Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the
... eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fragments, whether digested with Sad, Aval, BamHI, Xbal, Hindm, Sail, PstI or PvuII (Figure 1). Thus it is proba ...
... eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fragments, whether digested with Sad, Aval, BamHI, Xbal, Hindm, Sail, PstI or PvuII (Figure 1). Thus it is proba ...
Answer Key 2016 Spring Biology (General) Exam #2
... E) Enzyme that unwinds and opens up the DNA helix. II Definition. Please define each term in one or two sentence. Drawings would also help. (3 points each) 1. semiconservative replication the method used to replicate DNA in which the double-stranded molecule is separated and each strand acts as a te ...
... E) Enzyme that unwinds and opens up the DNA helix. II Definition. Please define each term in one or two sentence. Drawings would also help. (3 points each) 1. semiconservative replication the method used to replicate DNA in which the double-stranded molecule is separated and each strand acts as a te ...
Plant RNA/DNA Purification Kit
... and DNA simultaneously from a single sample of plants. The total RNA and DNA (including genomic DNA) and are both column purified in under 30 minutes using a single column. It is often necessary to isolate total RNA and genomic DNA from a single plant sample, such as for studies of gene expression, ...
... and DNA simultaneously from a single sample of plants. The total RNA and DNA (including genomic DNA) and are both column purified in under 30 minutes using a single column. It is often necessary to isolate total RNA and genomic DNA from a single plant sample, such as for studies of gene expression, ...
Genetic engineering
... Started with Douglas Prasher (1987) Prasher wanted to find a specific gene in a jellyfish that codes for a molecule called green fluorescent protein, or GFP • GFP is a natural protein that absorbs energy from light and makes parts of the jellyfish glow ...
... Started with Douglas Prasher (1987) Prasher wanted to find a specific gene in a jellyfish that codes for a molecule called green fluorescent protein, or GFP • GFP is a natural protein that absorbs energy from light and makes parts of the jellyfish glow ...
jan4
... Activities within the cell performed by proteins - Twenty kinds of subunits (amino acids) ...
... Activities within the cell performed by proteins - Twenty kinds of subunits (amino acids) ...
Ch 8 Genetic Technology and Diagnostics
... •Sensitive enough to detect cancer from a single cell or diagnose an infection from a single gene copy •Rapid enough to replicate target DNA from a few copies to billions of copies in a few hours ...
... •Sensitive enough to detect cancer from a single cell or diagnose an infection from a single gene copy •Rapid enough to replicate target DNA from a few copies to billions of copies in a few hours ...
Mutations - nimitz163
... Mutations in body cells • What happens if powerful radiation, such as gamma radiation, hits the DNA of a nonreproductive cell, a cell of the body such as in skin, muscle, or bone? • If the cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not be passed on to offspring. • However, the mutation may cause pro ...
... Mutations in body cells • What happens if powerful radiation, such as gamma radiation, hits the DNA of a nonreproductive cell, a cell of the body such as in skin, muscle, or bone? • If the cell’s DNA is changed, this mutation would not be passed on to offspring. • However, the mutation may cause pro ...
The Genetic Code - Marengo Community Middle School
... molecular meaning • Universal: same code used by all organisms on earth • Triplet: 3 bases = one “word” • Unambiguous: each triplet has only one meaning • Degenerate: individual amino acids may be called for by more than one triplet (this is also referred to as redundant) ...
... molecular meaning • Universal: same code used by all organisms on earth • Triplet: 3 bases = one “word” • Unambiguous: each triplet has only one meaning • Degenerate: individual amino acids may be called for by more than one triplet (this is also referred to as redundant) ...
71370_Forensic_DNA_Analysis
... that cuts DNA at specific base pair sequences DNA loaded into gel, attracted to positive end due to negative charge DNA strands separate based on size (restriction fragment length) Labeled radioactively or with dye, compared to known standard for analysis ...
... that cuts DNA at specific base pair sequences DNA loaded into gel, attracted to positive end due to negative charge DNA strands separate based on size (restriction fragment length) Labeled radioactively or with dye, compared to known standard for analysis ...
File
... • DNA unzips, exposing the strand that will code for the message • Free-floating nucleotides match up with the appropriate exposed base creating a strand of mRNA – what protein do you think brings the mRNA nucleotides to DNA? ...
... • DNA unzips, exposing the strand that will code for the message • Free-floating nucleotides match up with the appropriate exposed base creating a strand of mRNA – what protein do you think brings the mRNA nucleotides to DNA? ...
Topic 1: Cell biology (15 hours)
... within the cell. binding sites are expected as well as their roles. 6. Bound ribosomes synthesize proteins primarily for secretion or for use in lysosomes. 7. Translation can occur immediately after transcription in prokaryotes due to the absence of a nuclear membrane. 8. The sequence and number of ...
... within the cell. binding sites are expected as well as their roles. 6. Bound ribosomes synthesize proteins primarily for secretion or for use in lysosomes. 7. Translation can occur immediately after transcription in prokaryotes due to the absence of a nuclear membrane. 8. The sequence and number of ...
5-16
... • RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is another molecule that helps to make proteins. RNA serves as a copy of DNA outside the nucleus. • RNA copies of DNA genes are made, then sent to the cytoplasm to code for proteins. • RNA is very much like DNA, except it has the base uracil (U) instead of ...
... • RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is another molecule that helps to make proteins. RNA serves as a copy of DNA outside the nucleus. • RNA copies of DNA genes are made, then sent to the cytoplasm to code for proteins. • RNA is very much like DNA, except it has the base uracil (U) instead of ...
C16 DNA
... Origins of replication – special sites where the two parental strands of DNA separate to form “bubbles”. In eukaryotes there are 100’s – 1000’s of origin sites along the giant DNA molecule of each chromosome. In bacteria, there is only 1 origin of replication. Replication fork – found at each end of ...
... Origins of replication – special sites where the two parental strands of DNA separate to form “bubbles”. In eukaryotes there are 100’s – 1000’s of origin sites along the giant DNA molecule of each chromosome. In bacteria, there is only 1 origin of replication. Replication fork – found at each end of ...
An in vitro RNA synthesis reaction was set up and allowed to
... c. When DNA ligase is inhibited, it differentially affects the synthesis from the leading and the lagging strands. Explain which strand (leading or lagging) is more affected by the lack of DNA ligase and why. d. The next nucleotide to be added to a growing DNA strand is dCTP (shown). i. Circle the p ...
... c. When DNA ligase is inhibited, it differentially affects the synthesis from the leading and the lagging strands. Explain which strand (leading or lagging) is more affected by the lack of DNA ligase and why. d. The next nucleotide to be added to a growing DNA strand is dCTP (shown). i. Circle the p ...
Molecular Biochemistry (Bioc432) student part 2
... •DNA replication occurs when the complementary strands of DNA break apart and unwind. •This is accomplished with the help of enzymes called helicases. •Each half will then be the template for a new, complementary strand. •Because the newly unwound single strands have a tendency to rejoin, another gr ...
... •DNA replication occurs when the complementary strands of DNA break apart and unwind. •This is accomplished with the help of enzymes called helicases. •Each half will then be the template for a new, complementary strand. •Because the newly unwound single strands have a tendency to rejoin, another gr ...
Gene Expression - Phillips Scientific Methods
... 1. Write out the sequence of BOTH products of replication. What do you notice about these products? ...
... 1. Write out the sequence of BOTH products of replication. What do you notice about these products? ...
Y12 Biology Year 1 AS LOs Student Teacher 1
... The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes, is the same. The arrangement and any movement of phospholipids, proteins, glycoproteins and glycolipids in the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure. Cholesterol ...
... The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes, is the same. The arrangement and any movement of phospholipids, proteins, glycoproteins and glycolipids in the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure. Cholesterol ...
Document
... Plasmids carrying cloned eukaryotic genes can be introduced into animal cells grown in culture by transfection. In transient transfection (Fig. 5.32a), the introduced plasmid contains a viral replication origin, which allows it to propagate for a short time until diluted out in the cells due to inef ...
... Plasmids carrying cloned eukaryotic genes can be introduced into animal cells grown in culture by transfection. In transient transfection (Fig. 5.32a), the introduced plasmid contains a viral replication origin, which allows it to propagate for a short time until diluted out in the cells due to inef ...
Document
... Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein (RNP). The enzyme contains RNA and proteins. The RNA templates DNA synthesis. The proteins include the telomerase reverse transcriptase TERT. ...
... Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein (RNP). The enzyme contains RNA and proteins. The RNA templates DNA synthesis. The proteins include the telomerase reverse transcriptase TERT. ...
Honors Biology Module 7 Cellular Reproduction
... A strand of mRNA can be thought of as a bunch of three-nucleotide sequence. Each threenucleotide base sequence is called a codon. A strand of tRNA contains a three-nucleotide base seque4nce called an anticodon. A certain anticodon on tRNA results in an certan amino acid boded to the tRNA. Since the ...
... A strand of mRNA can be thought of as a bunch of three-nucleotide sequence. Each threenucleotide base sequence is called a codon. A strand of tRNA contains a three-nucleotide base seque4nce called an anticodon. A certain anticodon on tRNA results in an certan amino acid boded to the tRNA. Since the ...
TOPIC: Applied Genetics AIM: What methods can be used to
... DNA from complex organism is cut and placed into the DNA of a simple organism Simple cells with recombinant DNA can ...
... DNA from complex organism is cut and placed into the DNA of a simple organism Simple cells with recombinant DNA can ...
problem set
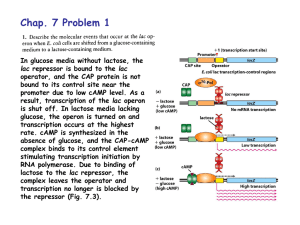
... bound to its control site near the promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex ...
... bound to its control site near the promoter due to low cAMP level. As a result, transcription of the lac operon is shut off. In lactose media lacking glucose, the operon is turned on and transcription occurs at the highest rate. cAMP is synthesized in the absence of glucose, and the CAP-cAMP complex ...
Identification of fertility genes required for microgametogenesis in
... The process of microgametogenesis occurs within the developing pollen. It depends on two rounds of meiosis of microspore, and sporophitic functions provided by the surrounding anther tissues. Employing our rice T-DNA insertional mutant library, we identified three mutants exhibit a phenotype of comp ...
... The process of microgametogenesis occurs within the developing pollen. It depends on two rounds of meiosis of microspore, and sporophitic functions provided by the surrounding anther tissues. Employing our rice T-DNA insertional mutant library, we identified three mutants exhibit a phenotype of comp ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.