Document
... • Luria-Bertani (LB) broth • Medium that contains nutrients for bacterial growth and gene expression ...
... • Luria-Bertani (LB) broth • Medium that contains nutrients for bacterial growth and gene expression ...
limited warranty
... µl of appropriate growth medium containing serum and antibiotics on the day before transfection. Incubate the cells at 37 °C and 5% CO2. The plate should be 60~80% confluent on the day of transfection. One hour before transfection, the serum-containing medium is replaced with 360 µl Opti-Medium (In ...
... µl of appropriate growth medium containing serum and antibiotics on the day before transfection. Incubate the cells at 37 °C and 5% CO2. The plate should be 60~80% confluent on the day of transfection. One hour before transfection, the serum-containing medium is replaced with 360 µl Opti-Medium (In ...
Genetic Control of Metabolism
... • New strains are also produced by bacteria taking up DNA fragments from their environment. • Scientists try to produce new strains of useful bacteria by culturing existing strains together in conditions where horizontal transfer of DNA is most likely to occur. ...
... • New strains are also produced by bacteria taking up DNA fragments from their environment. • Scientists try to produce new strains of useful bacteria by culturing existing strains together in conditions where horizontal transfer of DNA is most likely to occur. ...
Objective Questions
... 11) Which of the following proteins are not coded for by genes carried on plasmids? A) Enzymes necessary for conjugation B) Enzymes that catabolize hydrocarbons C) Bacteriocins D) Enzymes that inactivate antibiotics E) None of the above 12) Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a donor to a rec ...
... 11) Which of the following proteins are not coded for by genes carried on plasmids? A) Enzymes necessary for conjugation B) Enzymes that catabolize hydrocarbons C) Bacteriocins D) Enzymes that inactivate antibiotics E) None of the above 12) Transformation is the transfer of DNA from a donor to a rec ...
Cloning and functional analysis of
... detected with the DIG Nucleic Acid Detection Kit and NBT/BCIP solution (Roche) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Consequently, three positive clones (c594A, c594B, and c594C) were obtained and the corresponding cosmids were extracted using a standard protocol. Southern hybridization with the ...
... detected with the DIG Nucleic Acid Detection Kit and NBT/BCIP solution (Roche) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Consequently, three positive clones (c594A, c594B, and c594C) were obtained and the corresponding cosmids were extracted using a standard protocol. Southern hybridization with the ...
Chapter 9 answers
... Your friend Gorinda wants to know if there are ever mutations that don’t cause problems. What do you tell him? Certainly. If a mutation is in a place that is not actually read to make an amino acid chain, then it may not cause any change at all. If the mutation falls at the end of a codon, it may st ...
... Your friend Gorinda wants to know if there are ever mutations that don’t cause problems. What do you tell him? Certainly. If a mutation is in a place that is not actually read to make an amino acid chain, then it may not cause any change at all. If the mutation falls at the end of a codon, it may st ...
The Genetic Code of Genes and Genomes
... • DNA fragments on a gel can often be visualized by staining with ethidium bromide, a dye which binds DNA • Particular DNA fragments can be isolated by cutting out the small region of the gel that contains the fragment and removing the DNA from the gel. • Specific DNA fragments are identified by hyb ...
... • DNA fragments on a gel can often be visualized by staining with ethidium bromide, a dye which binds DNA • Particular DNA fragments can be isolated by cutting out the small region of the gel that contains the fragment and removing the DNA from the gel. • Specific DNA fragments are identified by hyb ...
Document
... RNA Polymerase Binding and Initiation of Transcription The promoter of the a gene includes within it the transcription ____________ __________ (the nucleotides where RNA synthesis actually begins) and typically extends several dozen nucleotides upstream from the start point. In addition to serving ...
... RNA Polymerase Binding and Initiation of Transcription The promoter of the a gene includes within it the transcription ____________ __________ (the nucleotides where RNA synthesis actually begins) and typically extends several dozen nucleotides upstream from the start point. In addition to serving ...
Lab - Protein Synthesis
... The coding sequence (5’ 3’ “antisense”) of DNA below leads to the production of a specific protein. That makes it a gene. The gene was sequenced from samples taken from healthy human patients. As a genetic researcher you must first transcribe the sequence into an mRNA sequence. Then, using the gen ...
... The coding sequence (5’ 3’ “antisense”) of DNA below leads to the production of a specific protein. That makes it a gene. The gene was sequenced from samples taken from healthy human patients. As a genetic researcher you must first transcribe the sequence into an mRNA sequence. Then, using the gen ...
013368718X_CH15_229-246.indd
... Copying DNA Genetic engineers can transfer a gene from one organism to another to achieve a goal, but first, individual genes must be identified and separated from DNA. The original method (used by Douglas Prasher) involved several steps: Determine the amino acid sequence in a protein. Predict the m ...
... Copying DNA Genetic engineers can transfer a gene from one organism to another to achieve a goal, but first, individual genes must be identified and separated from DNA. The original method (used by Douglas Prasher) involved several steps: Determine the amino acid sequence in a protein. Predict the m ...
15.2 Study Workbook
... Copying DNA Genetic engineers can transfer a gene from one organism to another to achieve a goal, but first, individual genes must be identified and separated from DNA. The original method (used by Douglas Prasher) involved several steps: Determine the amino acid sequence in a protein. Predict the m ...
... Copying DNA Genetic engineers can transfer a gene from one organism to another to achieve a goal, but first, individual genes must be identified and separated from DNA. The original method (used by Douglas Prasher) involved several steps: Determine the amino acid sequence in a protein. Predict the m ...
Introduction to Biochemistry, Cell and Molecular Biology II Losiana
... The central dogma states that once “information” has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is impossible. Inf ...
... The central dogma states that once “information” has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is impossible. Inf ...
Chapter 13 DNA Technology
... Cloning Vector – a carrier that is used to clone a gene and transfer it to another organism. Plasmid – a ring of DNA found in many bacteria in addition to its main chromosome. Can be used in gene transfer in the following manner: 1. Plasmid is removed from a bacterium. 2. Using restriction enzymes, ...
... Cloning Vector – a carrier that is used to clone a gene and transfer it to another organism. Plasmid – a ring of DNA found in many bacteria in addition to its main chromosome. Can be used in gene transfer in the following manner: 1. Plasmid is removed from a bacterium. 2. Using restriction enzymes, ...
chromosome2
... 2. These sequences usually represent genes that code for proteins a) Only 1 - 2% of the human genome codes for proteins 3. Introns are regions of DNA in genes that are transcribed, but removed from RNA before transcription a) These account for about 10% of the human genome B. Moderately repetitive D ...
... 2. These sequences usually represent genes that code for proteins a) Only 1 - 2% of the human genome codes for proteins 3. Introns are regions of DNA in genes that are transcribed, but removed from RNA before transcription a) These account for about 10% of the human genome B. Moderately repetitive D ...
No Slide Title
... In galactose, cln2 will be made and cells survive In glucose, promoter is shut off and cells do not grow 2. Create a human cDNA library in a yeast expression vector (regulatory sequences that allow for expressio ...
... In galactose, cln2 will be made and cells survive In glucose, promoter is shut off and cells do not grow 2. Create a human cDNA library in a yeast expression vector (regulatory sequences that allow for expressio ...
in Power-Point Format
... 1. Illustrate principle of DNA gel electrophoresis; indicate comparative mobilities of DNAs with 150, 600, 1200 bp. 2. Compare process of Southern blot and RNA blot in terms of process, and what information can be provided. 12. Diagram imaginary Sanger sequencing gel, and provide DNA sequence. ...
... 1. Illustrate principle of DNA gel electrophoresis; indicate comparative mobilities of DNAs with 150, 600, 1200 bp. 2. Compare process of Southern blot and RNA blot in terms of process, and what information can be provided. 12. Diagram imaginary Sanger sequencing gel, and provide DNA sequence. ...
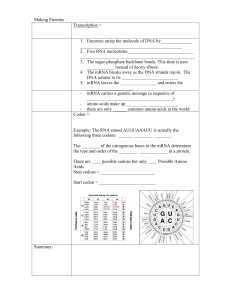
Transcription Activity Guide
... 1. How many possible triplet codes can be generated from these four base letters? 64, calculation: 4 different bases, in groups of three, 43 = 64. _______________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. How many possible triplet codes can be generated from these four base letters? 64, calculation: 4 different bases, in groups of three, 43 = 64. _______________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ...
PHYSgeneticsnotes
... to another, complementary one, by hydrogen bonds 3. This is called a “base pair” D. Codon 1. Group of 3 nucleotides in a row 2. Each codon codes for placement of one amino acid in a protein ...
... to another, complementary one, by hydrogen bonds 3. This is called a “base pair” D. Codon 1. Group of 3 nucleotides in a row 2. Each codon codes for placement of one amino acid in a protein ...
PR Reagent (Plant Total RNA Isolation Kit)
... The PR Reagent provides an easy 3-step method to isolate the total RNA from plant samples. This unique reagent system ensures the total RNA with a high yield and good quality from the most common plant samples as well as samples high in polysaccharides. If a larger sample is required, the kit volume ...
... The PR Reagent provides an easy 3-step method to isolate the total RNA from plant samples. This unique reagent system ensures the total RNA with a high yield and good quality from the most common plant samples as well as samples high in polysaccharides. If a larger sample is required, the kit volume ...
Identify the three parts of cell theory All living things are made of
... made of cells. Cells are the basic unit of life. Cells come from other cells. ...
... made of cells. Cells are the basic unit of life. Cells come from other cells. ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... RNA polymerase recognizes a specific base sequence in the DNA called a promoter and binds to it. The promoter identifies the start of a gene, which strand is to be copied, and the direction that it is to be copied. Complementary bases are assembled (U instead of T). A termination code in the DNA ind ...
... RNA polymerase recognizes a specific base sequence in the DNA called a promoter and binds to it. The promoter identifies the start of a gene, which strand is to be copied, and the direction that it is to be copied. Complementary bases are assembled (U instead of T). A termination code in the DNA ind ...
Unit 6 Protein Synthesis
... Anticodon- region of tRNA that is a sequence of 3 bases that are complementary to a codon in the mRNA mRNA- messenger RNA; copies directions from DNA takes them to ribosomes tRNA- transfer RNA; picks up certain AA & brings them to the ribosome for assembly Translation- DNA protein ...
... Anticodon- region of tRNA that is a sequence of 3 bases that are complementary to a codon in the mRNA mRNA- messenger RNA; copies directions from DNA takes them to ribosomes tRNA- transfer RNA; picks up certain AA & brings them to the ribosome for assembly Translation- DNA protein ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.