Physiology, Health & Exercise
... Strengthened cardiac muscle- capable of more forceful contraction- higher SV- even at rest Athlete’s heart actually gets bigger- cardiac hypertrophy Increase in protein synthesis in cardiac muscle fibres increase in contractile elements within each fibre increase in size ...
... Strengthened cardiac muscle- capable of more forceful contraction- higher SV- even at rest Athlete’s heart actually gets bigger- cardiac hypertrophy Increase in protein synthesis in cardiac muscle fibres increase in contractile elements within each fibre increase in size ...
AFA Ablation of The Atrioventricular Node and Pacemaker
... heart chambers, the atria, bombards the atrioventricular node (AV node – the normal pathway for electrical activity flowing from the atria to the ventricles) and much of this electrical activity gets through this gateway, the result being rapid and irregular pumping activity. Although drugs in some p ...
... heart chambers, the atria, bombards the atrioventricular node (AV node – the normal pathway for electrical activity flowing from the atria to the ventricles) and much of this electrical activity gets through this gateway, the result being rapid and irregular pumping activity. Although drugs in some p ...
Goes the Heart- Atrial Fibrillation
... reaching respiring tissues, but it also means, due to less blood leaving the left side of the heart, that the little blood that does reach these tissues is very low in oxygen saturation, so even less oxygen is available to the tissues. Tiredness, dizziness and fainting are all symptoms of this poor ...
... reaching respiring tissues, but it also means, due to less blood leaving the left side of the heart, that the little blood that does reach these tissues is very low in oxygen saturation, so even less oxygen is available to the tissues. Tiredness, dizziness and fainting are all symptoms of this poor ...
ZLYHANIE SRDCA - TOP Recommended Websites
... • Heart failure is the pathophysiological state in which an abnormality of cardiac function is responsible for failure of the heart to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of the metabolizing tissue, or to do so only from an elevated filling pressure. • Clinical syndrome due to di ...
... • Heart failure is the pathophysiological state in which an abnormality of cardiac function is responsible for failure of the heart to pump blood at a rate commensurate with the requirements of the metabolizing tissue, or to do so only from an elevated filling pressure. • Clinical syndrome due to di ...
Cardiac Arrhythmias
... Depolarization—myocardial stimulation due to change in polarity of cell from negative to positive Repolarization—return of myocardial cell to resting state and negative charge ...
... Depolarization—myocardial stimulation due to change in polarity of cell from negative to positive Repolarization—return of myocardial cell to resting state and negative charge ...
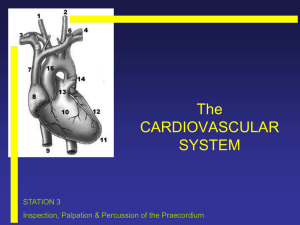
Station 1
... • PARARSTERNAL HEAVE place heel of hand just lateral to the left parasternal border right ventricular enlargement & severe left atrial enlargement ...
... • PARARSTERNAL HEAVE place heel of hand just lateral to the left parasternal border right ventricular enlargement & severe left atrial enlargement ...
InaHRS_2016_-_Atrial_Fibrillation
... and mandates PPM implantation which is indicated in TAVB. Ideal treatment for this patient is revascularization, however it is limited by patient’s refusal and kidney function, PPM is considered. Ventricular pacing by PPM will increase cardiac output, ease symptoms and improve quality of life althou ...
... and mandates PPM implantation which is indicated in TAVB. Ideal treatment for this patient is revascularization, however it is limited by patient’s refusal and kidney function, PPM is considered. Ventricular pacing by PPM will increase cardiac output, ease symptoms and improve quality of life althou ...
Cardiovascular Unit Vocab List 1. Heart: the muscle that makes the
... of blood vessels, particularly large arteries, as it is pumped through the body. 9. Angina pectoris: chest pain that results when the heart does not get enough oxygen 10. Congestive heart failure: a condition that occurs when the heart weakens and can no longer maintain its pumping rate and force 11 ...
... of blood vessels, particularly large arteries, as it is pumped through the body. 9. Angina pectoris: chest pain that results when the heart does not get enough oxygen 10. Congestive heart failure: a condition that occurs when the heart weakens and can no longer maintain its pumping rate and force 11 ...
Cardiovascular Disorders
... cycle ◦ Slight increase in HR increases CO ◦ Very rapid HR prevents adequate filling in ...
... cycle ◦ Slight increase in HR increases CO ◦ Very rapid HR prevents adequate filling in ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... Figure 1. Fibrosis of the aging heart. Cardiac aging is associated with significant alterations in cardiac structure and function. Elderly patients often present with left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction while the systolic function is usually preserved. Age-dependent remodeling of ...
... Figure 1. Fibrosis of the aging heart. Cardiac aging is associated with significant alterations in cardiac structure and function. Elderly patients often present with left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction while the systolic function is usually preserved. Age-dependent remodeling of ...
Cardiovascular Pharmacology
... Rhythms generated by this called “Sinus”, e.g., Sinus Rhythm, Normal Sinus Rhythm, Sinus Bradycardia, Sinus Tachycardia, Sinus Arrhythmia ...
... Rhythms generated by this called “Sinus”, e.g., Sinus Rhythm, Normal Sinus Rhythm, Sinus Bradycardia, Sinus Tachycardia, Sinus Arrhythmia ...
General Medical Officer (GMO) Manual: Clinical Section
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
Anatomy and Physiology for Emergency Care
... Physiology for Emergency Care Chapter 13 The Heart ...
... Physiology for Emergency Care Chapter 13 The Heart ...
Arrhythmias - The Brookside Associates
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
Grade 5: Lesson PLan 1 - Texas Heart Institute
... The walls of the heart are a special kind of thick muscle known as cardiac muscle. The conduction system of the heart causes cardiac muscle to beat (contract and relax). Each heartbeat is a 2-step process that begins in a small group of neural cells located in the upper right atrium. This group of c ...
... The walls of the heart are a special kind of thick muscle known as cardiac muscle. The conduction system of the heart causes cardiac muscle to beat (contract and relax). Each heartbeat is a 2-step process that begins in a small group of neural cells located in the upper right atrium. This group of c ...
Arrhythmias - American Heart Association
... Each heartbeat begins in a specialized area of the right atrium called the sinus node. The sinus node starts each heartbeat by generating a small amount of electricity, which spreads into the muscle cells of the atria. This causes these upper chambers to contract. Next, the electrical activity moves ...
... Each heartbeat begins in a specialized area of the right atrium called the sinus node. The sinus node starts each heartbeat by generating a small amount of electricity, which spreads into the muscle cells of the atria. This causes these upper chambers to contract. Next, the electrical activity moves ...
Preventing SCA Fact sheet
... healthy heart, some blood always remains within this chamber after each heartbeat. Therefore an ejection fraction is a percentage of the blood within the ciamber that is pumped outwith every heartbeat. An EF of 55 to 75 percent is considered normal. A higher than normal ejection fraction could indic ...
... healthy heart, some blood always remains within this chamber after each heartbeat. Therefore an ejection fraction is a percentage of the blood within the ciamber that is pumped outwith every heartbeat. An EF of 55 to 75 percent is considered normal. A higher than normal ejection fraction could indic ...
Ventricular Tachycardias - e
... a wide QRS complex. Identifying wide- versus narrow-complex tachycardia is one important factor in attempting to differentiate between ventricular and atrial tachycardia. The most common type of wide-complex tachycardia is ventricular tachycardia (VT), followed by supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), ...
... a wide QRS complex. Identifying wide- versus narrow-complex tachycardia is one important factor in attempting to differentiate between ventricular and atrial tachycardia. The most common type of wide-complex tachycardia is ventricular tachycardia (VT), followed by supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), ...
he heart - TECC Science
... structures of the human heart, describe the problems that can develop in blood vessels in the human heart, and their treatments. Suggest advantages and disadvantages of using stents and statins. Challenge Flightpath A): Explain in detail how the structure of the different parts of the human heart is ...
... structures of the human heart, describe the problems that can develop in blood vessels in the human heart, and their treatments. Suggest advantages and disadvantages of using stents and statins. Challenge Flightpath A): Explain in detail how the structure of the different parts of the human heart is ...
Arrhythmias Complicating AMI
... With either anterior or inferior infarct. With inferior infarcts , the defect is likely to be in the AV node, with escape rhythms exceeding 40 beats/min and exhibiting a narrow QRS complex. With anterior infarct, the conduction defect is infranodal and the escape rhythm (if present) is usually less ...
... With either anterior or inferior infarct. With inferior infarcts , the defect is likely to be in the AV node, with escape rhythms exceeding 40 beats/min and exhibiting a narrow QRS complex. With anterior infarct, the conduction defect is infranodal and the escape rhythm (if present) is usually less ...
Cardiac Checklist (Health Plan)
... a. For pacemaker or Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) requests, include EKG and/or telemetry strips showing bradycardia, EKG showing conduction abnormalities, EP study report, and/or tilt table test report, if applicable. b. For cardiac resynchronization therapy requests, include left ven ...
... a. For pacemaker or Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) requests, include EKG and/or telemetry strips showing bradycardia, EKG showing conduction abnormalities, EP study report, and/or tilt table test report, if applicable. b. For cardiac resynchronization therapy requests, include left ven ...
Electrocardiogram (EKG) - Imperial Cardiac Center
... signal spreads from the top of the heart to the bottom. As it travels, the signal causes the heart to contract and pump blood. The process repeats with each new heartbeat. The heart's electrical signals set the rhythm of the heartbeat. An EKG shows how fast your heart is beating, whether the rhythm ...
... signal spreads from the top of the heart to the bottom. As it travels, the signal causes the heart to contract and pump blood. The process repeats with each new heartbeat. The heart's electrical signals set the rhythm of the heartbeat. An EKG shows how fast your heart is beating, whether the rhythm ...
Boredom at its HEART by Dhravid - Fitz
... A heart attack is like a huge tidal wave in the ocean while a cardiac arrest is like a destructive Tsunami. A heart attack occurs when the heart does not receive sufficient blood because of blockage in the coronary artery. This causes the muscles of the heart (myocardium) to be damaged. Cardiac arr ...
... A heart attack is like a huge tidal wave in the ocean while a cardiac arrest is like a destructive Tsunami. A heart attack occurs when the heart does not receive sufficient blood because of blockage in the coronary artery. This causes the muscles of the heart (myocardium) to be damaged. Cardiac arr ...