Nucleic Acid Notes
... •lys-arg-his-asp-glu-ala-val-leu-ile-pro-phemet-trp-gly-cys-ser-thr-tyr-asn-gln ...
... •lys-arg-his-asp-glu-ala-val-leu-ile-pro-phemet-trp-gly-cys-ser-thr-tyr-asn-gln ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Spring 2011 Lecture Outline Chemistry of the
... High specific heat Hydrogen bonds act as buffer for increased energy Buffer cells from heat released during chemical reactions High heat of vaporization Cooling effect of sweating, panting, etc. D. Universal solvent Most molecules in cells are polar = hydrophilic Some are nonpolar = hydrophobic Sphe ...
... High specific heat Hydrogen bonds act as buffer for increased energy Buffer cells from heat released during chemical reactions High heat of vaporization Cooling effect of sweating, panting, etc. D. Universal solvent Most molecules in cells are polar = hydrophilic Some are nonpolar = hydrophobic Sphe ...
Unit III: Introduction to Cells Unit IV: Cell Processes
... codon, point mutation, frameshift mutation 1. Create a flow chart summarizing the central dogma of protein synthesis; 2. Explain the DNA code; 3. Define gene and describe the human genome; 4. ____________ is a rough estimate of the number of human genes found in the human genome 5. Why are proteins ...
... codon, point mutation, frameshift mutation 1. Create a flow chart summarizing the central dogma of protein synthesis; 2. Explain the DNA code; 3. Define gene and describe the human genome; 4. ____________ is a rough estimate of the number of human genes found in the human genome 5. Why are proteins ...
Practice Quiz
... 5. A red blood cell would swell if its surrounding solution was _____________. 6. The substance that dissolves in a mixture is called the _________________. 7. The ________________ are organelles that contain intracellular digestive enzymes. 8. _______________ is a lipid that helps to stabilize anim ...
... 5. A red blood cell would swell if its surrounding solution was _____________. 6. The substance that dissolves in a mixture is called the _________________. 7. The ________________ are organelles that contain intracellular digestive enzymes. 8. _______________ is a lipid that helps to stabilize anim ...
Macromolecules
... Macromolecules are formed when monomers are linked together to form longer chains called polymers. The same process of making and breaking polymers is found in all living organisms. ...
... Macromolecules are formed when monomers are linked together to form longer chains called polymers. The same process of making and breaking polymers is found in all living organisms. ...
1-3 Studying Life
... Obtain & use energy Respond to their environment Maintain homeostasis AS A GROUP, living things change over time (evolve) ...
... Obtain & use energy Respond to their environment Maintain homeostasis AS A GROUP, living things change over time (evolve) ...
This project aims to identify differences in DNA structure of cells in
... BACKGROUND: Neuron death in Alzheimer’s disease may be amplified by a loss of protection by microglia, the immune cells of the central nervous system. Like replicating cells, microglia become less functional as they age. Aging of cells throughout the body can be regulated by how tightly their DNA is ...
... BACKGROUND: Neuron death in Alzheimer’s disease may be amplified by a loss of protection by microglia, the immune cells of the central nervous system. Like replicating cells, microglia become less functional as they age. Aging of cells throughout the body can be regulated by how tightly their DNA is ...
Chapter 3
... Fertilization then restores the diploid number of chromosomes from 2 haploid cells (one egg, one sperm) ...
... Fertilization then restores the diploid number of chromosomes from 2 haploid cells (one egg, one sperm) ...
Q11 Outline the formation, structure and function of the adult red
... decreases in size, gradually losing cytoplasmic organelles and increasing its haemoglobin content Reticulocytes then lose their ribosomes to become mature erythrocytes The differentiation from stem cell to erythro ...
... decreases in size, gradually losing cytoplasmic organelles and increasing its haemoglobin content Reticulocytes then lose their ribosomes to become mature erythrocytes The differentiation from stem cell to erythro ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... o Polymer built from set of 20 amino acids o Linked by peptide bonds via dehydration reaction o Each has unique amino acid sequence; can be a few to more than a thousand Amino Acid Structure o -Carbon bonded to: Hydrogen Carboxyl group Amino group Side Chain (R group) – accounts for diffe ...
... o Polymer built from set of 20 amino acids o Linked by peptide bonds via dehydration reaction o Each has unique amino acid sequence; can be a few to more than a thousand Amino Acid Structure o -Carbon bonded to: Hydrogen Carboxyl group Amino group Side Chain (R group) – accounts for diffe ...
Anatomy I - Unit 3: Basic Biochemistry
... Biochemistry is the study of the chemical interactions of living things. Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
... Biochemistry is the study of the chemical interactions of living things. Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
Cells
... Non-polar molecules penetrate by actually dissolving into the lipid bilayer. Most polar compounds such as amino acids, organic acids and inorganic salts are not allowed entry, but instead must be specifically transported across the membrane by proteins. ...
... Non-polar molecules penetrate by actually dissolving into the lipid bilayer. Most polar compounds such as amino acids, organic acids and inorganic salts are not allowed entry, but instead must be specifically transported across the membrane by proteins. ...
The spreading out of particles from an area of high concentration to
... The remains of plants and animals made from the gradual replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). ...
... The remains of plants and animals made from the gradual replacement of hard parts with minerals (or from casts and impressions or, by preservation when no decay occurs). ...
Unit 4 Study Guide: Cell Membrane and Homeostasis Answer Key
... materials can travel through the lipid bilayer. Neither process requires energy. 5. Structure of the cell membrane is - lipid bilayer (flexible) - hydrophilic heads (outside membrane) attract water (water-loving) - hydrophobic tails (inside membrane) repel water (water-hating) - transport proteins m ...
... materials can travel through the lipid bilayer. Neither process requires energy. 5. Structure of the cell membrane is - lipid bilayer (flexible) - hydrophilic heads (outside membrane) attract water (water-loving) - hydrophobic tails (inside membrane) repel water (water-hating) - transport proteins m ...
Transport by Carriers
... Describe and compare: facilitated transport and active transport in terms of: Method of transport (use of channel or carrier protein) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Concentration gradient Type / size of molecule transported ...
... Describe and compare: facilitated transport and active transport in terms of: Method of transport (use of channel or carrier protein) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Concentration gradient Type / size of molecule transported ...
Summer Review Package: `16-`17 1. Vocabulary
... (F) Mice will fill a different niche in the ecosystem. (G) The following year the spring will be warm again. (H) Birds of prey that eat mice will become more numerous. (I) Animals that compete with mice will adapt to find new niches. 17. A tall pea plant with red flowers has the genotype Rr . This p ...
... (F) Mice will fill a different niche in the ecosystem. (G) The following year the spring will be warm again. (H) Birds of prey that eat mice will become more numerous. (I) Animals that compete with mice will adapt to find new niches. 17. A tall pea plant with red flowers has the genotype Rr . This p ...
Cell Cycle Notes
... D. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes = 46 total (diploid/2n) II. The Cell Cycle: A. somatic (body) cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form 2 identical daughter cells Consists of 2 phases: Interphase (G1 ...
... D. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes = 46 total (diploid/2n) II. The Cell Cycle: A. somatic (body) cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form 2 identical daughter cells Consists of 2 phases: Interphase (G1 ...
Ch 18.2-18.5 PPT
... ◦ Mutations of ras occurs in 30% of cancers p53 gene: tumor-suppresor gene ◦ Functions: halt cell cycle for DNA repair, turn on DNA repair, activate apoptosis (cell death) ◦ Mutations of p53 in 50+% of cancers ...
... ◦ Mutations of ras occurs in 30% of cancers p53 gene: tumor-suppresor gene ◦ Functions: halt cell cycle for DNA repair, turn on DNA repair, activate apoptosis (cell death) ◦ Mutations of p53 in 50+% of cancers ...
Cell Introduction Powerpoint
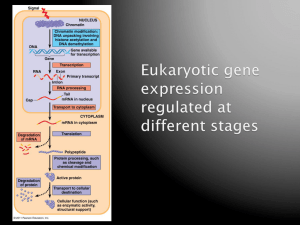
... GENOME SIZE: stated as the total number of base pairs the human genome = 3 billion base pairs Each DNA Molecule contains many genes (the basic physical and functional unit of heredity). a gene is a sequence of nucleotides bases, who carry the info required for constructing proteins, which carry ...
... GENOME SIZE: stated as the total number of base pairs the human genome = 3 billion base pairs Each DNA Molecule contains many genes (the basic physical and functional unit of heredity). a gene is a sequence of nucleotides bases, who carry the info required for constructing proteins, which carry ...
Summer Review Package: `14 -`15 PART I 1. Vocabulary – Please b
... (G) Prokaryotes cannot live without a host. (H) Eukaryotes copy DNA and are able to reproduce. (I) Prokaryotes do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. 7. What are the structures specialized for taking blood away from the heart called? (A) arteries (B) bronchioles (C) capillaries (D) veins 8. In the 18 ...
... (G) Prokaryotes cannot live without a host. (H) Eukaryotes copy DNA and are able to reproduce. (I) Prokaryotes do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. 7. What are the structures specialized for taking blood away from the heart called? (A) arteries (B) bronchioles (C) capillaries (D) veins 8. In the 18 ...
Ch. 7 part 2 (PM and Osmosis)
... How do you build a barrier that keeps the watery contents of the cell separate from the watery environment? FATS ...
... How do you build a barrier that keeps the watery contents of the cell separate from the watery environment? FATS ...
One step ahead: light-based combinations to combat treatment resistance in cancers
... Resistance of cancer cells to treatment is multifactorial and may be inherent or acquired. Treatment resistance can be broken down into two broad categories. The first results from changes within cancer cells that prevent drugs from being able to do damage through a variety of mechanisms such as enh ...
... Resistance of cancer cells to treatment is multifactorial and may be inherent or acquired. Treatment resistance can be broken down into two broad categories. The first results from changes within cancer cells that prevent drugs from being able to do damage through a variety of mechanisms such as enh ...
Endoplasmic reticulum - Protein synthesis
... ER, Golgi retrieved by the KDEL-receptors. They recognize the KDEL signal (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu at C-terminus). ...
... ER, Golgi retrieved by the KDEL-receptors. They recognize the KDEL signal (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu at C-terminus). ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.