Genetic Analysis of Brain Circuits Underlying Pheromone Signaling
... The amenability of chemosensory systems to molecular approaches and genetic manipulations has led recently to a wealth of new information on the neural basis of olfactory detection and sensory processing. The nasal cavity of rodents contains two sets of chemosensory neurons located in the vomeronasa ...
... The amenability of chemosensory systems to molecular approaches and genetic manipulations has led recently to a wealth of new information on the neural basis of olfactory detection and sensory processing. The nasal cavity of rodents contains two sets of chemosensory neurons located in the vomeronasa ...
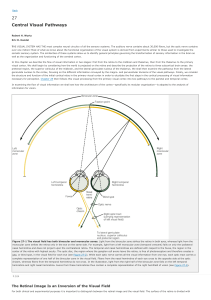
A simulation of parahippocampal and hippocampal structures guiding spatial navigation of
... spike. This could continue to generate spikes, but the persistent spiking must be terminated or it will cause excessive buildup of spiking activity. Therefore a third dual exponential potential with an even slower time course is added to the simulation. This terminates the firing of the neurons afte ...
... spike. This could continue to generate spikes, but the persistent spiking must be terminated or it will cause excessive buildup of spiking activity. Therefore a third dual exponential potential with an even slower time course is added to the simulation. This terminates the firing of the neurons afte ...
Principles of Neural Science - Weizmann Institute of Science
... The superior colliculus is a structure of alternating gray cellular and white (axonal) layers lying on the roof of the midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells project directly to the superficial layers and form a map of the contralateral visual field. Cells in the superficial layers in turn project through ...
... The superior colliculus is a structure of alternating gray cellular and white (axonal) layers lying on the roof of the midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells project directly to the superficial layers and form a map of the contralateral visual field. Cells in the superficial layers in turn project through ...
The neuronal structure of the substantia nigra in the guinea pig
... Triangular neurons (Fig. 3). Their cell bodies measure from 20 to 35 µm. They have 3 primary dendrites which arise conically from a perikaryon. Most of them bifurcate for the first time near the cell body, and the second time at a different distance from a perikaryon. In our material we also observe ...
... Triangular neurons (Fig. 3). Their cell bodies measure from 20 to 35 µm. They have 3 primary dendrites which arise conically from a perikaryon. Most of them bifurcate for the first time near the cell body, and the second time at a different distance from a perikaryon. In our material we also observe ...
Diversity and wiring variability of visual local neurons in the
... the lamina, medulla, lobula, and lobula plate (Morante and Desplan, 2004). Starting with the compound eye, visual signals are transmitted through a twodimensional array of modular longitudinal structures called cartridges in the lamina and columns in the other three neuropils, which retains the spat ...
... the lamina, medulla, lobula, and lobula plate (Morante and Desplan, 2004). Starting with the compound eye, visual signals are transmitted through a twodimensional array of modular longitudinal structures called cartridges in the lamina and columns in the other three neuropils, which retains the spat ...
propofol alters vesicular transport in rat cortical neuronal cultures
... of the picture) immediately after propofol application at time 0, which continues throughout the experiment. Scale bar =10 µm. (B) Time-lapse data of the vesicular velocity obtained from the experiments described above, with data obtained each minute, from time -5 min to time 10 min, where propofol ...
... of the picture) immediately after propofol application at time 0, which continues throughout the experiment. Scale bar =10 µm. (B) Time-lapse data of the vesicular velocity obtained from the experiments described above, with data obtained each minute, from time -5 min to time 10 min, where propofol ...
Olfactory tract transection in neonatal rats: Evidence for Mitral cell
... recordings were carried out in their familiar home cage concurrent with the spontaneous behaviour. After 4-6 days of post surgical recovery, the rats were connected to the 8-channel LFPS Polygraph (Grass Model 78D Polygraph) via a flexible, shielded cable, which did not restrain or cause discomfort ...
... recordings were carried out in their familiar home cage concurrent with the spontaneous behaviour. After 4-6 days of post surgical recovery, the rats were connected to the 8-channel LFPS Polygraph (Grass Model 78D Polygraph) via a flexible, shielded cable, which did not restrain or cause discomfort ...
Histamine reduces firing and bursting of anterior and intralaminar
... rat only very few interneurons have been observed in the thalamic nuclei studied in this work [27]. On the other hand, the reduction of low-threshold bursts and the change to more regular occurring spikes not involved in bursts has been shown to be the result of depolarizing effects that inactivate ...
... rat only very few interneurons have been observed in the thalamic nuclei studied in this work [27]. On the other hand, the reduction of low-threshold bursts and the change to more regular occurring spikes not involved in bursts has been shown to be the result of depolarizing effects that inactivate ...
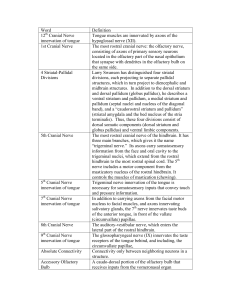
Word Definition 12 Cranial Nerve innervation of
... vascular system (see “Median Eminence”), and also reach multiple structures of the limbic system. Some cells of the nucleus are involved in the regulation of feeding. A region of the caudal hindbrain just rostral to the obex, where specialized ependymal cells are located. The region is one of the ci ...
... vascular system (see “Median Eminence”), and also reach multiple structures of the limbic system. Some cells of the nucleus are involved in the regulation of feeding. A region of the caudal hindbrain just rostral to the obex, where specialized ependymal cells are located. The region is one of the ci ...
Septins promote dendrite and axon development by negatively
... Figure 1 | The core septin subunit SEPT7 is required for the growth of dendrites and axons of cerebrocortical neurons in vivo. (a) Representative immunofluorescence images of primary cerebrocortical neurons at div2 co-expressing GFP with control (left) or shRNA#1 against SEPT7 (right). Endogenous SEP ...
... Figure 1 | The core septin subunit SEPT7 is required for the growth of dendrites and axons of cerebrocortical neurons in vivo. (a) Representative immunofluorescence images of primary cerebrocortical neurons at div2 co-expressing GFP with control (left) or shRNA#1 against SEPT7 (right). Endogenous SEP ...
Glia–Neuron Interactions in Nervous System Function
... the central nervous system (CNS) generally fall into three categories: oligodendrocytes, which myelinate CNS axons; astrocytes, which extend many processes that contact both blood vessels and neurons; and microglia, cells thought to be of mesodermal origin that are hypothesized to function in an imm ...
... the central nervous system (CNS) generally fall into three categories: oligodendrocytes, which myelinate CNS axons; astrocytes, which extend many processes that contact both blood vessels and neurons; and microglia, cells thought to be of mesodermal origin that are hypothesized to function in an imm ...
Cover page
... received relatively little attention in the modern era. Although often overlooked, the LS is likely to play critical roles in human affective disorders as it is robustly activated by stressful stimuli and required for persistent behavioral responses to stress (e.g. increased anxiety). However, the L ...
... received relatively little attention in the modern era. Although often overlooked, the LS is likely to play critical roles in human affective disorders as it is robustly activated by stressful stimuli and required for persistent behavioral responses to stress (e.g. increased anxiety). However, the L ...
Can regenerating axons recapitulate developmental
... Oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein (OMgp). OMgp was identified as a MAI in 2002 (REF.127). It is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked protein. Genetic studies are in progress. Nogo-66 Receptor (NgR). NgR was identified in 2001 (REF. 117). It is a GPI-linked protein that was also found to be ...
... Oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein (OMgp). OMgp was identified as a MAI in 2002 (REF.127). It is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked protein. Genetic studies are in progress. Nogo-66 Receptor (NgR). NgR was identified in 2001 (REF. 117). It is a GPI-linked protein that was also found to be ...
Anatomical origins of the classical receptive field and modulatory
... response.Fit, direct thalamic input can determine the size of the initial activating RF at high contrast. Second lateral connections can enlarge the RF at low contrast by pooling information from larger regions of cortex that are otherwise ineft%ctive when high contrast thalamic inpnt is driving the ...
... response.Fit, direct thalamic input can determine the size of the initial activating RF at high contrast. Second lateral connections can enlarge the RF at low contrast by pooling information from larger regions of cortex that are otherwise ineft%ctive when high contrast thalamic inpnt is driving the ...
Volitional enhancement of firing synchrony and oscillation
... waiting periods, the single neuron was considered an operantly conditioned neuron. The firing rates of conditioned neurons increased instantaneously after a trial onset and the bottle entered the drinking zone within a very short time. The time-to-reward for the conditioned neurons soon decreased an ...
... waiting periods, the single neuron was considered an operantly conditioned neuron. The firing rates of conditioned neurons increased instantaneously after a trial onset and the bottle entered the drinking zone within a very short time. The time-to-reward for the conditioned neurons soon decreased an ...
Original Article Female Rat Hippocampal Cell
... The present study demonstrates that CPP is able to affect the hippocampal cell density. The number of neurons decreased and that of astrocytes increased after CPP. In our previous study we showed that the number of astrocytes increases after CPP in male Wistar rats (Shaabani et al., 2011) and in the ...
... The present study demonstrates that CPP is able to affect the hippocampal cell density. The number of neurons decreased and that of astrocytes increased after CPP. In our previous study we showed that the number of astrocytes increases after CPP in male Wistar rats (Shaabani et al., 2011) and in the ...
CNS Distribution of Members of the Two-Pore
... resting K ⫹ currents in neurons. They are major targets for endogenous modulators, as well as for clinically important compounds such as volatile anesthetics. In the current study, we report on the CNS distribution in the rat and mouse of mRNA encoding seven two-pore-domain K ⫹ channel family member ...
... resting K ⫹ currents in neurons. They are major targets for endogenous modulators, as well as for clinically important compounds such as volatile anesthetics. In the current study, we report on the CNS distribution in the rat and mouse of mRNA encoding seven two-pore-domain K ⫹ channel family member ...
Distribution, classification, and development of Drosophila glial cells
... adults) such as the housefly (Sohal et al. 1972; Strausfeld 1976), locust (Hoyle 1986), and moth (Cantera 1993). In this study, we describe the number, distribution and morphology of Drosophila glial cells in more detail by observing GAL4 enhancer-trap strains that label certain subsets of CNS cells ...
... adults) such as the housefly (Sohal et al. 1972; Strausfeld 1976), locust (Hoyle 1986), and moth (Cantera 1993). In this study, we describe the number, distribution and morphology of Drosophila glial cells in more detail by observing GAL4 enhancer-trap strains that label certain subsets of CNS cells ...
Brain stem representation of thermal and psychogenic sweating in
... responses with fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography during whole body warming and cooling. These workers identified a small midline region of the posterior cingulate cortex whose metabolic activity was inversely related to sweat rate, but found no cerebral areas with a positive correlatio ...
... responses with fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography during whole body warming and cooling. These workers identified a small midline region of the posterior cingulate cortex whose metabolic activity was inversely related to sweat rate, but found no cerebral areas with a positive correlatio ...
Amyloid Precursor Protein in Cortical Neurons: Coexistence of Two
... Sisodia, 1992). In the brain, all of these processesmay act to different degreesto produce PA4 amyloid deposits. However, the specific cells in which APP metabolism is disrupted are unknown. One likely possibility are the neurons that contain considerableAPP immunoreactivity in the vicinity of amylo ...
... Sisodia, 1992). In the brain, all of these processesmay act to different degreesto produce PA4 amyloid deposits. However, the specific cells in which APP metabolism is disrupted are unknown. One likely possibility are the neurons that contain considerableAPP immunoreactivity in the vicinity of amylo ...
Early Progenitor Cell Marker Expression Distinguishes Type II From
... IIA) and/or balloon cells (BCs; type IIB) (2, 4). The histopathologic differences between type I and type II FCDs suggest that there are distinct mechanistic differences that lead to their formation, but the molecular pathogenesis of sporadic type I and type II FCDs has not been fully elucidated. Un ...
... IIA) and/or balloon cells (BCs; type IIB) (2, 4). The histopathologic differences between type I and type II FCDs suggest that there are distinct mechanistic differences that lead to their formation, but the molecular pathogenesis of sporadic type I and type II FCDs has not been fully elucidated. Un ...
Ethanol Neurotoxicity in the Developing Cerebellum
... regulated by various factors which include genes involved in cell cycle regulation, receptors (e.g., the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and the retinoic acid receptors), and nerve growth factors such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-I), and basic ...
... regulated by various factors which include genes involved in cell cycle regulation, receptors (e.g., the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and the retinoic acid receptors), and nerve growth factors such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-I), and basic ...
Cation-Chloride Cotransporters and Neuronal Function
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
Neuronal Control of Mucus Secretion by Leeches: Toward a General
... more quantitative study of this effect, equalsized deganglionated sections of body wall (lateral halves, three segments long) were The mammalian gastro-intestinal tract each bathed in high Mg2+ saline to which different amounts of 5-HT had been added. The abundant serotonin of the gastroAfter 45 min ...
... more quantitative study of this effect, equalsized deganglionated sections of body wall (lateral halves, three segments long) were The mammalian gastro-intestinal tract each bathed in high Mg2+ saline to which different amounts of 5-HT had been added. The abundant serotonin of the gastroAfter 45 min ...
The occipitoparietal pathway of the macaque monkey: comparison
... V1 to the parietal and temporal lobes. Indeed, in a recent study of marmoset monkey visual cortex (Elston et al., 1996), we found a progressive increase in the dendritic field area of layer III pyramidal cells between V1, V2, the dorsolateral area (DL) and the fundus of the superior temporal area (F ...
... V1 to the parietal and temporal lobes. Indeed, in a recent study of marmoset monkey visual cortex (Elston et al., 1996), we found a progressive increase in the dendritic field area of layer III pyramidal cells between V1, V2, the dorsolateral area (DL) and the fundus of the superior temporal area (F ...
Subventricular zone

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a paired brain structure situated throughout the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles. It is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density, as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has been found to occur in the adult mammalian brain.