Topic Definition 3` Refers to the third carbon of the nucleic acid
... A frame is a single series of adjacent nucleotide triplets in DNA or RNA: one frame would have bases at positions 1, 4, 7, etc. as the first base of sequential codons. There are 3 possible reading frames in an mRNA strand and six in a double stranded DNA molecule due to the two strands from which tr ...
... A frame is a single series of adjacent nucleotide triplets in DNA or RNA: one frame would have bases at positions 1, 4, 7, etc. as the first base of sequential codons. There are 3 possible reading frames in an mRNA strand and six in a double stranded DNA molecule due to the two strands from which tr ...
Epigenetic Clock and Biological Age Steve Horvath, Professor of
... Epigenetic Clock and Biological Age Steve Horvath, Professor of Human Genetics and Biostatistics, University of California, Los Angeles The DNA methylation based biomarker of aging known as the "epigenetic clock" can be used to measure the DNA methylation (DNAm) age of any human (or chimpanzee) tiss ...
... Epigenetic Clock and Biological Age Steve Horvath, Professor of Human Genetics and Biostatistics, University of California, Los Angeles The DNA methylation based biomarker of aging known as the "epigenetic clock" can be used to measure the DNA methylation (DNAm) age of any human (or chimpanzee) tiss ...
Genetics
... Antisense DNA; strand of DNA that carries the information necessary to make proteins by binding to the corresponding messenger RNA . Although these are MIRROR IMAGES, only the antisense strand contains the information for making proteins Antisense strand is known as noncoding DNA ...
... Antisense DNA; strand of DNA that carries the information necessary to make proteins by binding to the corresponding messenger RNA . Although these are MIRROR IMAGES, only the antisense strand contains the information for making proteins Antisense strand is known as noncoding DNA ...
Topic Definition 3` Refers to the third carbon of the nucleic acid
... A frame is a single series of adjacent nucleotide triplets in DNA or RNA: one frame would have bases at positions 1, 4, 7, etc. as the first base of sequential codons. There are 3 possible reading frames in an mRNA strand and six in a double stranded DNA molecule due to the two strands from which tr ...
... A frame is a single series of adjacent nucleotide triplets in DNA or RNA: one frame would have bases at positions 1, 4, 7, etc. as the first base of sequential codons. There are 3 possible reading frames in an mRNA strand and six in a double stranded DNA molecule due to the two strands from which tr ...
cis667-1 - Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
... • Chain have an amino group at one end and a carboxy group at the other giving the chain an orientation (start - end) • The sequence of residues in the chain is called the protein’s primary structure ...
... • Chain have an amino group at one end and a carboxy group at the other giving the chain an orientation (start - end) • The sequence of residues in the chain is called the protein’s primary structure ...
Whole Genome Scale DNA Methylation Differences in
... We have established a protocol for thymocyte and stromal cell isolation and good quality DNA and RNA from these paired samples from the same individual. In addition, fresh thymic tissue was mounted in preservative blocks and frozen for later use in microscopy studies and for nPOD collection. Summary ...
... We have established a protocol for thymocyte and stromal cell isolation and good quality DNA and RNA from these paired samples from the same individual. In addition, fresh thymic tissue was mounted in preservative blocks and frozen for later use in microscopy studies and for nPOD collection. Summary ...
Extraction of RNA File
... strands of DNA by some enzymes in order to transcription the genetic material from DNA to RNA and used the one strand of DNA as a template creating the m RNA strand by help of RNA polymerase after thtat the mRNA will be leaving the nucleus to cytoplasm where Ribosomes found. 5) The second step inclu ...
... strands of DNA by some enzymes in order to transcription the genetic material from DNA to RNA and used the one strand of DNA as a template creating the m RNA strand by help of RNA polymerase after thtat the mRNA will be leaving the nucleus to cytoplasm where Ribosomes found. 5) The second step inclu ...
PotuS!977m - BioMedSearch
... Stratagene Cloning Systems, 11099 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA Submitted October 9, 1989 ...
... Stratagene Cloning Systems, 11099 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA Submitted October 9, 1989 ...
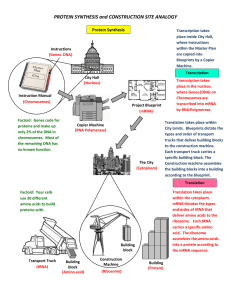
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
... Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truck carries a specific building block. The Construction machine a ...
Chap 3
... • These enzymes cleave at a particular DNA sequence, typically 4 or 6 nucleotides long. • Smith, Kelly and Wilcox (1970) isolate the first enzyme HindII, for which they share the Nobel Prize in 1978. ...
... • These enzymes cleave at a particular DNA sequence, typically 4 or 6 nucleotides long. • Smith, Kelly and Wilcox (1970) isolate the first enzyme HindII, for which they share the Nobel Prize in 1978. ...
The DNA Connection
... • Proteins are made of amino acids – A group of 3 base pairs codes for a specific amino acid • Ex. CGT = alanine (an amino acid) • The order of the 3 base code units determines the order of the amino acids and makes the different ...
... • Proteins are made of amino acids – A group of 3 base pairs codes for a specific amino acid • Ex. CGT = alanine (an amino acid) • The order of the 3 base code units determines the order of the amino acids and makes the different ...
DNA Transcription & Translation
... 2. RNA is generally single-stranded 3. RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. ...
... 2. RNA is generally single-stranded 3. RNA contains uracil in place of thymine. ...
APC004 DNA Quantification/Nanodrop
... Add Your DNA sample to the Nanodrop and click Measure. A measurement will appear. If the sample is very high in concentration it is advisable to dilute it 1:5 or 1:10 as Genomic DNA can be very viscous and may yield in incorrect readings. ...
... Add Your DNA sample to the Nanodrop and click Measure. A measurement will appear. If the sample is very high in concentration it is advisable to dilute it 1:5 or 1:10 as Genomic DNA can be very viscous and may yield in incorrect readings. ...
DNA as Genetic Material
... Helicase enzyme breaks hydrogen bond between base pairs Opens up DNA for replication enzymes to have access ...
... Helicase enzyme breaks hydrogen bond between base pairs Opens up DNA for replication enzymes to have access ...
Compendium 11 Learning Outcomes • Describe the structure and
... • Define the components of a nucleotide • Differentiate between the nucleotide bases of DNA and RNA • Explain what the genetic code is and what it is coding for • Describe the two-step process (transcription & translation) that results in gene expression • Explain the role of DNA, rRNA, tRNA and mRN ...
... • Define the components of a nucleotide • Differentiate between the nucleotide bases of DNA and RNA • Explain what the genetic code is and what it is coding for • Describe the two-step process (transcription & translation) that results in gene expression • Explain the role of DNA, rRNA, tRNA and mRN ...
3rd of 7 Review Packets
... If in ER then: polypeptide is released into ER, then to Golgi complex, vesicle to cell membrane, then exocytosis (may be given signals for exit/destination) Free ribosomes typically make products for the cell and are not exported ...
... If in ER then: polypeptide is released into ER, then to Golgi complex, vesicle to cell membrane, then exocytosis (may be given signals for exit/destination) Free ribosomes typically make products for the cell and are not exported ...
Unit 4 Review Sheet - Answers
... - What is a mutation? A change in the DNA sequence. - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide is deleted)? Deletion, insertion. - Do all mutations result in a faulty protein? Why or why not? No, because if you make mRNA that codes for same amino acids, you will end up with the sa ...
... - What is a mutation? A change in the DNA sequence. - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide is deleted)? Deletion, insertion. - Do all mutations result in a faulty protein? Why or why not? No, because if you make mRNA that codes for same amino acids, you will end up with the sa ...
Study Guide Genetic Systems 2015 File
... I can describe the process of transcription and translation o Tutorial: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h3b9ArupXZg o Resources: Transcription and translation Notes I can identify the base pair sequence of a complimentary strand of RNA if given the template strand I can use a chart to identify which ...
... I can describe the process of transcription and translation o Tutorial: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h3b9ArupXZg o Resources: Transcription and translation Notes I can identify the base pair sequence of a complimentary strand of RNA if given the template strand I can use a chart to identify which ...
Transcription and Translation Eukaryotic Cell
... Amino Acid- Organic molecule possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Serve as monomers of proteins. mRNA- is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides, each of which contains a nitrogenous base, a sugar and a phosphate group. Messenger RNA contains genetic information. It carries genetic informati ...
... Amino Acid- Organic molecule possessing both carboxyl and amino groups. Serve as monomers of proteins. mRNA- is a single-stranded polymer of nucleotides, each of which contains a nitrogenous base, a sugar and a phosphate group. Messenger RNA contains genetic information. It carries genetic informati ...
Study Guide MBMB 451A Fall 2002
... 7. What is an enhancer? What is a response element? 8. Describe two models for how an enhancer could effect the level of transcription. 9. What are the transcription factors called that are used by Pol I and Pol III? 10. Discuss how transcription activity can be regulated by protein phosphorylation ...
... 7. What is an enhancer? What is a response element? 8. Describe two models for how an enhancer could effect the level of transcription. 9. What are the transcription factors called that are used by Pol I and Pol III? 10. Discuss how transcription activity can be regulated by protein phosphorylation ...
Glossary
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) :【伝令 RNA】Protein-coding RNA that encodes and carries information from DNA to sites of protein synthesis to undergo translation. The mRNA bears the 5´ m7G cap structure (a specially altered nucleotide) and the 3´ poly(A) tail (a long sequence of adenine nucleotides), both of whic ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) :【伝令 RNA】Protein-coding RNA that encodes and carries information from DNA to sites of protein synthesis to undergo translation. The mRNA bears the 5´ m7G cap structure (a specially altered nucleotide) and the 3´ poly(A) tail (a long sequence of adenine nucleotides), both of whic ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.