Packet 2 - w/answers
... Amino acids have ___amino_____ and ____carboxyl______ groups. They are made unique by the “R” group that is attached to carbon “R” is like a variable in algebra class. It can have many values (structures). The Function of the amino acid is determined by the structure and conformation of the “R” grou ...
... Amino acids have ___amino_____ and ____carboxyl______ groups. They are made unique by the “R” group that is attached to carbon “R” is like a variable in algebra class. It can have many values (structures). The Function of the amino acid is determined by the structure and conformation of the “R” grou ...
Standard 4 study guide
... to its slow movement (and the presence of warmth and moisture), a green mold will often grow on the fur of the sloth, helping it to blend in or camouflage with its surroundings. If the rainforest this organism occupies is cut down and eventually turns into a much drier, grassy plain, what will be th ...
... to its slow movement (and the presence of warmth and moisture), a green mold will often grow on the fur of the sloth, helping it to blend in or camouflage with its surroundings. If the rainforest this organism occupies is cut down and eventually turns into a much drier, grassy plain, what will be th ...
Biological Molecules
... optimal pH in which it can function • Tertiary structure can be radically altered by changes in pH ...
... optimal pH in which it can function • Tertiary structure can be radically altered by changes in pH ...
Programming Gene Expression
... CAP binds with cAMP to forms a dimer. and then stimulates the transcription of lactose- and arabinose-catabolizing genes as sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. The E. coli genome contains many CAP-binding sites in positions appropriate for interactions with RNA polymerase. Thus, an increase in th ...
... CAP binds with cAMP to forms a dimer. and then stimulates the transcription of lactose- and arabinose-catabolizing genes as sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. The E. coli genome contains many CAP-binding sites in positions appropriate for interactions with RNA polymerase. Thus, an increase in th ...
Honors BIOLOGY
... DNA: the code for proteins RNA: carries the code to make proteins into the cytoplasm ATP: energy molecule of the cell All of these contain the double-ringed nitrogen base: adenine. Is it just a coincidence that caffeine and chocolate have VERY similar structures to other ESSENTIAL molecules of life? ...
... DNA: the code for proteins RNA: carries the code to make proteins into the cytoplasm ATP: energy molecule of the cell All of these contain the double-ringed nitrogen base: adenine. Is it just a coincidence that caffeine and chocolate have VERY similar structures to other ESSENTIAL molecules of life? ...
Notes
... RNA polymerase and the polymerase dissociates from the template DNA. Once released, an RNA polymerase is free to transcribe a new gene. Regulation of transcription Environmental changes induce changes in gene expression. Regulation of transcription initiation is the most common form of gene control ...
... RNA polymerase and the polymerase dissociates from the template DNA. Once released, an RNA polymerase is free to transcribe a new gene. Regulation of transcription Environmental changes induce changes in gene expression. Regulation of transcription initiation is the most common form of gene control ...
Bioinformatics course 10.09.15
... ︎I have to constructed a artificial gene, how do I design the primers, how to check if I have the right sequence? ...
... ︎I have to constructed a artificial gene, how do I design the primers, how to check if I have the right sequence? ...
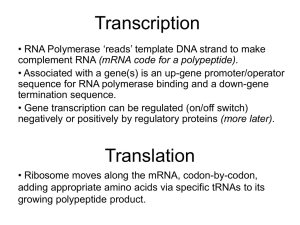
Transcription & Translation
... • Associated with a gene(s) is an up-gene promoter/operator sequence for RNA polymerase binding and a down-gene termination sequence. • Gene transcription can be regulated (on/off switch) negatively or positively by regulatory proteins (more later). ...
... • Associated with a gene(s) is an up-gene promoter/operator sequence for RNA polymerase binding and a down-gene termination sequence. • Gene transcription can be regulated (on/off switch) negatively or positively by regulatory proteins (more later). ...
Advances in the diagnosis of infection
... genomic sequence. Validation data should be available to detail both the analytical and clinical specificity and sensitivity for every “home-brewed” and commercial assay. In practice, however, these tests may have only modest sensitivity in specimens that have a low bacillary load. Data from severa ...
... genomic sequence. Validation data should be available to detail both the analytical and clinical specificity and sensitivity for every “home-brewed” and commercial assay. In practice, however, these tests may have only modest sensitivity in specimens that have a low bacillary load. Data from severa ...
3. Genetic Drift
... marks of this bottleneck. They have much less genetic variation than a population of southern elephant seals that was not so intensely hunted. ...
... marks of this bottleneck. They have much less genetic variation than a population of southern elephant seals that was not so intensely hunted. ...
protocol: restriction endonuclease digestion/analysis of
... A single PCR-generated band in a gel does not always indicate a single amplification product. One way to quickly determine if there is more than one product is to digest the PCR product with restriction endonucleases. For example, following restriction endonuclease digestion, if DNA fragments are vi ...
... A single PCR-generated band in a gel does not always indicate a single amplification product. One way to quickly determine if there is more than one product is to digest the PCR product with restriction endonucleases. For example, following restriction endonuclease digestion, if DNA fragments are vi ...
Genetics Vocabulary Note-Taking Chart
... _____________ for each trait. chromosomes. Dominant, n. An inherited trait which is present even ______________ eye color is dominant when inherited _________ from one over other eye color parent. Recessive, n. The form of the gene that shows up only When______ parents have the recessive when inheri ...
... _____________ for each trait. chromosomes. Dominant, n. An inherited trait which is present even ______________ eye color is dominant when inherited _________ from one over other eye color parent. Recessive, n. The form of the gene that shows up only When______ parents have the recessive when inheri ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 8e
... The molecular basis of phenotypes was known before it was known that DNA is the genetic material. Studies of many different organisms showed that major phenotypic differences were due to specific proteins. ...
... The molecular basis of phenotypes was known before it was known that DNA is the genetic material. Studies of many different organisms showed that major phenotypic differences were due to specific proteins. ...
Gene Section RBM15 (RNA binding motif protein 15) in Oncology and Haematology
... 5' OTT - 3' MAL, comprisng most of OTT fused to most of MAL; the reciprocal 5' MAL - 3' OTT may or may not be present. Abnormal protein Includes most of OTT with the RNA recognition motifs and the SPOC domain in N-term, and most of MAL, with the scaffold attachment factor box in C-term. Oncogenesis ...
... 5' OTT - 3' MAL, comprisng most of OTT fused to most of MAL; the reciprocal 5' MAL - 3' OTT may or may not be present. Abnormal protein Includes most of OTT with the RNA recognition motifs and the SPOC domain in N-term, and most of MAL, with the scaffold attachment factor box in C-term. Oncogenesis ...
Problem set 7 - Review for final
... nucleic acid. Circle the backbone of the polynucleotide. What is(are) the secondary product(s)? You have constructed DNA or RNA? Why? ...
... nucleic acid. Circle the backbone of the polynucleotide. What is(are) the secondary product(s)? You have constructed DNA or RNA? Why? ...
DNA Replication, Transcript
... that only one of the two strands of the DNA will be used as a template to create the mRNA molecule. The enzyme RNA polymerase is used as the catalyst for this process. – As RNA polymerase moves along the strand of DNA acting as the template, RNA nucleotides float into place by complementary base pai ...
... that only one of the two strands of the DNA will be used as a template to create the mRNA molecule. The enzyme RNA polymerase is used as the catalyst for this process. – As RNA polymerase moves along the strand of DNA acting as the template, RNA nucleotides float into place by complementary base pai ...
Cloning The Insulin Gene
... to differ from human insulin by one amino acid; beef insulin by three. Although both work in humans to lower blood sugar, they are seen by the immune system as "foreign" and induce an antibody response in the patient that blunts their effect and requires higher doses. Two approaches have been tried ...
... to differ from human insulin by one amino acid; beef insulin by three. Although both work in humans to lower blood sugar, they are seen by the immune system as "foreign" and induce an antibody response in the patient that blunts their effect and requires higher doses. Two approaches have been tried ...
Chapter 4 - Chemical Engineering - Michigan Technological University
... Metabolic Regulation Genetic-Level Control - Which Proteins are Made? Repression of Transcription (m-RNA) an end product of enzyme activity or of the metabolic pathway (co-repressor) blocks m-RNA synthesis ...
... Metabolic Regulation Genetic-Level Control - Which Proteins are Made? Repression of Transcription (m-RNA) an end product of enzyme activity or of the metabolic pathway (co-repressor) blocks m-RNA synthesis ...
Lecture 3 Slides
... Three DNA sequence elements are needed to produce a eukaryotic chromosome that can be replicated and segregated [Fig. 5-18] ...
... Three DNA sequence elements are needed to produce a eukaryotic chromosome that can be replicated and segregated [Fig. 5-18] ...
Nanotechnology in Medicine Krešimir Pavelić Division of Molecular
... hybrids by RnaseH enzyme • formation of triple helix between genomic double-stranded DNA and oligonucleotides • the cleavage of target RNA by ribozymes. ...
... hybrids by RnaseH enzyme • formation of triple helix between genomic double-stranded DNA and oligonucleotides • the cleavage of target RNA by ribozymes. ...
3-Session 5-Lec 9 What is a gene and transcription
... Compare and contrast gene expression in mammalian and bacterial cells and explain how the differences can be exploited clinically. (LO 7.8) Predict the effects of various mutations in a gene. (LO 7.9) Explain how mutations outside the coding region can affect ...
... Compare and contrast gene expression in mammalian and bacterial cells and explain how the differences can be exploited clinically. (LO 7.8) Predict the effects of various mutations in a gene. (LO 7.9) Explain how mutations outside the coding region can affect ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.