Vampy Astronomy Syllabus
... Vampy Astronomy Syllabus This course is intended to be an accelerated introduction to important concepts in astronomy and will cover topics related to both observational astronomy and physical astronomy. While some of you may have some astronomyrelated experience, the assumption is that each student ...
... Vampy Astronomy Syllabus This course is intended to be an accelerated introduction to important concepts in astronomy and will cover topics related to both observational astronomy and physical astronomy. While some of you may have some astronomyrelated experience, the assumption is that each student ...
The role of Jupiter in driving Earth`s orbital evolution
... orbiting nearby stars, and the search for life beyond our Solar system will be able to begin in earnest. However, the observations required to detect evidence of life on Earth-like planets orbiting other stars will be hugely time-consuming and costly – which will in turn mean that we will only be ab ...
... orbiting nearby stars, and the search for life beyond our Solar system will be able to begin in earnest. However, the observations required to detect evidence of life on Earth-like planets orbiting other stars will be hugely time-consuming and costly – which will in turn mean that we will only be ab ...
ASTR1010_HW06
... others because it takes many years (decades, really) to confirm and it only works for nearby stars (which have typically the largest proper motions). This was the “oldtimey” way to detect planets which basically never really worked out. Probably why the book doesn’t mention it. But it is possible, i ...
... others because it takes many years (decades, really) to confirm and it only works for nearby stars (which have typically the largest proper motions). This was the “oldtimey” way to detect planets which basically never really worked out. Probably why the book doesn’t mention it. But it is possible, i ...
The Dynamics-Based Approach to Studying Terrestrial Exoplanets
... expect 10,000 M-dwarf stars within 35 pc. This estimate is consistent with the number of Mdwarfs in that volume identified by large proper motions and 2MASS photometry (Lepine & Shara 2005; Lepine 2005) but for which parallaxes have not yet been obtained. Whether these low-mass stars have the same r ...
... expect 10,000 M-dwarf stars within 35 pc. This estimate is consistent with the number of Mdwarfs in that volume identified by large proper motions and 2MASS photometry (Lepine & Shara 2005; Lepine 2005) but for which parallaxes have not yet been obtained. Whether these low-mass stars have the same r ...
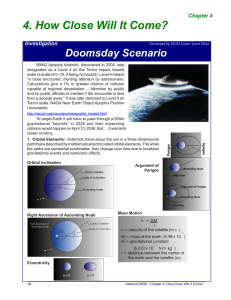
4. How Close Will It Come?
... capable of regional devastation. ...Attention by public and by public officials is merited if the encounter is less than a decade away.” It was later demoted to Level 0 on Torino scale. NASA Near Earth Object Apophis Position Uncertainty: http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/apophis/apophis_image3.html ...
... capable of regional devastation. ...Attention by public and by public officials is merited if the encounter is less than a decade away.” It was later demoted to Level 0 on Torino scale. NASA Near Earth Object Apophis Position Uncertainty: http://neo.jpl.nasa.gov/apophis/apophis_image3.html ...
Solar SyStem - Lorenz Educational Press
... exploding nuclear bomb. It is the center of our Solar System. It provides us with heat and light. The Sun has been spinning on its axis and exploding for about 5 billion years. The Sun is an average-size star, but seems larger because it is the star nearest to us—only 93,000,000 miles (150,000,000 k ...
... exploding nuclear bomb. It is the center of our Solar System. It provides us with heat and light. The Sun has been spinning on its axis and exploding for about 5 billion years. The Sun is an average-size star, but seems larger because it is the star nearest to us—only 93,000,000 miles (150,000,000 k ...
The Sky from Your Point of View
... • must be able to predict when an object will be up • light from Sun, Moon should not interfere ...
... • must be able to predict when an object will be up • light from Sun, Moon should not interfere ...
Decline of Western Civilization (extended) knowledge of ancient
... regular observations of Sun, Moon and Planets large number of observations greatest precision to date did not detect any stellar parallax [parallax.avi] heliocentric model rejected due to lack of observed stellar parallax Tycho Brahe’s geocentric model [figure 4-12] Sun and Moon orbit Earth, while p ...
... regular observations of Sun, Moon and Planets large number of observations greatest precision to date did not detect any stellar parallax [parallax.avi] heliocentric model rejected due to lack of observed stellar parallax Tycho Brahe’s geocentric model [figure 4-12] Sun and Moon orbit Earth, while p ...
1. What are the four branches of earth? -Geology
... A shift in wavelength of energy emitted by an energy source moving to or away is called the Doppler effect. Elements found in our atmosphere are made up of different chemicals and when heated can also create a spectra of colors. Spectroscopes were used to determine the elements the stars were made o ...
... A shift in wavelength of energy emitted by an energy source moving to or away is called the Doppler effect. Elements found in our atmosphere are made up of different chemicals and when heated can also create a spectra of colors. Spectroscopes were used to determine the elements the stars were made o ...
Patterns in the Sky - Madison Public Schools
... Earth orbits the Sun (revolves) once every year: • at an average distance of 1 AU ≈ 150 million kilometers. • with Earth’s axis tilted by 23.5º (pointing to Polaris) It rotates in the same direction it orbits, counterclockwise as viewed from above the North Pole. ...
... Earth orbits the Sun (revolves) once every year: • at an average distance of 1 AU ≈ 150 million kilometers. • with Earth’s axis tilted by 23.5º (pointing to Polaris) It rotates in the same direction it orbits, counterclockwise as viewed from above the North Pole. ...
The Hill Sphere
... The Moon, like almost all other moons in the solar system, is in synchronous rotation about the Earth meaning it shows the same face to Earth at all times (its rotation period about its own axis is the same as its orbital period about the Earth), which is a result of tidal forces between the Earth a ...
... The Moon, like almost all other moons in the solar system, is in synchronous rotation about the Earth meaning it shows the same face to Earth at all times (its rotation period about its own axis is the same as its orbital period about the Earth), which is a result of tidal forces between the Earth a ...
Astronomy Unit BM study guide
... following seasonal changes: temperature changes, angle of sunlight, number of daylight hours. As Earth revolves around the Sun, the tilt of its axis (23½ degrees) determines the amount of time that the Sun is shining on a specific portion of Earth. The tilt remains at the same angle and points in th ...
... following seasonal changes: temperature changes, angle of sunlight, number of daylight hours. As Earth revolves around the Sun, the tilt of its axis (23½ degrees) determines the amount of time that the Sun is shining on a specific portion of Earth. The tilt remains at the same angle and points in th ...
Practice Midterm 1
... B) From your point of view, time runs slower in the reference frame of anyone moving relative to you. C) If one observer measures two events to be simultaneous, all observers must agree on their simultaneity. D) Time dilation is an observationally verified fact. E) Time runs slower near a black hole ...
... B) From your point of view, time runs slower in the reference frame of anyone moving relative to you. C) If one observer measures two events to be simultaneous, all observers must agree on their simultaneity. D) Time dilation is an observationally verified fact. E) Time runs slower near a black hole ...
WHERE DO WE SEARCH FOR LIFE IN THE UNIVERSE?
... Eliminate Multiple Star Systems? Consider Stellar Luminosity (not too high, not to low) Consider Stellar Mass (not to high, not too low) ...
... Eliminate Multiple Star Systems? Consider Stellar Luminosity (not too high, not to low) Consider Stellar Mass (not to high, not too low) ...
december 2010 - Holt Planetarium
... Season’s greetings to one and all. There are a couple of interesting astronomical events this month. On December 21 there is a total eclipse of the Moon. The total phase of this eclipse lasts for just over 72 minutes, with the partial umbral eclipse spanning almost 3.5 hours. All stages of the total ...
... Season’s greetings to one and all. There are a couple of interesting astronomical events this month. On December 21 there is a total eclipse of the Moon. The total phase of this eclipse lasts for just over 72 minutes, with the partial umbral eclipse spanning almost 3.5 hours. All stages of the total ...
december 2010 - Holt Planetarium
... Season’s greetings to one and all. There are a couple of interesting astronomical events this month. On December 21 there is a total eclipse of the Moon. The total phase of this eclipse lasts for just over 72 minutes, with the partial umbral eclipse spanning almost 3.5 hours. All stages of the total ...
... Season’s greetings to one and all. There are a couple of interesting astronomical events this month. On December 21 there is a total eclipse of the Moon. The total phase of this eclipse lasts for just over 72 minutes, with the partial umbral eclipse spanning almost 3.5 hours. All stages of the total ...
June 2013 Kepler Space Telescope Update
... chemical evidence for the Lego building blocks of rocky planets," says Jay Farihi of the University of Cambridge in England, lead author of a new study that appeared in the May 2 issue of the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. "When these stars were born, they built planets, and ther ...
... chemical evidence for the Lego building blocks of rocky planets," says Jay Farihi of the University of Cambridge in England, lead author of a new study that appeared in the May 2 issue of the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. "When these stars were born, they built planets, and ther ...
Kepler`s Law - New Mexico Tech
... The Sun’s Lifecycle • The Sun was formed about 4.57 billion years ago when a hydrogen molecular cloud collapsed. • It is about halfway through its main-sequence evolution, during this time, nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium. • It will spend approx. 10 billion years as a ...
... The Sun’s Lifecycle • The Sun was formed about 4.57 billion years ago when a hydrogen molecular cloud collapsed. • It is about halfway through its main-sequence evolution, during this time, nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium. • It will spend approx. 10 billion years as a ...
Solar System from Web
... The Sun’s Lifecycle • The Sun was formed about 4.57 billion years ago when a hydrogen molecular cloud collapsed. • It is about halfway through its main-sequence evolution, during this time, nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium. • It will spend approx. 10 billion years as a ...
... The Sun’s Lifecycle • The Sun was formed about 4.57 billion years ago when a hydrogen molecular cloud collapsed. • It is about halfway through its main-sequence evolution, during this time, nuclear fusion reactions in its core fuse hydrogen into helium. • It will spend approx. 10 billion years as a ...
Age aspects of habitability - Cambridge University Press
... might differ significantly from the value calculated from largely uncertain parameters that were, in turn, derived from observables. Indeed, uncertainties in estimates of the equilibrium temperature |δT|/Te are heavily amplified for habitable planets with VC/Te ≃ 10 − 20 for VC ≃ 30 − 60 kJ mol−1 an ...
... might differ significantly from the value calculated from largely uncertain parameters that were, in turn, derived from observables. Indeed, uncertainties in estimates of the equilibrium temperature |δT|/Te are heavily amplified for habitable planets with VC/Te ≃ 10 − 20 for VC ≃ 30 − 60 kJ mol−1 an ...
Exoplanets - An ESO/OPTICON/IAU summer school on modern
... History of Exoplanet Researches 1./ A very few scientists and philosophers in the ancient times and middle-ages : planets may be / should be existing orbiting other stars than Sun. 2./ Struve (1952) proposes the transit-method. 3./ 1989: an exoplanet suspected first time by RV-method (many years lat ...
... History of Exoplanet Researches 1./ A very few scientists and philosophers in the ancient times and middle-ages : planets may be / should be existing orbiting other stars than Sun. 2./ Struve (1952) proposes the transit-method. 3./ 1989: an exoplanet suspected first time by RV-method (many years lat ...
MagdaStavinschi_bothtalks
... The astrometric information is generally NOT the direction from which the light arrives, but a quantity more directly related to the geometric position of the celestial body in space in a certain reference coordinated system. To achieve this one we must apply a certain number of corrections to the ...
... The astrometric information is generally NOT the direction from which the light arrives, but a quantity more directly related to the geometric position of the celestial body in space in a certain reference coordinated system. To achieve this one we must apply a certain number of corrections to the ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.