GENETICS - St. Bonaventure University
... having an effect….the complete answer remains to be discovered when more research is done. ...
... having an effect….the complete answer remains to be discovered when more research is done. ...
Enhancing and Evolving to “Perfection”? Unit Study Guide 2013
... 6. Evolutionary Trees / Common Ancestry: The diagram shows an interpretation of relationships based on evolutionary evidence. The letters represent different species. A common ancestor for species C and E is species ________. The most recent common ancestor for species A and B is species ________. W ...
... 6. Evolutionary Trees / Common Ancestry: The diagram shows an interpretation of relationships based on evolutionary evidence. The letters represent different species. A common ancestor for species C and E is species ________. The most recent common ancestor for species A and B is species ________. W ...
Questions
... each with two new strands one with two new strands and the other with two original each with one new strand and one original strand each with two original strands 6. The backbone of a DNA molecule is made up of alternating _______ and _____ groups. Hide answers nitrogen bases, phosphate enzymes, nit ...
... each with two new strands one with two new strands and the other with two original each with one new strand and one original strand each with two original strands 6. The backbone of a DNA molecule is made up of alternating _______ and _____ groups. Hide answers nitrogen bases, phosphate enzymes, nit ...
swetha sonwani - Gulf Job Seeker
... Biochemistry, CIMS, and Bilaspur (03.0.1.2005 – 25.01.2005). Undergone 2 days training on the usage of automated high throughput microscope named Axio Plan 2 Imaging by Carl Zeiss, Metasystems, Germany under Benjamin, and W.K.Ching at Bangalore. (March.2010). ...
... Biochemistry, CIMS, and Bilaspur (03.0.1.2005 – 25.01.2005). Undergone 2 days training on the usage of automated high throughput microscope named Axio Plan 2 Imaging by Carl Zeiss, Metasystems, Germany under Benjamin, and W.K.Ching at Bangalore. (March.2010). ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... from mixture of other nucleic acids Phenotype the observable characteristics of an organism Plasmid an extrachromosomal genetic element that has no extracellular form Point mutation a mutation that involves one or only a very few base pairs Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) a method used to amplify a ...
... from mixture of other nucleic acids Phenotype the observable characteristics of an organism Plasmid an extrachromosomal genetic element that has no extracellular form Point mutation a mutation that involves one or only a very few base pairs Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) a method used to amplify a ...
Chapter 31 - Department of Chemistry [FSU]
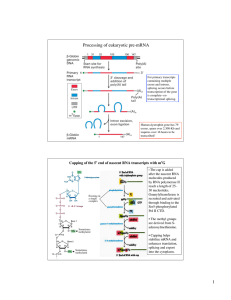
... • CAP structure may protect against RNase degradation • CAP structure also important in binding orientation on ribosome ...
... • CAP structure may protect against RNase degradation • CAP structure also important in binding orientation on ribosome ...
Notes for Part B
... Crick and Watson made the connection between how proteins have a sequence of amino acids and the DNA has a sequence of nucleotides. They also knew that proteins are the major building blocks of cells and are involved in cell metabolism. Some examples of proteins include keratin, hemoglobin, enzymes, ...
... Crick and Watson made the connection between how proteins have a sequence of amino acids and the DNA has a sequence of nucleotides. They also knew that proteins are the major building blocks of cells and are involved in cell metabolism. Some examples of proteins include keratin, hemoglobin, enzymes, ...
Role of Tension and Twist in Single
... Despite its stiffness and high charge density, doublestranded DNA (ds-DNA) is condensed in vivo into highly compact structures by positively charged proteins. Morphologies and packing densities similar to those observed in sperm nuclei and in certain viruses [1,2] can be reproduced in vitro using a ...
... Despite its stiffness and high charge density, doublestranded DNA (ds-DNA) is condensed in vivo into highly compact structures by positively charged proteins. Morphologies and packing densities similar to those observed in sperm nuclei and in certain viruses [1,2] can be reproduced in vitro using a ...
Genetics unit study guide (notes)
... Each codon codes for a specific amino acid. Important to the process of translation is another type of RNA called transfer RNA, which function to carry the amino acids to the site of protein synthesis on the ribosome. tRNA contains ANTICODONs, which are also three nucleotide base sequences. This all ...
... Each codon codes for a specific amino acid. Important to the process of translation is another type of RNA called transfer RNA, which function to carry the amino acids to the site of protein synthesis on the ribosome. tRNA contains ANTICODONs, which are also three nucleotide base sequences. This all ...
Sea Urchin Genome
... develop tools to identify such regions and merge them (e.g., Polyjoin). – simple altering of mismatch parameters was not sufficient ...
... develop tools to identify such regions and merge them (e.g., Polyjoin). – simple altering of mismatch parameters was not sufficient ...
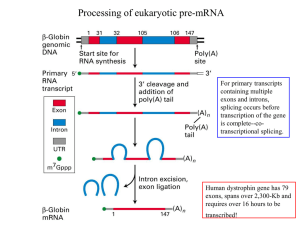
1 Processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA
... The correct 5’ GU and 3’ AG splice sites are recognized by splicing factors on the basis of their proximity to exons. The exons contain exonic splicing enhancers (ESEs) that are binding sites for SR proteins. When bound to ESEs, the SR proteins interact with one another and promote the cooperative b ...
... The correct 5’ GU and 3’ AG splice sites are recognized by splicing factors on the basis of their proximity to exons. The exons contain exonic splicing enhancers (ESEs) that are binding sites for SR proteins. When bound to ESEs, the SR proteins interact with one another and promote the cooperative b ...
Bio101 Midterm II Study Guide 10/25/10
... (italics) lists the relevant chapter or chapters in your text. As an additional aid, at the top of each section of the notes, I have placed the specific objectives addressed by that section of the notes. note: learning objectives learned earlier in the semester are used in the rest of the semester a ...
... (italics) lists the relevant chapter or chapters in your text. As an additional aid, at the top of each section of the notes, I have placed the specific objectives addressed by that section of the notes. note: learning objectives learned earlier in the semester are used in the rest of the semester a ...
AgrawalGizer_ARTSS_part2
... • Transcription: One of the two DNA strands is transcribed to a single-stranded nucleic acid called ribonucleic acid (RNA) RNA has the same bases as DNA except uracil (U) substitutes for thymine (T). • Translation: Conversion of the basic informational unit of 3 nucleotide bases (called a codon) int ...
... • Transcription: One of the two DNA strands is transcribed to a single-stranded nucleic acid called ribonucleic acid (RNA) RNA has the same bases as DNA except uracil (U) substitutes for thymine (T). • Translation: Conversion of the basic informational unit of 3 nucleotide bases (called a codon) int ...
Powerpoint slides
... Analysis of gene order (synteny). Genes with a related function are frequently clustered on the chromosome. Ex: E.coli genes responsible for synthesis of Trp are clustered and order is conserved between ...
... Analysis of gene order (synteny). Genes with a related function are frequently clustered on the chromosome. Ex: E.coli genes responsible for synthesis of Trp are clustered and order is conserved between ...
Biotechnology-
... Genomic—DNA exactly as found in the genome, including introns and other non-coding portions of DNA INTRONS-junk DNA 3’ untranslated region ...
... Genomic—DNA exactly as found in the genome, including introns and other non-coding portions of DNA INTRONS-junk DNA 3’ untranslated region ...
Document
... • Selection: Culture a naturally-occurring microbe that produces desired product • Mutation: Mutagens cause mutations that might result in a microbe with a desirable trait • Site-directed mutagenesis: Change a specific DNA code to change a protein • Select and culture microbe with the desired mutati ...
... • Selection: Culture a naturally-occurring microbe that produces desired product • Mutation: Mutagens cause mutations that might result in a microbe with a desirable trait • Site-directed mutagenesis: Change a specific DNA code to change a protein • Select and culture microbe with the desired mutati ...
Convergent evolution
... will increase in the population as more individuals survive & leave offspring 2. Harmful mutations decrease fitness of the individual in that environment & cause a higher mortality rate – Frequency of the mutation will decrease & might or might not disappear from the gene pool ...
... will increase in the population as more individuals survive & leave offspring 2. Harmful mutations decrease fitness of the individual in that environment & cause a higher mortality rate – Frequency of the mutation will decrease & might or might not disappear from the gene pool ...
Isolation and identification of viral DNA from
... Epifluorescent microscopy to determine viral-particle concentration and purity. Red arrows indicate microbial cells or debris, blue arrows desired VLPs. All the samples had 5-10 viral particles per field on average, indicating a constant concentration of viral DNA. (A) Sample treated with lysozyme a ...
... Epifluorescent microscopy to determine viral-particle concentration and purity. Red arrows indicate microbial cells or debris, blue arrows desired VLPs. All the samples had 5-10 viral particles per field on average, indicating a constant concentration of viral DNA. (A) Sample treated with lysozyme a ...
Goal 2.01 Biochem
... Proteins are synthesized by bonding amino acids amino acids = building block ...
... Proteins are synthesized by bonding amino acids amino acids = building block ...
1030ExamFinal
... 29. A sequence of DNA nucleotides coding for a specific protein or RNA molecule is a: A. Gene B. Genome C. Chromosome D. All of the above are correct E. None of the above are correct 30. Which phrase does not belong? The polymerase chain reaction: A. Is used to amplify minute quantities of DNA into ...
... 29. A sequence of DNA nucleotides coding for a specific protein or RNA molecule is a: A. Gene B. Genome C. Chromosome D. All of the above are correct E. None of the above are correct 30. Which phrase does not belong? The polymerase chain reaction: A. Is used to amplify minute quantities of DNA into ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.




![Chapter 31 - Department of Chemistry [FSU]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017094902_1-c913d8622e17655318ad84818ec4b5cb-300x300.png)