Liver bile
... Bile secretion • Components of bile- bile salts and bile acids are formed by hepatocytes. • Conjugation of bilirubin occurs in ...
... Bile secretion • Components of bile- bile salts and bile acids are formed by hepatocytes. • Conjugation of bilirubin occurs in ...
Homeostasis of glucose
... • Exercise means high sympathetic stimulation which means low insulin secretion (see previous slide) • You would expect that with exercise not as much glucose would enter the cell due to low insulin levels…but this is not the case! • With exercise you have a high rate of glucose utilization thus the ...
... • Exercise means high sympathetic stimulation which means low insulin secretion (see previous slide) • You would expect that with exercise not as much glucose would enter the cell due to low insulin levels…but this is not the case! • With exercise you have a high rate of glucose utilization thus the ...
Chapter 6 Protein: Amino Acids The Chemist`s View of Proteins
... Proteins help maintain the volume and composition of body fluids Proteins help maintain the acid-base balance of body fluids by acting as buffers. Roles of Proteins Transportation Energy Proteins transport substances such as lipids, vitamins, minerals and oxygen, around the body Proteins provide som ...
... Proteins help maintain the volume and composition of body fluids Proteins help maintain the acid-base balance of body fluids by acting as buffers. Roles of Proteins Transportation Energy Proteins transport substances such as lipids, vitamins, minerals and oxygen, around the body Proteins provide som ...
Biochem19_Aerobic Respiration
... Compartments of Mitochondria • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through the electron transport system located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. • This transfer of electrons causes protons to be pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane compartment (resulting in a high ...
... Compartments of Mitochondria • Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through the electron transport system located in the inner mitochondrial membrane. • This transfer of electrons causes protons to be pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane compartment (resulting in a high ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Dr AN Boa Section 1
... Draw the structure of peptide Lys.Lys(ε→α)Asp and devise a synthesis for it starting from suitably protected amino acids. Note: (ε→α) here is to indicate that the side chain amine of the middle lysine is linked to the α-acid of the aspartic acid. ...
... Draw the structure of peptide Lys.Lys(ε→α)Asp and devise a synthesis for it starting from suitably protected amino acids. Note: (ε→α) here is to indicate that the side chain amine of the middle lysine is linked to the α-acid of the aspartic acid. ...
Chapter 6 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy In eukaryotes, cellular respiration
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules The citric acid cycle – is also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), – completes the oxidation of ...
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules The citric acid cycle – is also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), – completes the oxidation of ...
Tutorial 3 (Ans Scheme) ERT 317, Sem 1 2015/2016
... Briggs and Haldane first proposed Quasi-steady-state assumption ...
... Briggs and Haldane first proposed Quasi-steady-state assumption ...
VISUALIZING CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... Click the review button. Notice that ATP is generated on a membrane (the cristae) in a very similar manner to generation of ATP in the chloroplast (light reactions). Click on the animations to see how electrons are passed to the proteins on the membrane. Each time the electrons move energy is expend ...
... Click the review button. Notice that ATP is generated on a membrane (the cristae) in a very similar manner to generation of ATP in the chloroplast (light reactions). Click on the animations to see how electrons are passed to the proteins on the membrane. Each time the electrons move energy is expend ...
CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY
... usually results in a prompt recovery, but irreversible damage may occur. In patients with diabetes, the most common cause of hypoglycemia is excessive use of insulin or other glucose lowering medications, to lower the blood sugar level. In healthy subjects the blood glucose is maintained through a t ...
... usually results in a prompt recovery, but irreversible damage may occur. In patients with diabetes, the most common cause of hypoglycemia is excessive use of insulin or other glucose lowering medications, to lower the blood sugar level. In healthy subjects the blood glucose is maintained through a t ...
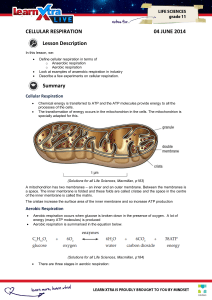
CELLULAR RESPIRATION 04 JUNE 2014 Lesson Description
... Question 8 In the presence of oxygen, all cells synthesize ATP via the process of glycolysis. Many cells also can metabolize pyruvate if oxygen is not present, via the process of: A. ...
... Question 8 In the presence of oxygen, all cells synthesize ATP via the process of glycolysis. Many cells also can metabolize pyruvate if oxygen is not present, via the process of: A. ...
Determination of 17 AQC derivatized Amino acids in
... development of an already described HPLC method using 6-aminoquinolyl-Nhydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) as the precolumn derivatization reagent. This highly reactive amine derivatization reagent can be used in an easy one step procedure.6 The compound reacts with amino acids to form stable urea d ...
... development of an already described HPLC method using 6-aminoquinolyl-Nhydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) as the precolumn derivatization reagent. This highly reactive amine derivatization reagent can be used in an easy one step procedure.6 The compound reacts with amino acids to form stable urea d ...
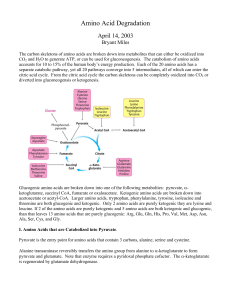
Amino Acid Degradation
... Glucogenic amino acids are broken down into one of the following metabolites: pyruvate, αketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, fumarate or oxaloacetate. Ketogenic amino acids are broken down into acetoacetate or acetyl-CoA. Larger amino acids, tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine, isoleucine and threonine are ...
... Glucogenic amino acids are broken down into one of the following metabolites: pyruvate, αketoglutarate, succinyl CoA, fumarate or oxaloacetate. Ketogenic amino acids are broken down into acetoacetate or acetyl-CoA. Larger amino acids, tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine, isoleucine and threonine are ...
Membrane Transport - Bioenergetics and Cell Metabolism
... lipids and proteins Most membrane lipids and protein can move through the membrane plane within limits ...
... lipids and proteins Most membrane lipids and protein can move through the membrane plane within limits ...
Synergistic Effects of Branched
... Higher alcohols were the main abundant group of volatiles in all wines. A positive relationship between higher alcohol production and amino acid supplementation was found. BCAA addition resulted in a 34.4% increase in 3-methyl butanol compared to the control. This was reasonable, considering the mec ...
... Higher alcohols were the main abundant group of volatiles in all wines. A positive relationship between higher alcohol production and amino acid supplementation was found. BCAA addition resulted in a 34.4% increase in 3-methyl butanol compared to the control. This was reasonable, considering the mec ...
Full-Text PDF
... carboxylase (ACC) phosphorylation and inhibit fatty acids (FA) synthesis. Sources of G3P and Acyl-CoA are plasma glycerol and FFA, but these substrates may also be synthesized de novo. The contribution of glyceroneogenesis and de novo lipogenesis to hepatic TG synthesis is significant, particularly ...
... carboxylase (ACC) phosphorylation and inhibit fatty acids (FA) synthesis. Sources of G3P and Acyl-CoA are plasma glycerol and FFA, but these substrates may also be synthesized de novo. The contribution of glyceroneogenesis and de novo lipogenesis to hepatic TG synthesis is significant, particularly ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION - Ms. Tripp
... • ATP is formed in glycolysis by substrate-level phosphorylation during which • an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP and ATP is formed. ...
... • ATP is formed in glycolysis by substrate-level phosphorylation during which • an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP and ATP is formed. ...
amino-acids - ChemConnections
... light to the left is called L- (laevus = “left”) and the other enantiomer is called D- (dexter = right). Enantiomers have identical physical and chemical properties. They only differ in their interaction with ...
... light to the left is called L- (laevus = “left”) and the other enantiomer is called D- (dexter = right). Enantiomers have identical physical and chemical properties. They only differ in their interaction with ...
Determination of Nutrient Contents and Amino acid Composition of
... production fix. Effect of Cu2+ at the expense of VEGF is not mediated by H2O2 but bound in thiol-redox status in the cell. Histological analyzes were performed on the edge of the wound tissue is known that the CuSO4-treatment not only speed up the process of wound closure but also the quality of dif ...
... production fix. Effect of Cu2+ at the expense of VEGF is not mediated by H2O2 but bound in thiol-redox status in the cell. Histological analyzes were performed on the edge of the wound tissue is known that the CuSO4-treatment not only speed up the process of wound closure but also the quality of dif ...
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1768:
... 0005-2736/$ - see front matter © 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.12.016 ...
... 0005-2736/$ - see front matter © 2007 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.12.016 ...
full text - pdf 348 kB
... Nomenclature Appendix No. 23 (June 1972) to IUPAC Information Bulletin and in: Arc/i. Biochem. Biophys. 150, 1 (1972); Biochem. J. 126, 773 (1972); Biochemistry. 11. 1726(1972): Biochi,n. Bioplivs. Acta. 263, 205 (1972); Europ. J. Biochem. 27, 201 (1972); J. Lio1. L:Iiem. 247, ...
... Nomenclature Appendix No. 23 (June 1972) to IUPAC Information Bulletin and in: Arc/i. Biochem. Biophys. 150, 1 (1972); Biochem. J. 126, 773 (1972); Biochemistry. 11. 1726(1972): Biochi,n. Bioplivs. Acta. 263, 205 (1972); Europ. J. Biochem. 27, 201 (1972); J. Lio1. L:Iiem. 247, ...