Cyclin-dependent kinase 12 (CDK12), human kinase domain
... Human CDK12 is an unusually large CDK family member (1,490 a.a.) that assembles with cyclin K (CCNK, or CycK). The CDK12/CycK complex phosphorylates Ser2 in the heptad repeats of the RNA Pol II CTD promoting transcriptional elongation of large DNA damage response genes, including BRCA1/2, ATR and FA ...
... Human CDK12 is an unusually large CDK family member (1,490 a.a.) that assembles with cyclin K (CCNK, or CycK). The CDK12/CycK complex phosphorylates Ser2 in the heptad repeats of the RNA Pol II CTD promoting transcriptional elongation of large DNA damage response genes, including BRCA1/2, ATR and FA ...
Cdc23 Polyclonal Antibody - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... Cell cycle regulated protein ubiquitination and degradation within subcellular domains is thought to be essential for the normal progression of mitosis. APC8 is a highly conserved component of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), a cell cycle-regulated E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls ...
... Cell cycle regulated protein ubiquitination and degradation within subcellular domains is thought to be essential for the normal progression of mitosis. APC8 is a highly conserved component of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C), a cell cycle-regulated E3 ubiquitin ligase that controls ...
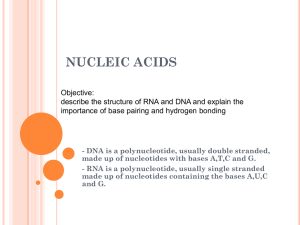
Synthesis and Characterization of Peptide Nucleic Acid for
... In the age of the genome, many diseases and disorders can be attributed to the over-expression of specific genes, even some forms of cancer (1); countermeasures to moderate these disorders include the control of gene expression with DNA-binding small molecules or anti-sense, RNA interfering, small m ...
... In the age of the genome, many diseases and disorders can be attributed to the over-expression of specific genes, even some forms of cancer (1); countermeasures to moderate these disorders include the control of gene expression with DNA-binding small molecules or anti-sense, RNA interfering, small m ...
Dr.A.K.AL-Yassari 2016-2017 Microbiology Year:third Bacterial cell
... The Gram-staining procedure consists of a primary stain (crystal violet), a mordant (Gram’s iodine), alcohol as a decolorizer and a counterstain (carbol fuchsin). The crystal violet penetrates the cell wall of both Gram-positive and Gramnegative bacteria. Following addition of the iodine, a co ...
... The Gram-staining procedure consists of a primary stain (crystal violet), a mordant (Gram’s iodine), alcohol as a decolorizer and a counterstain (carbol fuchsin). The crystal violet penetrates the cell wall of both Gram-positive and Gramnegative bacteria. Following addition of the iodine, a co ...
Biology Keystone Cliffnotes Chapter Review
... the results of manipulating only 1 variable. In a lab the independent variable is the variable you have control over (the variable you choose) and the dependent variable is what you are measuring. For example, in an experiment that tests how colors of light effect plant growth the colors chosen for ...
... the results of manipulating only 1 variable. In a lab the independent variable is the variable you have control over (the variable you choose) and the dependent variable is what you are measuring. For example, in an experiment that tests how colors of light effect plant growth the colors chosen for ...
Preface
... Molecular oxidation affects cell function and can lead to cell degeneration or cell death. Free radicals are a major factor in inducing this oxidation and they can attack and inactivate or alter the biological activity of molecules such as lipids and proteins that are essential for cell function. If ...
... Molecular oxidation affects cell function and can lead to cell degeneration or cell death. Free radicals are a major factor in inducing this oxidation and they can attack and inactivate or alter the biological activity of molecules such as lipids and proteins that are essential for cell function. If ...
The Genetic Code and Translation
... – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Signals the beginning of protein production ...
... – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Signals the beginning of protein production ...
Control of microbial growth: Sterilization and disinfectants
... material (like blood, vomit, feces..) • Effective, but non-toxic to humans. • Penetrate materials without damaging them. • Easy to prepare and stable over time. • Inexpensive and easy to apply. • Not stink! ...
... material (like blood, vomit, feces..) • Effective, but non-toxic to humans. • Penetrate materials without damaging them. • Easy to prepare and stable over time. • Inexpensive and easy to apply. • Not stink! ...
Transcription and Translation
... Remember: MR CATAP (mRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acid, polypeptide) • mRNA binds to a ribosome which initiates translation • The mRNA is read in codons (from start codon = AUG) • Anticodons on tRNA align opposite appropriate codons ...
... Remember: MR CATAP (mRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acid, polypeptide) • mRNA binds to a ribosome which initiates translation • The mRNA is read in codons (from start codon = AUG) • Anticodons on tRNA align opposite appropriate codons ...
Observed Rate of Bubble Formation Distance to Light Observations
... A nerve cell and a liver cell in the same organism contain different combinations of proteins. Which of these statements BEST explains why different cells are different proteins? The different cells in an organism contain different genes Each cell in an organism transcribes only the genes that cell ...
... A nerve cell and a liver cell in the same organism contain different combinations of proteins. Which of these statements BEST explains why different cells are different proteins? The different cells in an organism contain different genes Each cell in an organism transcribes only the genes that cell ...
Document
... RNA has catalytic role (snRNA) in Eukaryotic Cells and in protozoan (p. 336) Why can RNA act as an enzyme (Ribozyme)? Alternative RNA splicing --- One exon codes for one domain of a protein (p. 336) Introns allow for more crossing over without disrupting domain coding = new proteins sequences. ...
... RNA has catalytic role (snRNA) in Eukaryotic Cells and in protozoan (p. 336) Why can RNA act as an enzyme (Ribozyme)? Alternative RNA splicing --- One exon codes for one domain of a protein (p. 336) Introns allow for more crossing over without disrupting domain coding = new proteins sequences. ...
FPIA - IMGT
... between membrane proteins. So a ligand can be either a soluble protein or a membrane protein at the cell surface (GPI-anchored or transmembrane). It can be also intracellular in a cell pathway. The notion of receptor is often associated to ‘membrane’ protein however many receptors can become natural ...
... between membrane proteins. So a ligand can be either a soluble protein or a membrane protein at the cell surface (GPI-anchored or transmembrane). It can be also intracellular in a cell pathway. The notion of receptor is often associated to ‘membrane’ protein however many receptors can become natural ...
NIH Biosketch
... critical to cell physiology (eg GTPases, kinases, scaffolds). We were among the first to focus on nonchannel optogenetics, controlling GTPases with light in living cells. We have developed alternate approaches for optogenetic control that are suitable for different protein families, and with complem ...
... critical to cell physiology (eg GTPases, kinases, scaffolds). We were among the first to focus on nonchannel optogenetics, controlling GTPases with light in living cells. We have developed alternate approaches for optogenetic control that are suitable for different protein families, and with complem ...
Fibroblast Growth Factor- acidic
... Description: FGF acidic, also known as FGF-1 and endothelial cell growth factor, is a member of the FGF family of mitogenic peptides which currently is comprised of at least seven proteins which show 35-55% amino acid sequence conservation. FGF acidic and basic, unlike the other members of the famil ...
... Description: FGF acidic, also known as FGF-1 and endothelial cell growth factor, is a member of the FGF family of mitogenic peptides which currently is comprised of at least seven proteins which show 35-55% amino acid sequence conservation. FGF acidic and basic, unlike the other members of the famil ...
MEIOSIS
... chromosomes. In human, the haploid cells are the sex cells – sperm & egg – which contain 23 chromosomes. • Sex cells = gametes = germ cells. • A regular body cell is a diploid cell that contains two full sets of chromosomes – one from mom and one from dad. The number of chromosomes in a human diploi ...
... chromosomes. In human, the haploid cells are the sex cells – sperm & egg – which contain 23 chromosomes. • Sex cells = gametes = germ cells. • A regular body cell is a diploid cell that contains two full sets of chromosomes – one from mom and one from dad. The number of chromosomes in a human diploi ...
Answers
... ii. Fish / Organisms with gills counter current flow between blood in the gills and the water over the gills iii. Worms / Slugs gases dissolve in mucous surrounding worm/slug then diffuse into organism iv. Insects air enters and leaves holes on the side of the body called spiracles – air circulates ...
... ii. Fish / Organisms with gills counter current flow between blood in the gills and the water over the gills iii. Worms / Slugs gases dissolve in mucous surrounding worm/slug then diffuse into organism iv. Insects air enters and leaves holes on the side of the body called spiracles – air circulates ...
Biology Review PPT
... •Growth - increase in cellular mass, and/or increase in number of cells •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
... •Growth - increase in cellular mass, and/or increase in number of cells •Reproduction - formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as living organisms. ...
Mutation Reading--How the Gene for Sickle Cell Hemoglobin
... …result in differences in the nucleotide sequence in mRNA… …result in differences in the amino acid sequence in the protein… …result in differences in the structure and function of the protein… …result in differences in a person's characteristics. For example, if a person has an allele that codes fo ...
... …result in differences in the nucleotide sequence in mRNA… …result in differences in the amino acid sequence in the protein… …result in differences in the structure and function of the protein… …result in differences in a person's characteristics. For example, if a person has an allele that codes fo ...
Cell-penetrating peptide

Cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) are short peptides that facilitate cellular uptake of various molecular cargo (from nanosize particles to small chemical molecules and large fragments of DNA). The ""cargo"" is associated with the peptides either through chemical linkage via covalent bonds or through non-covalent interactions. The function of the CPPs are to deliver the cargo into cells, a process that commonly occurs through endocytosis with the cargo delivered to the endosomes of living mammalian cells.CPPs hold great potential as in vitro and in vivo delivery vectors for use in research and medicine. Current use is limited by a lack of cell specificity in CPP-mediated cargo delivery and insufficient understanding of the modes of their uptake.CPPs typically have an amino acid composition that either contains a high relative abundance of positively charged amino acids such as lysine or arginine or has sequences that contain an alternating pattern of polar/charged amino acids and non-polar, hydrophobic amino acids. These two types of structures are referred to as polycationic or amphipathic, respectively. A third class of CPPs are the hydrophobic peptides, containing only apolar residues, with low net chargeor have hydrophobic amino acid groups that are crucial for cellular uptake.The first CPP was discovered independently by two laboratories in 1988, when it was found that the trans-activating transcriptional activator (TAT) from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) could be efficiently taken up from the surrounding media by numerous cell types in culture. Since then, the number of known CPPs has expanded considerably and small molecule synthetic analogues with more effective protein transduction properties have been generated.