Ch 22-2
... o Moon’s rotation and revolution around Earth are the same • Same side of the moon always faces the Earth • This is where the dark side of the moon comes from o Only satellites and astronauts have seen the other side of the moon o More cratered than the side facing the Earth • Same side of the moon ...
... o Moon’s rotation and revolution around Earth are the same • Same side of the moon always faces the Earth • This is where the dark side of the moon comes from o Only satellites and astronauts have seen the other side of the moon o More cratered than the side facing the Earth • Same side of the moon ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... c. the structure and evolution of the earth's crust. d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. spectroscope d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only ...
... c. the structure and evolution of the earth's crust. d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. spectroscope d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only ...
Trivia Question of the Day
... Caused by Earth’s tilt and Earth’s revolution around the Sun If Earth did not revolve around the Sun, the same part of Earth would tilt toward the Sun all the time ...
... Caused by Earth’s tilt and Earth’s revolution around the Sun If Earth did not revolve around the Sun, the same part of Earth would tilt toward the Sun all the time ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy
... The solar day and the sidereal day The motion of the Sun along the ecliptic causes the time from sunrise to sunrise (the solar day = 24 hours) to differ from the time from when one star rises until when it next rises (the sidereal day = 23 hours, 56 minutes). There are 365.24 solar days in a year. ...
... The solar day and the sidereal day The motion of the Sun along the ecliptic causes the time from sunrise to sunrise (the solar day = 24 hours) to differ from the time from when one star rises until when it next rises (the sidereal day = 23 hours, 56 minutes). There are 365.24 solar days in a year. ...
Investigation 1 Solar Nebula Theory Student Guide 3_16_13_draft
... Scientists believe that some 13.7 billion years ago all matter, energy and our universe itself was formed from of a huge sudden expansion now known in theory as the “Big Bang”. The matter created from this genesis eventually cooled off, condensed and formed the most basic building blocks of matter k ...
... Scientists believe that some 13.7 billion years ago all matter, energy and our universe itself was formed from of a huge sudden expansion now known in theory as the “Big Bang”. The matter created from this genesis eventually cooled off, condensed and formed the most basic building blocks of matter k ...
Our Universe
... • In Nuclear fusion, hydrogen atoms are converted into helium, releasing the ENORMOUS amount of energy that causes stars to become very hot! • The amount of energy released per gram of mass is equal to the amount of energy released by 22,000 tons of TNT. (The nuclear explosion at Hiroshima only rele ...
... • In Nuclear fusion, hydrogen atoms are converted into helium, releasing the ENORMOUS amount of energy that causes stars to become very hot! • The amount of energy released per gram of mass is equal to the amount of energy released by 22,000 tons of TNT. (The nuclear explosion at Hiroshima only rele ...
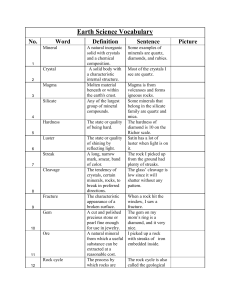
Earth Science Vocabulary No. Word Definition Sentence Picture 1
... A mountain that builds up around an opening in Earth’s crust. An opening at the earth's surface from which volcanic material is emitted. The cavity on the surface of the earth marking the orifice of a volcano. The linear zone of seismic and volcanic activity that coincides in general with the margin ...
... A mountain that builds up around an opening in Earth’s crust. An opening at the earth's surface from which volcanic material is emitted. The cavity on the surface of the earth marking the orifice of a volcano. The linear zone of seismic and volcanic activity that coincides in general with the margin ...
Formation of the Solar System
... Earth rocks, Moon rocks, and meteorites • The oldest Earth rock date back to 4 billion years and some small grains go back to 4.4 billion years. Moon rock brought back from the Apollo mission date as far back as 4.4 billion years. ...
... Earth rocks, Moon rocks, and meteorites • The oldest Earth rock date back to 4 billion years and some small grains go back to 4.4 billion years. Moon rock brought back from the Apollo mission date as far back as 4.4 billion years. ...
Student Text, pp. 278-284
... Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) travelling in orbits around Earth. Using Earth as the frame of reference, the “geocentric model” of the universe was explained by introducing complicated motions (Figure 2). The detailed observations and analysis needed to invent these complex orbits were amazingly accurat ...
... Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) travelling in orbits around Earth. Using Earth as the frame of reference, the “geocentric model” of the universe was explained by introducing complicated motions (Figure 2). The detailed observations and analysis needed to invent these complex orbits were amazingly accurat ...
2015-2016 Year at a Glance Earth Science
... All matter in our universe originated during the Big Bang 14 billion years ago. 1. Where in its life cycle is our Sun and what is its approximate life span? 2. How was the solar system formed and how has it changed and evolved in the 5 billion years since its formation? 3. How do distant galaxies pr ...
... All matter in our universe originated during the Big Bang 14 billion years ago. 1. Where in its life cycle is our Sun and what is its approximate life span? 2. How was the solar system formed and how has it changed and evolved in the 5 billion years since its formation? 3. How do distant galaxies pr ...
the earth in space - North Salem Schools Teachers Module
... a. model was the product of Ptolemy - celestial objects revolved westward around the Earth b. outer planets moved on an epicycle while the epicycle followed a deferent c. it does explain what you see in the nighttime sky - it could be correct d. it does NOT account for terrestrial motions and phenom ...
... a. model was the product of Ptolemy - celestial objects revolved westward around the Earth b. outer planets moved on an epicycle while the epicycle followed a deferent c. it does explain what you see in the nighttime sky - it could be correct d. it does NOT account for terrestrial motions and phenom ...
Study Guide for Stars and Galaxies Quiz ANSWER KEY
... 1. Are stars usually by themselves or in groups of two or more? Stars are usually found in groups of two (binary stars) or three (triple stars) 2. List the three types of galaxies, and give properties of each. Be able to sketch each. a. elliptical contains old stars and little gas/dust b. irr ...
... 1. Are stars usually by themselves or in groups of two or more? Stars are usually found in groups of two (binary stars) or three (triple stars) 2. List the three types of galaxies, and give properties of each. Be able to sketch each. a. elliptical contains old stars and little gas/dust b. irr ...
Testing
... that allows a planet’s orbit to move inward? A. It transfers energy and angular momentum to another object. B. The gravity of the other object forces the planet to move inward. C. It gains mass from the other object, causing its gravitational pull to become stronger. ...
... that allows a planet’s orbit to move inward? A. It transfers energy and angular momentum to another object. B. The gravity of the other object forces the planet to move inward. C. It gains mass from the other object, causing its gravitational pull to become stronger. ...
Teacher`s Guide - Discovery Education
... There are three kinds of galaxies—spiral, elliptical, and irregular. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is a spiral galaxy. ...
... There are three kinds of galaxies—spiral, elliptical, and irregular. Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is a spiral galaxy. ...
Goals of the day Clickers Order of Magnitude Astronomy
... the local group). The remnants from such explosions disperse in about 10,000 years. A. The supernova remnant still exists now, and we will watch it disperse over the next 10,000 Earth years. B. In reality, the supernova remnant has already dispersed, but we will watch it disperse over the next 10, ...
... the local group). The remnants from such explosions disperse in about 10,000 years. A. The supernova remnant still exists now, and we will watch it disperse over the next 10,000 Earth years. B. In reality, the supernova remnant has already dispersed, but we will watch it disperse over the next 10, ...
Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan
... 6.7 How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Edu ...
... 6.7 How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Edu ...
Star and Planet Formation Star and Planet - A
... 1. If the Earth rotates around the Sun, birds should actually stay behind because of the movement of the Earth on its orbit. Inadequate understanding of physics ! 2. If the Earth rotates around its axis (as required to explain day and night), things should fly off the spinning planet. Inadequate u ...
... 1. If the Earth rotates around the Sun, birds should actually stay behind because of the movement of the Earth on its orbit. Inadequate understanding of physics ! 2. If the Earth rotates around its axis (as required to explain day and night), things should fly off the spinning planet. Inadequate u ...
Chapter 6
... 6.7 How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Edu ...
... 6.7 How Did the Solar System Form? Nebular contraction is followed by condensation around dust grains, known to exist in interstellar clouds such as the one shown here. Accretion then leads to larger and larger clumps; finally gravitational attraction takes over and planets form. © 2011 Pearson Edu ...
The life and times of stars
... A galaxy will give out a continuous spectrum as it has billions of different sources The surface of the Sun gives out a continuous spectrum – it is an incandescent body The Sun’s atmosphere will produce an absorption spectrum as it is a gas that the Sun’s light is shining through Most nebula will pr ...
... A galaxy will give out a continuous spectrum as it has billions of different sources The surface of the Sun gives out a continuous spectrum – it is an incandescent body The Sun’s atmosphere will produce an absorption spectrum as it is a gas that the Sun’s light is shining through Most nebula will pr ...
Exoplanets
... Humans have always wondered if life exists elsewhere in the universe. Such life could take many forms, including some very different from our own, but because we only have information about Earth-life (carbon-based organisms) we may as well start by looking for life like us. This means we can test n ...
... Humans have always wondered if life exists elsewhere in the universe. Such life could take many forms, including some very different from our own, but because we only have information about Earth-life (carbon-based organisms) we may as well start by looking for life like us. This means we can test n ...
The origin of life - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... Colonization of land by animals Appearance of animals and land plants First multicellular organisms ...
... Colonization of land by animals Appearance of animals and land plants First multicellular organisms ...
Boy Scout Astronomy Merit Badge Workbook
... b. Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude 1 or brighter. c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper’s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the North St ...
... b. Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude 1 or brighter. c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper’s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the North St ...
Earth Science - Middlesex County Public Schools
... 1a) volume, area, mass, elapsed time, direction, temperature, pressure, distance, density, and changes in elevation/depth are calculated utilizing the most appropriate tools 1b) technologies including computers, probeware, and geospatial technologies, are used to collect, analyze, and report data to ...
... 1a) volume, area, mass, elapsed time, direction, temperature, pressure, distance, density, and changes in elevation/depth are calculated utilizing the most appropriate tools 1b) technologies including computers, probeware, and geospatial technologies, are used to collect, analyze, and report data to ...
AST111, Lecture 1b
... emitted. For many bodies the total energy absorbed by the sun balances that emitted thermally. However, many planets also have internal heat sources. • There can be diurnal (daily), latitudinal and seasonal variations in temperature. Radiation transfer through the atmosphere can be complex (such as ...
... emitted. For many bodies the total energy absorbed by the sun balances that emitted thermally. However, many planets also have internal heat sources. • There can be diurnal (daily), latitudinal and seasonal variations in temperature. Radiation transfer through the atmosphere can be complex (such as ...
Ethan Kessinger and Amanda Brockbank
... Kitab Muzan al-hikma was superior to anything written up to this point. Most importantly, alKhazini, in this book, was the first to propose the gravity of a body varies with its distance from the center of the earth. Like much of al-Biruni’s works, this was not completely accurate. It was, however, ...
... Kitab Muzan al-hikma was superior to anything written up to this point. Most importantly, alKhazini, in this book, was the first to propose the gravity of a body varies with its distance from the center of the earth. Like much of al-Biruni’s works, this was not completely accurate. It was, however, ...
Astrobiology

Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe: extraterrestrial life and life on Earth. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry, laboratory and field research into the origins and early evolution of life on Earth, and studies of the potential for life to adapt to challenges on Earth and in outer space. Astrobiology addresses the question of whether life exists beyond Earth, and how humans can detect it if it does. (The term exobiology is similar but more specific—it covers the search for life beyond Earth, and the effects of extraterrestrial environments on living things.)Astrobiology makes use of physics, chemistry, astronomy, biology, molecular biology, ecology, planetary science, geography, and geology to investigate the possibility of life on other worlds and help recognize biospheres that might be different from the biosphere on Earth. The origin and early evolution of life is an inseparable part of the discipline of astrobiology. Astrobiology concerns itself with interpretation of existing scientific data; given more detailed and reliable data from other parts of the universe, the roots of astrobiology itself—physics, chemistry and biology—may have their theoretical bases challenged. Although speculation is entertained to give context, astrobiology concerns itself primarily with hypotheses that fit firmly into existing scientific theories.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. According to research published in August 2015, very large galaxies may be more favorable to the creation and development of habitable planets than smaller galaxies, like the Milky Way galaxy. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently.Current studies on the planet Mars by the Curiosity and Opportunity rovers are now searching for evidence of ancient life as well as plains related to ancient rivers or lakes that may have been habitable. The search for evidence of habitability, taphonomy (related to fossils), and organic molecules on the planet Mars is now a primary NASA objective on Mars.