Chapter 3
... • Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through channels in ATP synthase • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • Th ...
... • Electron transfer in the electron transport chain causes proteins to pump H+ from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space • H+ then moves back across the membrane, passing through channels in ATP synthase • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • Th ...
Protein
... of protein is determined by genetic information. Protein is constantly being broken down and synthesized in the body. Researchers measure nitrogen balance to study synthesis, degradation and excretion of protein. Protein has many important functions in the body. Protein can be used for energy if nee ...
... of protein is determined by genetic information. Protein is constantly being broken down and synthesized in the body. Researchers measure nitrogen balance to study synthesis, degradation and excretion of protein. Protein has many important functions in the body. Protein can be used for energy if nee ...
HONORS BIOLOGY CHAPTER 6 - Hudson City Schools / Homepage
... • Rotenone-binds to first ETC protein to prevent epassing on • Cyanide-bind to fourth protein in ETC (was in famous Tylenol tampering in 1982) ...
... • Rotenone-binds to first ETC protein to prevent epassing on • Cyanide-bind to fourth protein in ETC (was in famous Tylenol tampering in 1982) ...
L-Serine, D- and L-proline and alanine as respiratory substrates of
... 1995). These results suggested that glucose is not a preferred energy substrate of H. pylori. Candidates for the substrates of energy metabolism in this organism are thought to be organic acids such as pyruvate, D-lactate and succinate. Chang et al. (1995) reported that lower concentrations (25 mM) ...
... 1995). These results suggested that glucose is not a preferred energy substrate of H. pylori. Candidates for the substrates of energy metabolism in this organism are thought to be organic acids such as pyruvate, D-lactate and succinate. Chang et al. (1995) reported that lower concentrations (25 mM) ...
Characterization of Lamprey Fibrinopeptides
... peptidase-A activities. Incubations were carried out at room temperature, and samples were removed periodically and spotted or streaked directly on paper strips for analysis by combination paper electrophoresis-paper chromatography. Subtilisin was a generous gift from S. Paleus. The enzyme was disso ...
... peptidase-A activities. Incubations were carried out at room temperature, and samples were removed periodically and spotted or streaked directly on paper strips for analysis by combination paper electrophoresis-paper chromatography. Subtilisin was a generous gift from S. Paleus. The enzyme was disso ...
5-Metabolism of Pyrimidine Nucleotides
... SOURCES OF ATOMS OF PYRIMIDINE NUCLEUS N1, C6, C5 and C4 are derived from aspartate N3 is derived from glutamine C2 is derived from HCO3- (bicarbonate) ...
... SOURCES OF ATOMS OF PYRIMIDINE NUCLEUS N1, C6, C5 and C4 are derived from aspartate N3 is derived from glutamine C2 is derived from HCO3- (bicarbonate) ...
Biosynthesis of `essential` amino acids by
... radiolabelled glucose, synthesized amino acids, and translocated them to the animal. Although translocation of radiolabelled amino acids from the algae to the animal was not assessed in these experiments, the magnitude of their potential contribution was estimated from the percentage of the total ra ...
... radiolabelled glucose, synthesized amino acids, and translocated them to the animal. Although translocation of radiolabelled amino acids from the algae to the animal was not assessed in these experiments, the magnitude of their potential contribution was estimated from the percentage of the total ra ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduce ...
... In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduce ...
The ketogenic diet component decanoic acid increases
... 2002; Itkonen et al. 2013). Time– and dose–response experiments revealed that exposure of the SH-SY5Y cells, for 6 days, to 250-lM C10 elicited a maximal significant increase in citrate synthase activity. In contrast, incubations with C8 under comparable conditions revealed no significant effect ...
... 2002; Itkonen et al. 2013). Time– and dose–response experiments revealed that exposure of the SH-SY5Y cells, for 6 days, to 250-lM C10 elicited a maximal significant increase in citrate synthase activity. In contrast, incubations with C8 under comparable conditions revealed no significant effect ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis However, the processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in f ...
... All use glycolysis (net ATP = 2) to oxidize glucose and harvest chemical energy of food In all three, NAD+ is the oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis However, the processes have different final electron acceptors: an organic molecule (such as pyruvate or acetaldehyde) in f ...
Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas and Entner–Doudoroff pathways in
... At the moment, we can only speculate about the physiological meaning of the different pathways, since nothing is known about the regulation of the ED pathways at the protein and gene levels. However, the organization of the ED genes coding for KDG kinase and KDG aldolase together with a gene homolog ...
... At the moment, we can only speculate about the physiological meaning of the different pathways, since nothing is known about the regulation of the ED pathways at the protein and gene levels. However, the organization of the ED genes coding for KDG kinase and KDG aldolase together with a gene homolog ...
Plasma Amino Acids
... The 24-hour urine amino acid analysis has the highest probability of detecting abnormalities if renal function is normal. The 24-hour test indicates what is high and low over the course of a day, reflects blood and tissue amino acid pools, and is not affected by circadian rhythm. Healthy kidneys eff ...
... The 24-hour urine amino acid analysis has the highest probability of detecting abnormalities if renal function is normal. The 24-hour test indicates what is high and low over the course of a day, reflects blood and tissue amino acid pools, and is not affected by circadian rhythm. Healthy kidneys eff ...
LACTATE/PYRUVATE RATIO Relevant disorders Related
... Pyruvate should only be analysed when lactate is elevated to determine the patients redox state. Pyruvate is an end product of glycolysis. It can either be converted to lactate under anaerobic conditions or transported into mitochondria to feed into the Kreb’s cycle under aerobic conditions. Lactate ...
... Pyruvate should only be analysed when lactate is elevated to determine the patients redox state. Pyruvate is an end product of glycolysis. It can either be converted to lactate under anaerobic conditions or transported into mitochondria to feed into the Kreb’s cycle under aerobic conditions. Lactate ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... • Allosteric regulation is the regulation of an enzyme’s activity by the binding of an effector molecule at a site other than the active site. It can be positive or negative • The inactive phosphorylated form, b, of glycogen synthase is allosterically activated by glucose-6phosphate ...
... • Allosteric regulation is the regulation of an enzyme’s activity by the binding of an effector molecule at a site other than the active site. It can be positive or negative • The inactive phosphorylated form, b, of glycogen synthase is allosterically activated by glucose-6phosphate ...
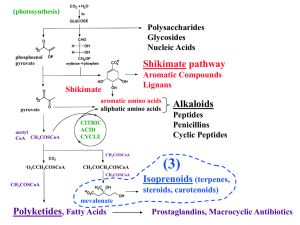
Lecture 03, NEW - terpenes + polyketides
... enzyme, passed from one active site to the next Different active sites carry out the ...
... enzyme, passed from one active site to the next Different active sites carry out the ...
Stoking the Brightest Fires of Life Among Vertebrates
... the resulting high capacities for glucose phosphorylation show the contrast between the flight muscles of hummingbirds and bat species with high sugar diets and those of birds of other species (Crabtree and Newsholme 1972b) and non-nectarivorous bats (Yacoe et al. 1982). However, hexokinase is not e ...
... the resulting high capacities for glucose phosphorylation show the contrast between the flight muscles of hummingbirds and bat species with high sugar diets and those of birds of other species (Crabtree and Newsholme 1972b) and non-nectarivorous bats (Yacoe et al. 1982). However, hexokinase is not e ...
Original papers QJM
... infected countries.2,14 There is good evidence that some common disorders of central monoamine metabolism may underlie the pathogenesis of metabolic encephalopathies.15,16 Studies in mice and rats with Plasmodium berghei infection indicate significantly reduced whole brain contents of 5-hydroxytrypt ...
... infected countries.2,14 There is good evidence that some common disorders of central monoamine metabolism may underlie the pathogenesis of metabolic encephalopathies.15,16 Studies in mice and rats with Plasmodium berghei infection indicate significantly reduced whole brain contents of 5-hydroxytrypt ...
Proficiency Test Lyon 2008
... metabolic pathway remained unknown for a long time. It had been showed that urinary excretion of L2-hydroxyglutaric acid (L2OHGA) was independent of feeding, but relied exclusively on endogenous production: approximately 25% from liver and 75 % from muscle. The toxicity of L-2-hydroxyglutaric is due ...
... metabolic pathway remained unknown for a long time. It had been showed that urinary excretion of L2-hydroxyglutaric acid (L2OHGA) was independent of feeding, but relied exclusively on endogenous production: approximately 25% from liver and 75 % from muscle. The toxicity of L-2-hydroxyglutaric is due ...
Origin of amino acid homochirality: Relationship with the RNA world
... Watson–Crick duplex. The CCA end of an RNA minihelix and the aminoacyl phosphate (deoxyribo)oligonucleotide adaptors assemble the A-form double helix containing the bridging (ribo)oligonucleotides (Arnott et al., 1986). In this conformation, the position of the aminoacyl residue that is linked to th ...
... Watson–Crick duplex. The CCA end of an RNA minihelix and the aminoacyl phosphate (deoxyribo)oligonucleotide adaptors assemble the A-form double helix containing the bridging (ribo)oligonucleotides (Arnott et al., 1986). In this conformation, the position of the aminoacyl residue that is linked to th ...
The Effect of Alkaline pH on Growth and Metabolic
... Characterization tests. The following tests suggested by Sherman (1937) and by Deibel & Seeley (1974) for the differentiation of enterococci from other streptococci were made. 1. Growth at 10 "C; 2. Growth at 45 "C; 3. Growth in media containing 6.5% (w/v) NaCl; 4. Growth in media containing 40% (v/ ...
... Characterization tests. The following tests suggested by Sherman (1937) and by Deibel & Seeley (1974) for the differentiation of enterococci from other streptococci were made. 1. Growth at 10 "C; 2. Growth at 45 "C; 3. Growth in media containing 6.5% (w/v) NaCl; 4. Growth in media containing 40% (v/ ...
- World Journal of Gastroenterology
... are strong predictors of type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, atherothrombotic risk profile, and overall risk of metabolic disease. Therefore, it is plausible to suggest that aminotransferases are surrogate biomarkers of “liver metabolic functioning” beyond the classical concept of liver cellula ...
... are strong predictors of type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, atherothrombotic risk profile, and overall risk of metabolic disease. Therefore, it is plausible to suggest that aminotransferases are surrogate biomarkers of “liver metabolic functioning” beyond the classical concept of liver cellula ...