System formed
... What are Moons? • Moons are like little planets that encircle the real planets. • Usually, they are much smaller than planets. • Planets can have no moons (like Mercury and Venus), one moon (like Earth) or up to a very large number of moons (e.g. >63 for Jupiter). • Mars (2), Saturn (>34), Uranus ( ...
... What are Moons? • Moons are like little planets that encircle the real planets. • Usually, they are much smaller than planets. • Planets can have no moons (like Mercury and Venus), one moon (like Earth) or up to a very large number of moons (e.g. >63 for Jupiter). • Mars (2), Saturn (>34), Uranus ( ...
Unit 2 Lesson 1
... • The gas giant planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. • The gas giant planets have thick, gaseous atmospheres; small, rocky cores; and ring systems of ice, rock, and dust. ...
... • The gas giant planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. • The gas giant planets have thick, gaseous atmospheres; small, rocky cores; and ring systems of ice, rock, and dust. ...
Phobos
... gravitational field of a foreground star amplifies the light of a background star that momentarily aligns with it. The particular character of the light magnification can reveal clues to the nature of the foreground star and any associated planets. However, without identification and characterizatio ...
... gravitational field of a foreground star amplifies the light of a background star that momentarily aligns with it. The particular character of the light magnification can reveal clues to the nature of the foreground star and any associated planets. However, without identification and characterizatio ...
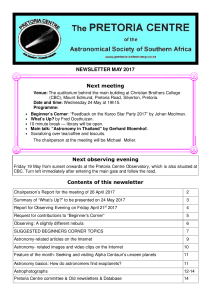
the May 2017 Newsletter!
... Jupiter was the only planet visible, quite high up in the east. All four Galilean moons were visible early on, with Io close in to the west of Jupiter. Not long after observing started, Io disappeared into occultation i.e it moved into Jupiter’s shadow. Although the disappearance was not observed, i ...
... Jupiter was the only planet visible, quite high up in the east. All four Galilean moons were visible early on, with Io close in to the west of Jupiter. Not long after observing started, Io disappeared into occultation i.e it moved into Jupiter’s shadow. Although the disappearance was not observed, i ...
The Changing Earth Atmosphere
... a) The Earth’s atmosphere is simply called air. It is primarily composed of many discrete gases, each with its own physical properties, in which varying quantities of tiny solid and liquid particles are suspended. b) ...
... a) The Earth’s atmosphere is simply called air. It is primarily composed of many discrete gases, each with its own physical properties, in which varying quantities of tiny solid and liquid particles are suspended. b) ...
draft - Standards Aligned System
... The universe is composed of a variety of different objects that are organized into systems each of which develops according to accepted physical processes and laws. The universe is composed of a variety of different objects that are organized into systems each of which develops according to accepted ...
... The universe is composed of a variety of different objects that are organized into systems each of which develops according to accepted physical processes and laws. The universe is composed of a variety of different objects that are organized into systems each of which develops according to accepted ...
List of Illustrations
... The most important thing that science has taught us about our place in the Universe is that we are not special. The process began with the work of Nicolaus Copernicus in the sixteenth century, which suggested that the Earth is not at the centre of the Universe, and gained momentum after Galileo, ear ...
... The most important thing that science has taught us about our place in the Universe is that we are not special. The process began with the work of Nicolaus Copernicus in the sixteenth century, which suggested that the Earth is not at the centre of the Universe, and gained momentum after Galileo, ear ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.