Overview of Transcription
... transcription, since RNA polymerase can't resume synthesis of an incompletely transcribed gene, and must be assured of remaining bound for 104-105 reaction cycles. The hybrid DNA-RNA is only 8-9 nt long. ...
... transcription, since RNA polymerase can't resume synthesis of an incompletely transcribed gene, and must be assured of remaining bound for 104-105 reaction cycles. The hybrid DNA-RNA is only 8-9 nt long. ...
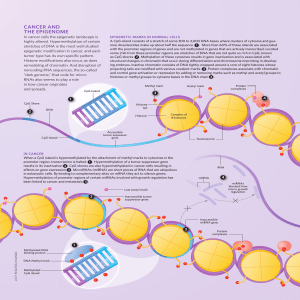
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... In cancer cells the epigenetic landscape is highly altered. Hypermethylation of certain stretches of DNA is the most well-studied epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of ...
... In cancer cells the epigenetic landscape is highly altered. Hypermethylation of certain stretches of DNA is the most well-studied epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of ...
Lecture 3 - Computing for Bioinformatics I
... same libraries and the same sets of books. • Books represent all the information (DNA) that every cell in the body needs so it can grow and carry out its various functions. ...
... same libraries and the same sets of books. • Books represent all the information (DNA) that every cell in the body needs so it can grow and carry out its various functions. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
... Webbing of fingers of human embryo, production of mature xylem, loss of tadpole tails Human fibroblasts in cell culture stop reproducing and degenerate and die after 50 divisions other cell types have different number Aging may be accumulation of mutations and other problems resulting in functional ...
... Webbing of fingers of human embryo, production of mature xylem, loss of tadpole tails Human fibroblasts in cell culture stop reproducing and degenerate and die after 50 divisions other cell types have different number Aging may be accumulation of mutations and other problems resulting in functional ...
Topic 4: Genetics (15 hours)
... Predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring of monohybrid crosses involving any of the above patterns of ...
... Predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of offspring of monohybrid crosses involving any of the above patterns of ...
Answers to Exam Practice Questions 1. Mitosis produces two
... through a secretory vesicle with then goes to the cell membrane to be released. ...
... through a secretory vesicle with then goes to the cell membrane to be released. ...
Nervous System
... It has a beginning (the “promoter”) and an end (the “termination signal”). A gene holds the information (“recipe”) for making a specific polypeptide (protein). ...
... It has a beginning (the “promoter”) and an end (the “termination signal”). A gene holds the information (“recipe”) for making a specific polypeptide (protein). ...
evolution model - EmperorPenguinsGoneWild
... individuals within a population are extremely similar, however DNA varies slightly between each individual ...
... individuals within a population are extremely similar, however DNA varies slightly between each individual ...
PartThreeAnswers.doc
... One of the key signals for cleavage and 3' polyadenylation is the sequence AAUAAA. After RNA polymerase II has transcribed beyond this sequence, an endonuclease (uncharacterized at this time) cleaves the primary transcript at a position about 25 to 30 nucleotides 3' to the AAUAAA. Then the enzyme po ...
... One of the key signals for cleavage and 3' polyadenylation is the sequence AAUAAA. After RNA polymerase II has transcribed beyond this sequence, an endonuclease (uncharacterized at this time) cleaves the primary transcript at a position about 25 to 30 nucleotides 3' to the AAUAAA. Then the enzyme po ...
dna ppt
... • He is guilty • Suspect might be guilty, but more evidence is needed • Swab is from the wrong victim • The suspect must be excluded as a source of the DNA in the evidence • NONE of the above ...
... • He is guilty • Suspect might be guilty, but more evidence is needed • Swab is from the wrong victim • The suspect must be excluded as a source of the DNA in the evidence • NONE of the above ...
Organic Molecules
... • The starch found in whole grains and vegetables is a complex carbohydrate made of chains of simpler glucose molecules. • Our body contains enzymes which breaks down carbohydrates in the food you eat into glucose, which your cells can use as energy. ...
... • The starch found in whole grains and vegetables is a complex carbohydrate made of chains of simpler glucose molecules. • Our body contains enzymes which breaks down carbohydrates in the food you eat into glucose, which your cells can use as energy. ...
Chapter 16
... Part of the DNA of the Ti plasmid is transferred to the plant cell nucleus. The vir genes of the Ti plasmid are located outside the transferred region and are required for the transfer process. The vir genes are induced by phenolic compounds released by plants in response to wounding. The membrane p ...
... Part of the DNA of the Ti plasmid is transferred to the plant cell nucleus. The vir genes of the Ti plasmid are located outside the transferred region and are required for the transfer process. The vir genes are induced by phenolic compounds released by plants in response to wounding. The membrane p ...
DNA: the Molecule of Heredity
... • Positions Available in the genetics industry. Hundreds of entrylevel openings for tireless workers. No previous experience necessary. Must be able to transcribe code in a nuclear environment. The ability to work in close association with ribosomes is a must. • Accuracy and Speed vital for this job ...
... • Positions Available in the genetics industry. Hundreds of entrylevel openings for tireless workers. No previous experience necessary. Must be able to transcribe code in a nuclear environment. The ability to work in close association with ribosomes is a must. • Accuracy and Speed vital for this job ...
The Genetics of Microorganisms
... • The master code of DNA is used to synthesize an RNA molecule (transcription) • The information in the RNA is used to produce proteins (translation) • Exceptions: RNA viruses and retroviruses ...
... • The master code of DNA is used to synthesize an RNA molecule (transcription) • The information in the RNA is used to produce proteins (translation) • Exceptions: RNA viruses and retroviruses ...
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
... for a specific reaction Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions ...
... for a specific reaction Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions ...
Protein Synthesis
... language of DNA into the language of amino acids. In other words, mRNA which now contains the critical information for making a protein, is a ‘blueprint’ for synthesizing the correct amino acids on the ribosomes. The process begins with the newly synthesized mRNA leaving the nucleus through the nucl ...
... language of DNA into the language of amino acids. In other words, mRNA which now contains the critical information for making a protein, is a ‘blueprint’ for synthesizing the correct amino acids on the ribosomes. The process begins with the newly synthesized mRNA leaving the nucleus through the nucl ...
Ch 20 Reading Guide - Dublin City Schools
... 3. Explain the rationale for including a gene for antibiotic resistance and a gene that codes for a hydrolytic enzyme in the plasmid. 4. Describe the role of an expression vector. 5. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. ...
... 3. Explain the rationale for including a gene for antibiotic resistance and a gene that codes for a hydrolytic enzyme in the plasmid. 4. Describe the role of an expression vector. 5. Describe two advantages of using yeast cells instead of bacteria as hosts for cloning or expressing eukaryotic genes. ...
STUDY GUIDE for Dr. Mohnen`s part of Exam #3
... Histone acetyltransferases (HATS) acetylate histones; this reduces affinity of histones for DNA and generates docking site for transcription factors that have Bromodomains (domains that bind to acetylated histones and acetyllysine) Bromodomains are present in chromatin-remodeling machines (ATP-power ...
... Histone acetyltransferases (HATS) acetylate histones; this reduces affinity of histones for DNA and generates docking site for transcription factors that have Bromodomains (domains that bind to acetylated histones and acetyllysine) Bromodomains are present in chromatin-remodeling machines (ATP-power ...
Mitosis, Meiosis, DNA Notes
... out by RNA. A. Translation – process of forming proteins from mRNA. 1. mRNA leaves nucleus (nuclear pores) and goes to ribosomes. 2. mRNA is grouped into 3 consecutive bases called codons. a) Each codon corresponds with a certain amino acid. ...
... out by RNA. A. Translation – process of forming proteins from mRNA. 1. mRNA leaves nucleus (nuclear pores) and goes to ribosomes. 2. mRNA is grouped into 3 consecutive bases called codons. a) Each codon corresponds with a certain amino acid. ...
Review 16-27 - Madeira City Schools
... nucleotide is added ◦ other proteins do this as well (they continually monitor) ...
... nucleotide is added ◦ other proteins do this as well (they continually monitor) ...
Chapter 16 - drtracey.net
... clones with DNA fragment of interest identified from clone library preliminary screening - eliminate any clones without a vector and clones with vectors that do not contain DNA employ vector with gene for antibiotic resistance and lac Z’ gene expose to growth medium ...
... clones with DNA fragment of interest identified from clone library preliminary screening - eliminate any clones without a vector and clones with vectors that do not contain DNA employ vector with gene for antibiotic resistance and lac Z’ gene expose to growth medium ...
First week lectures
... enzymatic (machine-like) activity – Can be dangerous for the data to process itself! ...
... enzymatic (machine-like) activity – Can be dangerous for the data to process itself! ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.