Lecture 3 — February 8, 2005 1 Introduction 2 The Cost of
... the sequence x. In particular, the algorithm knows the future: it can handle xi in a certain way, optimizing also for future accesses. So OP T is an offline optimum. We say that a BST algorithm is α-competitive if COST (x) ≤ αOP T (x) for all x. In this case, the BST algorithm should be online: it mus ...
... the sequence x. In particular, the algorithm knows the future: it can handle xi in a certain way, optimizing also for future accesses. So OP T is an offline optimum. We say that a BST algorithm is α-competitive if COST (x) ≤ αOP T (x) for all x. In this case, the BST algorithm should be online: it mus ...
Draintile versus Crushed Rock
... that will pass through a 2 inch sieve and be retained by a _ inch sieve. 2. A uniform layer of sand (native or fill), a minimum of 4 inches thick, overlain by a layer or strips of geotextile drainage matting designed to allow the lateral flow of soil gases. [My note: Not very effective] 3. Other mat ...
... that will pass through a 2 inch sieve and be retained by a _ inch sieve. 2. A uniform layer of sand (native or fill), a minimum of 4 inches thick, overlain by a layer or strips of geotextile drainage matting designed to allow the lateral flow of soil gases. [My note: Not very effective] 3. Other mat ...
binary search tree
... – If the item for which we are searching is less than the item in the middle, we know that the item won’t be in the second half of the list – Once again we examine the “middle” element (which is really the item 25% of the way into the list) – The process continues with each comparison cutting in hal ...
... – If the item for which we are searching is less than the item in the middle, we know that the item won’t be in the second half of the list – Once again we examine the “middle” element (which is really the item 25% of the way into the list) – The process continues with each comparison cutting in hal ...
Slide 1
... Trees consist of nodes (circles) connected by edges (lines). The root is the topmost node in a tree; it has no parent. In a binary tree, a node has at most two children. In a binary search tree, all the nodes that are left descendants of node A have key values less than A; all the nodes that are A’s ...
... Trees consist of nodes (circles) connected by edges (lines). The root is the topmost node in a tree; it has no parent. In a binary tree, a node has at most two children. In a binary search tree, all the nodes that are left descendants of node A have key values less than A; all the nodes that are A’s ...
Worst Case Constant Time Priority Queue
... is used in combination with a new memory topology Lower Bounds and some Matching it provides an O(1) worst case time solution. ...
... is used in combination with a new memory topology Lower Bounds and some Matching it provides an O(1) worst case time solution. ...
Chapter 15 Valuation Analysis: Income Discounting, Cap Rates and
... Simple multiplier models of value ...
... Simple multiplier models of value ...
The ND-Tree - Department of Computer Science
... – Domains that contain non-ordered discrete values are prevalent, e.g., sex, profession, etc. – There are many new and emerging applications that use vectors with non-ordered values • e.g. genomic sequences that are broken into fixed length substrings (vectors) with the domain: {a, g, t, c}: “aggcgg ...
... – Domains that contain non-ordered discrete values are prevalent, e.g., sex, profession, etc. – There are many new and emerging applications that use vectors with non-ordered values • e.g. genomic sequences that are broken into fixed length substrings (vectors) with the domain: {a, g, t, c}: “aggcgg ...
In segregating responsibilities, this office reconciles payments with
... 16. Which of the following is the exposure to a change in value of some market variables, such as interest rates, foreign exchange rates, equity or commodity prices? (A) credit risk (B) market risk (C) contract risk (D) value - at - risk ...
... 16. Which of the following is the exposure to a change in value of some market variables, such as interest rates, foreign exchange rates, equity or commodity prices? (A) credit risk (B) market risk (C) contract risk (D) value - at - risk ...
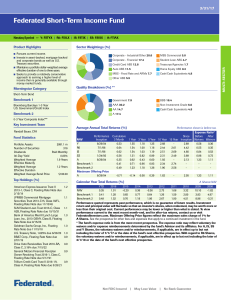
Short-Term Income Fund - Investor Fact Sheet
... maturity of debt securities held in the fund. Weighted Average Effective Duration (sometimes called “Option-Adjusted Duration”) is a measure of a security’s price sensitivity to changes in interest rates calculated using a model that recognizes that the probability of a bond being called or remainin ...
... maturity of debt securities held in the fund. Weighted Average Effective Duration (sometimes called “Option-Adjusted Duration”) is a measure of a security’s price sensitivity to changes in interest rates calculated using a model that recognizes that the probability of a bond being called or remainin ...
CS2351 Data Structures
... s parent now has at most B children Done • Else if L’ s parent now overflows Recursively split and insert middle key to its parent • Special case: If the current root is split into two nodes, we create a new root and joins it to the two nodes ...
... s parent now has at most B children Done • Else if L’ s parent now overflows Recursively split and insert middle key to its parent • Special case: If the current root is split into two nodes, we create a new root and joins it to the two nodes ...
the full report
... adjusted growth rate as well. Real personal spending growth will likely continue to be relatively strong on ...
... adjusted growth rate as well. Real personal spending growth will likely continue to be relatively strong on ...
8. Non-current liabilities- bonds
... historical cost accounting for assets. Since the book values of liabilities are based on historical rates, whereas their market values are based on current rates, book values and market values will differ subsequent to issuance. As we will see, this creates the potential for income management by ret ...
... historical cost accounting for assets. Since the book values of liabilities are based on historical rates, whereas their market values are based on current rates, book values and market values will differ subsequent to issuance. As we will see, this creates the potential for income management by ret ...
(Sam a +a $t$#$;t&%+
... C. Suppose host A is sending host B a large file over a TCP connection. The number of unacknowledged bytes that host A sends cannot exceed the size of the receiver buffer. D. Suppose host A is sending host B a large file over a TCP connection. If the sequence number for a segment of this connection ...
... C. Suppose host A is sending host B a large file over a TCP connection. The number of unacknowledged bytes that host A sends cannot exceed the size of the receiver buffer. D. Suppose host A is sending host B a large file over a TCP connection. If the sequence number for a segment of this connection ...
Euler Tour
... is a path that traverses each edge exactly once. In the context of a tree, we say that each edge is bidirectional, so the Euler tour is the path along the tree that begins at the root and ends at the root, traversing each edge exactly twice — once to enter the subtree at the other endpoint and once ...
... is a path that traverses each edge exactly once. In the context of a tree, we say that each edge is bidirectional, so the Euler tour is the path along the tree that begins at the root and ends at the root, traversing each edge exactly twice — once to enter the subtree at the other endpoint and once ...
The Time Value of Money
... value of money that is received in the future. A. The discount is a result of the investor waiting to receive the future payment rather than receiving it now and investing it in an alternative way. B. To determine the present value of money earned in the future, the following equation can be used: P ...
... value of money that is received in the future. A. The discount is a result of the investor waiting to receive the future payment rather than receiving it now and investing it in an alternative way. B. To determine the present value of money earned in the future, the following equation can be used: P ...
Binary Trees 1
... The general binary tree shown in the previous chapter is not terribly useful in practice. The chief use of binary trees is for providing rapid access to data (indexing, if you will) and the general binary tree does not have good performance. Suppose that we wish to store data elements that contain a ...
... The general binary tree shown in the previous chapter is not terribly useful in practice. The chief use of binary trees is for providing rapid access to data (indexing, if you will) and the general binary tree does not have good performance. Suppose that we wish to store data elements that contain a ...
Left-leaning Red-Black Trees
... search time bounded by a small constant multiple of lg N in a tree of N keys, and the behavior observed in practice is typically that same multiple faster than the worst-case bound, close the to optimal lg N nodes examined that would be observed in a perfectly balanced tree. This performance is also ...
... search time bounded by a small constant multiple of lg N in a tree of N keys, and the behavior observed in practice is typically that same multiple faster than the worst-case bound, close the to optimal lg N nodes examined that would be observed in a perfectly balanced tree. This performance is also ...
Lattice model (finance)

For other meanings, see lattice model (disambiguation)In finance, a lattice model [1] is a technique applied to the valuation of derivatives, where, because of path dependence in the payoff, 1) a discretized model is required and 2) Monte Carlo methods fail to account for optimal decisions to terminate the derivative by early exercise. For equity options, a typical example would be pricing an American option, where a decision as to option exercise is required at ""all"" times (any time) before and including maturity. A continuous model, on the other hand, such as Black Scholes, would only allow for the valuation of European options, where exercise is on the option's maturity date. For interest rate derivatives lattices are additionally useful in that they address many of the issues encountered with continuous models, such as pull to par.