Mechanisms underlying the essential role of mitochondrial
... Another aspect of lipid metabolism and transport known to define longevity of chronologically aging yeast is the abundance of triacylglycerols (TAGs) [67–70]. These so-called neutral lipids are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and then deposited in lipid droplets (LDs) [71–73]. The age-r ...
... Another aspect of lipid metabolism and transport known to define longevity of chronologically aging yeast is the abundance of triacylglycerols (TAGs) [67–70]. These so-called neutral lipids are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and then deposited in lipid droplets (LDs) [71–73]. The age-r ...
The blood sugar concentration or blood glucose
... rather than glucose). Glucose transported from the intestines or liver to body cells via the bloodstream, and made available for cell absorption via the hormone insulin, produced by the body primarily in the pancreas. The mean normal blood glucose level in humans is about 5.5 mill ...
... rather than glucose). Glucose transported from the intestines or liver to body cells via the bloodstream, and made available for cell absorption via the hormone insulin, produced by the body primarily in the pancreas. The mean normal blood glucose level in humans is about 5.5 mill ...
Carbs, Proteins, Lipids notes
... – Formed by a condensation reaction between three or more monosaccharides. • glucose + glucose + glucose glycogen + 2 H2O • Glycogen is called animal starch – It is stored as an energy reserve in our liver and muscles. ...
... – Formed by a condensation reaction between three or more monosaccharides. • glucose + glucose + glucose glycogen + 2 H2O • Glycogen is called animal starch – It is stored as an energy reserve in our liver and muscles. ...
IMPLICATION OF LONG-CHAIN FATTY ACIDS IN GLUCOSE-INDUCED INSULIN SECRETION IN THE PANCREATIC -CELL
... Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized by uncontrolled hyperglycemia, the result of either the failure of insulin production, or a combined defect in insulin production and action. This leads to the dysregulation of glucose metabolism. Concurrent with the spread of the western lifestyle, which ...
... Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized by uncontrolled hyperglycemia, the result of either the failure of insulin production, or a combined defect in insulin production and action. This leads to the dysregulation of glucose metabolism. Concurrent with the spread of the western lifestyle, which ...
Characterization of the mineral phosphate solubilizing activity of
... et al. 2006). Furthermore, the current developments in sustainability require a strong reduction in agrochemical inputs and their replacement by more ecological, eYcient and cheap natural products (Macias et al. 2003). For instance, insoluble inorganic phosphates including RP can be transformed into ...
... et al. 2006). Furthermore, the current developments in sustainability require a strong reduction in agrochemical inputs and their replacement by more ecological, eYcient and cheap natural products (Macias et al. 2003). For instance, insoluble inorganic phosphates including RP can be transformed into ...
actiona actionation of FFFFFrrrrractiona
... from carbohydrates and from some amino acids. In contrast, Abelson and Hoering (1961) pioneered the examination of intramolecular patterns of isotopic order. They studied the biosynthesis of amino acids, analyzing only the end products. However, they determined not only the δ values of the individua ...
... from carbohydrates and from some amino acids. In contrast, Abelson and Hoering (1961) pioneered the examination of intramolecular patterns of isotopic order. They studied the biosynthesis of amino acids, analyzing only the end products. However, they determined not only the δ values of the individua ...
The Utilization by Yeasts of Acids of the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
... The contents of the Warburg flask side arm were mixed with those of the main compartment, and a t the same moment 175 pmole of sodium acetate in 0.5 ml. water were added to the pipette flask and the contents we1 mixed. When the rate of acetate oxidation was steady (usually after about 20 min.) the a ...
... The contents of the Warburg flask side arm were mixed with those of the main compartment, and a t the same moment 175 pmole of sodium acetate in 0.5 ml. water were added to the pipette flask and the contents we1 mixed. When the rate of acetate oxidation was steady (usually after about 20 min.) the a ...
Fractionation of the isotopes of carbon and hydrogen in biosynthetic
... from carbohydrates and from some amino acids. In contrast, Abelson and Hoering (1961) pioneered the examination of intramolecular patterns of isotopic order. They studied the biosynthesis of amino acids, analyzing only the end products. However, they determined not only the δ values of the individua ...
... from carbohydrates and from some amino acids. In contrast, Abelson and Hoering (1961) pioneered the examination of intramolecular patterns of isotopic order. They studied the biosynthesis of amino acids, analyzing only the end products. However, they determined not only the δ values of the individua ...
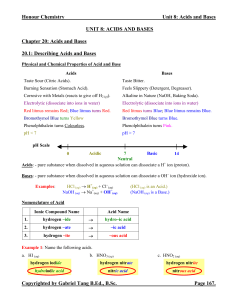
Unit 8 Acids and Bases Notes (answers)
... Polyprotic Acids: - acids that can donate more than one protons. - this includes all diprotic and triprotic acids (acids that can donate three protons). - polyprotic acids dissociate one proton at a time. Each successive proton donation has its own Ka, which gets smaller until the last proton is don ...
... Polyprotic Acids: - acids that can donate more than one protons. - this includes all diprotic and triprotic acids (acids that can donate three protons). - polyprotic acids dissociate one proton at a time. Each successive proton donation has its own Ka, which gets smaller until the last proton is don ...
Antibacterial action of several tannins against Staphylococcus aureus
... conditions need iron for a variety of functions, including reduction of the ribonucleotide precursor of DNA, formation of haem, and other essential purposes.17 Chung et al.17 reported that the inhibitory effect of tannic acid on the growth of intestinal bacteria may be caused by its strong iron-bind ...
... conditions need iron for a variety of functions, including reduction of the ribonucleotide precursor of DNA, formation of haem, and other essential purposes.17 Chung et al.17 reported that the inhibitory effect of tannic acid on the growth of intestinal bacteria may be caused by its strong iron-bind ...
Malo-ethanolic fermentation in Saccharomyces and
... for yeast and fungi, i.e. those that are repressed by glucose and those that are not. In the K(+) yeasts K. lactis, C. utilis, H. anomala and C. sphaerica, the malate transport system was found to be substrateinducible and subject to glucose repression (Camarasa et al. 2001; Cássio and Leão 1993; ...
... for yeast and fungi, i.e. those that are repressed by glucose and those that are not. In the K(+) yeasts K. lactis, C. utilis, H. anomala and C. sphaerica, the malate transport system was found to be substrateinducible and subject to glucose repression (Camarasa et al. 2001; Cássio and Leão 1993; ...
Metabolic Engineering of Tomato Fruit Organic
... that metabolite pool and efflux from it (Kruger and Ratcliffe, 2009). In the case of citrate, for example, one could envisage that a change in the balance of flux through the citrate synthase and aconitase reactions could be responsible for a change in citrate levels. However, the situation is complic ...
... that metabolite pool and efflux from it (Kruger and Ratcliffe, 2009). In the case of citrate, for example, one could envisage that a change in the balance of flux through the citrate synthase and aconitase reactions could be responsible for a change in citrate levels. However, the situation is complic ...
The Presence and Function of Cytochromes in
... strains of S. ruminantium formed lactate as the main fermentation product from lactose. Small and variable amounts of acetate, propionate and succinate were also found. These results are similar to those of Hobson (1965) who showed that lactate was the main fermentation product in batch cultures of ...
... strains of S. ruminantium formed lactate as the main fermentation product from lactose. Small and variable amounts of acetate, propionate and succinate were also found. These results are similar to those of Hobson (1965) who showed that lactate was the main fermentation product in batch cultures of ...
Pineapple Juice and Its Fractions in Enzymatic Browning Inhibition
... determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using the methods of Wen and Wrolstad (23). For L-ascorbic acid and organic acids analyses, columns ODS-2 and ODS-1 (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 µm particle size; Alltech Associates Inc.) were connected in series to a Dynamax model SD-300 pump ...
... determined by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using the methods of Wen and Wrolstad (23). For L-ascorbic acid and organic acids analyses, columns ODS-2 and ODS-1 (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 µm particle size; Alltech Associates Inc.) were connected in series to a Dynamax model SD-300 pump ...
Metabolism of lactate and sugars by dairy propionibacteria: A
... transport system and fumarate acts as the final acceptor. Although propionibacteria are mainly anaerobes, the electron transport system can be used in the presence of oxygen and they possess the citrate cycle, but can not grow under normal atmospheric oxygen pressure. The proportions of propionate a ...
... transport system and fumarate acts as the final acceptor. Although propionibacteria are mainly anaerobes, the electron transport system can be used in the presence of oxygen and they possess the citrate cycle, but can not grow under normal atmospheric oxygen pressure. The proportions of propionate a ...
Regulation of thiamine synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for
... of the major directions of carbon flow under fully aerobic conditions when sugars are present in excess. In this respect, substantial research effort has been directed to developing a method to improve pyruvate production and reduce metabolic by-products. Historically, studies on improving pyruvate p ...
... of the major directions of carbon flow under fully aerobic conditions when sugars are present in excess. In this respect, substantial research effort has been directed to developing a method to improve pyruvate production and reduce metabolic by-products. Historically, studies on improving pyruvate p ...
1. Introduction to Natural Products Chemistry
... 2. Although compounds are usually transformed from simple structures to more complex ones, this is not always the case. ...
... 2. Although compounds are usually transformed from simple structures to more complex ones, this is not always the case. ...
Carbon metabolism in transgenic roots with altered levels
... This study investigates the capacity of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway (oxPPP) and nitrogen metabolism in transgenic potato (Solanum tuberosum) roots modified to express different levels of hexokinase (HK) or cytosolic triosephosphate isomerase (cTPI) growing under different nitrogen regime ...
... This study investigates the capacity of the oxidative pentose phosphate pathway (oxPPP) and nitrogen metabolism in transgenic potato (Solanum tuberosum) roots modified to express different levels of hexokinase (HK) or cytosolic triosephosphate isomerase (cTPI) growing under different nitrogen regime ...
Effects of Amino Acids Replacing Nitrate on Growth - dl.edi
... These results were consistent with those for winter onion (Allium cepa L.) and winter lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) (Gunes et al., 1994, 1996). The reduction of nitrate concentrations in plant tissues after addition of amino acids may result from reduction in nitrate uptake in plant roots (Muller and ...
... These results were consistent with those for winter onion (Allium cepa L.) and winter lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) (Gunes et al., 1994, 1996). The reduction of nitrate concentrations in plant tissues after addition of amino acids may result from reduction in nitrate uptake in plant roots (Muller and ...
Chapter 8 Cellular Respiration
... Glycolysis 4 hydrogen (2 pair) atoms formed – First step in respiration picked up by 2NAD+ 2NADH + (2H+) ETS Occurs 2–ATP used in cytoplasm 4–ATP formedrequire oxygen Doesn’t ...
... Glycolysis 4 hydrogen (2 pair) atoms formed – First step in respiration picked up by 2NAD+ 2NADH + (2H+) ETS Occurs 2–ATP used in cytoplasm 4–ATP formedrequire oxygen Doesn’t ...
Vitamin B12
... Classify fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Study chemical structure and “ biological active ” coenzyme form of vitamin B12. List the dietary sources and daily requirement of vitamin B12. Biochemical functions of vitamin B12 in the body. How it is digested and absorbed, transported and stored; ...
... Classify fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Study chemical structure and “ biological active ” coenzyme form of vitamin B12. List the dietary sources and daily requirement of vitamin B12. Biochemical functions of vitamin B12 in the body. How it is digested and absorbed, transported and stored; ...
Carbon dioxide metabolism and ecological significance
... cyanobacteria, this enzyme is responsible for fixating 20% of the total carbon. It is essential as it plays an important anaplerotic role [36]. PEPc fix C to produce oxaloacetate which is an intermediate in the TCA cycle. Thus, cyanobacteria mainly fixate C into the C3 cycle but they also contain th ...
... cyanobacteria, this enzyme is responsible for fixating 20% of the total carbon. It is essential as it plays an important anaplerotic role [36]. PEPc fix C to produce oxaloacetate which is an intermediate in the TCA cycle. Thus, cyanobacteria mainly fixate C into the C3 cycle but they also contain th ...
Further characterization of the lipoic acid enantiomers
... activity levels. Suna is continuing to learn new tricks & has been begging for 22.5mg/kg/day RLA for the last 7 years. Suna is Willow’s aunt although they frequently pass as siblings. ...
... activity levels. Suna is continuing to learn new tricks & has been begging for 22.5mg/kg/day RLA for the last 7 years. Suna is Willow’s aunt although they frequently pass as siblings. ...