Chapters 1 and 2 Review
... Glucose from: http://www.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/BioBookCHEM2.html ...
... Glucose from: http://www.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/BioBookCHEM2.html ...
SURFIN` THROUGH STAAR
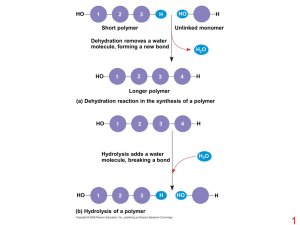
... group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the ...
... group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the ...
www.endogenet.org Molecular Genetics Service Profile d3
... responsiveness to exogenous Growth Hormone (GH). Therefore screening the d3polymorphism may be useful in SGA (small for gestational age) or ISS (idiopathic short stature) children before treatment with GH to predict the patients individual response. ...
... responsiveness to exogenous Growth Hormone (GH). Therefore screening the d3polymorphism may be useful in SGA (small for gestational age) or ISS (idiopathic short stature) children before treatment with GH to predict the patients individual response. ...
lecture 03 - phylogenetics - Cal State LA
... are very morphologically distinctive, such as birds and cetaceans ...
... are very morphologically distinctive, such as birds and cetaceans ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
Poster
... • Through DNA sequencing, our mentor and collaborators hope to be able to discover the cause of the mother and daughter’s cervical cancer. Providing this link between genome sequence and disease can be used to identify others at risk for developing cancer due to presence of specific mutations. These ...
... • Through DNA sequencing, our mentor and collaborators hope to be able to discover the cause of the mother and daughter’s cervical cancer. Providing this link between genome sequence and disease can be used to identify others at risk for developing cancer due to presence of specific mutations. These ...
High Frequency of Recombination (Hfr)
... • Untreated culture Do a serial dilution of the untreated wildtype E. coli culture: Fill 7 tubes with 4.5 ml of sterile saline. Transfer 0.5 ml of the undiluted culture to one of the tubes. This is a 10-1 dilution. Next make serial dilutions of 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6 and 10-7. Always change pi ...
... • Untreated culture Do a serial dilution of the untreated wildtype E. coli culture: Fill 7 tubes with 4.5 ml of sterile saline. Transfer 0.5 ml of the undiluted culture to one of the tubes. This is a 10-1 dilution. Next make serial dilutions of 10-2, 10-3, 10-4, 10-5, 10-6 and 10-7. Always change pi ...
slides available - The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering
... associated with a guide RNA that docks the nuclease to a target gene through base complementarity. The base sequence of the guide RNA can be freely chosen, therefore the nuclease can be targeted to any target gene in the genome. ...
... associated with a guide RNA that docks the nuclease to a target gene through base complementarity. The base sequence of the guide RNA can be freely chosen, therefore the nuclease can be targeted to any target gene in the genome. ...
DNA the Crown Jewels 2012
... quantities or broken pieces of DNA outside of a living cell. 2. DNA polymerases and an automatic machine called a DNA Thermal Cycler are used to copy the DNA once per cycle. 3. Within a few hours 30 cycles can multiply the small quantity of DNA to more than a million pieces of the DNA. 4. Once the D ...
... quantities or broken pieces of DNA outside of a living cell. 2. DNA polymerases and an automatic machine called a DNA Thermal Cycler are used to copy the DNA once per cycle. 3. Within a few hours 30 cycles can multiply the small quantity of DNA to more than a million pieces of the DNA. 4. Once the D ...
The effect of sodium ion concentration on
... Kt values is not very broad. (For example, if two types of hairpin-forming sequence with the same eM—e^ values were present in equal abundance, the data would imply that the two K values differed by less than a factor of four.) This allows formulation of an expression based on equation (A3) (substit ...
... Kt values is not very broad. (For example, if two types of hairpin-forming sequence with the same eM—e^ values were present in equal abundance, the data would imply that the two K values differed by less than a factor of four.) This allows formulation of an expression based on equation (A3) (substit ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... • Insecticides tend to be nonspecific, killing both pest and beneficial insects. They can also be blown or washed away to contaminate and pollute ...
... • Insecticides tend to be nonspecific, killing both pest and beneficial insects. They can also be blown or washed away to contaminate and pollute ...
Affinity Chromatography
... For large molecules, which can not enter any of the pores, at least half of the column volume is necessary. These molecules leave the column after half column volume. Intermediate sized molecules can enter some of the pores, but not all – they elute between the two other fractions. Ball shaped (isom ...
... For large molecules, which can not enter any of the pores, at least half of the column volume is necessary. These molecules leave the column after half column volume. Intermediate sized molecules can enter some of the pores, but not all – they elute between the two other fractions. Ball shaped (isom ...
natural selection 1
... in size from 4cm in length to 10cm in length. Their size is a polygenic trait. The average size in the 1920’s was 6cm. Today the average size is 9cm. • Draw a graph of this type of evolution. ...
... in size from 4cm in length to 10cm in length. Their size is a polygenic trait. The average size in the 1920’s was 6cm. Today the average size is 9cm. • Draw a graph of this type of evolution. ...
DNA Repair - WordPress.com
... Post Replicative Repair -When DNA polymerase encounters damage in DNA, it cannot proceed. Instead it gives a gap for replication and proceeds up to 800 bp without replicating. Then again it starts replicating after synthesizing a primer by primosome. These gaps are then repaired by using one of the ...
... Post Replicative Repair -When DNA polymerase encounters damage in DNA, it cannot proceed. Instead it gives a gap for replication and proceeds up to 800 bp without replicating. Then again it starts replicating after synthesizing a primer by primosome. These gaps are then repaired by using one of the ...
NUCLEUS
... to the surface. The outer membrane is also continuous with the inner nuclear membrane since the two layers are fused together at numerous tiny holes called nuclear pores that perforate the nuclear envelope. These pores regulate the selective passage of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm, Th ...
... to the surface. The outer membrane is also continuous with the inner nuclear membrane since the two layers are fused together at numerous tiny holes called nuclear pores that perforate the nuclear envelope. These pores regulate the selective passage of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm, Th ...
appendix ii - Shodhganga
... a) the 3’ to 5’ direction on both the leading and lagging strands. b) the 5’ to 3’ direction on both the leading and lagging strands. c) the 5’ to 3’ direction on the leading strands, and the 3’ to 5’ direction on the lagging strands. d) the 3’ to 5’ direction on the leading strands, and the 5’ to 3 ...
... a) the 3’ to 5’ direction on both the leading and lagging strands. b) the 5’ to 3’ direction on both the leading and lagging strands. c) the 5’ to 3’ direction on the leading strands, and the 3’ to 5’ direction on the lagging strands. d) the 3’ to 5’ direction on the leading strands, and the 5’ to 3 ...
Unfinished Material - Answer Key
... bases G and U, and bind towards the end of the intron marked by base A. - Other snRNPs assemble with the initial SnRNPs bound to bases G and U, and bound to base A. This assembly forms a spliceosome. - The intron is cut between the G base and the U base, forming a loop and a single stranded stem of ...
... bases G and U, and bind towards the end of the intron marked by base A. - Other snRNPs assemble with the initial SnRNPs bound to bases G and U, and bound to base A. This assembly forms a spliceosome. - The intron is cut between the G base and the U base, forming a loop and a single stranded stem of ...
Bioinformatics Take Home Test #1 –Due 9/19/16
... that there are non-homologous enzymes inhabiting completely different regions of protein space with the same function. C. An exact function does not need to be hit upon, because natural selection can take a protein with limited function and make it better. D. Similar structures have similar func ...
... that there are non-homologous enzymes inhabiting completely different regions of protein space with the same function. C. An exact function does not need to be hit upon, because natural selection can take a protein with limited function and make it better. D. Similar structures have similar func ...
Medical Applications of Bioinformatics
... • BLASTX makes automatic translation (in all 6 reading frames) of your DNA query sequence to compare with protein databanks • TBLASTN makes automatic translation of an entire DNA database to compare with your protein query sequence • Only make a DNA-DNA search if you are working with a sequence that ...
... • BLASTX makes automatic translation (in all 6 reading frames) of your DNA query sequence to compare with protein databanks • TBLASTN makes automatic translation of an entire DNA database to compare with your protein query sequence • Only make a DNA-DNA search if you are working with a sequence that ...
... – DNA or RNA molecules are charged in aqueous solution and move to a definite direction by the action of an electric field. – The DNA molecules are either labeled with radioisotopes or tagged with fluorescent dyes. In the latter, a laser beam can trace the dyes and send information to a computer. – ...
Presence of the DNA viral in Complex Cumulus Oóforus of
... Ultrassom (OPU). The DNA extraction was accomplished in a pool of COCs of all aspirations from the same donor and in the total blood. After this procedure, the Nested-PCR reactions were accomplished. The DNA of BoHV1 was identified in the pool of COCs from three serumpositive donors, but it was not ...
... Ultrassom (OPU). The DNA extraction was accomplished in a pool of COCs of all aspirations from the same donor and in the total blood. After this procedure, the Nested-PCR reactions were accomplished. The DNA of BoHV1 was identified in the pool of COCs from three serumpositive donors, but it was not ...
Decoding the message_2 - Molecular-Biology-Resource
... and solidify the concept that the genetic code provides the instructions for protein synthesis. This is an AfL activity to ensure that students understand the central dogma. In the chart below is the “DNA to amino acid dictionary.” Teachers can use this to make their own personalized messages for th ...
... and solidify the concept that the genetic code provides the instructions for protein synthesis. This is an AfL activity to ensure that students understand the central dogma. In the chart below is the “DNA to amino acid dictionary.” Teachers can use this to make their own personalized messages for th ...
Vectors for Even Larger Genomic DNA Inserts
... Bacteriophages such as lambda have been modified to make useful cloning vectors (Figures 10.38, 10.39). Larger amounts (longer) of foreign DNA can be cloned with lambda than with many other plasmids. In addition, the recombinant DNA can be packaged in vitro for efficient transfer to a host cell. Pla ...
... Bacteriophages such as lambda have been modified to make useful cloning vectors (Figures 10.38, 10.39). Larger amounts (longer) of foreign DNA can be cloned with lambda than with many other plasmids. In addition, the recombinant DNA can be packaged in vitro for efficient transfer to a host cell. Pla ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.