Gene Section SRSF3 (serine/arginine rich splicing factor 3) -
... keratinocytes in the basal and parabasal layers, but drops significantly in terminally differentiated keratinocytes in the superficial layers of the cervix or skin. In general, normal cells like muscle or nerve cells have no or little expression of SRSF3. In contrast, malignant tumor cells express r ...
... keratinocytes in the basal and parabasal layers, but drops significantly in terminally differentiated keratinocytes in the superficial layers of the cervix or skin. In general, normal cells like muscle or nerve cells have no or little expression of SRSF3. In contrast, malignant tumor cells express r ...
Eukaryotic Genome: Organization, Regulation, and Evolution
... Transferring such a sequence from a short-lived mRNA to a normally stable mRNA results in quick mRNA degradation. ...
... Transferring such a sequence from a short-lived mRNA to a normally stable mRNA results in quick mRNA degradation. ...
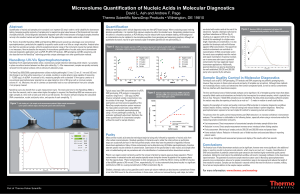
Microvolume Quantification of Nucleic Acids in Molecular Diagnostics
... testing. Assessing quantity and purity of samples prior to analysis has great value because of the financial and time costs of analytical failures. Clinical diagnostic laboratories frequently work with limited amounts of biological samples; therefore not only is the resultant nucleic acid yield ofte ...
... testing. Assessing quantity and purity of samples prior to analysis has great value because of the financial and time costs of analytical failures. Clinical diagnostic laboratories frequently work with limited amounts of biological samples; therefore not only is the resultant nucleic acid yield ofte ...
File
... 5. What process is used to link amino acids together? Removal of a water moleculecondensation 6. Name the bonds found between amino acids in a polypeptide chain. These are peptide bonds 7. Explain the difference between a disaccharide and a polysaccharide. Give an example of each. A disaccharide is ...
... 5. What process is used to link amino acids together? Removal of a water moleculecondensation 6. Name the bonds found between amino acids in a polypeptide chain. These are peptide bonds 7. Explain the difference between a disaccharide and a polysaccharide. Give an example of each. A disaccharide is ...
Genetics and Microbiology
... • This superficially resembles sex, but is not! • Cells containing the F factor are referred to as F+, and can change cells without it (F-) to F+. • If the F factor becomes integrated into the bacterial chromosome, we call that an Hfr strain because when it conjugates it causes a high frequency o ...
... • This superficially resembles sex, but is not! • Cells containing the F factor are referred to as F+, and can change cells without it (F-) to F+. • If the F factor becomes integrated into the bacterial chromosome, we call that an Hfr strain because when it conjugates it causes a high frequency o ...
GCE Biology Jan 2012 Unit 4 QP
... The most significant factor that affects the formation of growth rings is environmental temperature. In regions where there is an annual cycle of seasonal temperature changes, it is possible to estimate the year in which a particular ring was formed. ...
... The most significant factor that affects the formation of growth rings is environmental temperature. In regions where there is an annual cycle of seasonal temperature changes, it is possible to estimate the year in which a particular ring was formed. ...
January 2012 - 6BI04 - Edexcel
... total mark for this paper is 90. t The marks for each question are shown in brackets t The – use this as a guide as to how much time to spend on each question. Questions labelled with an asterisk (*) are ones where the quality of your ...
... total mark for this paper is 90. t The marks for each question are shown in brackets t The – use this as a guide as to how much time to spend on each question. Questions labelled with an asterisk (*) are ones where the quality of your ...
Case Study Learning via Simulations of Molecular Biology Techniques
... BRCA1 appears to encode a tumor suppressor protein. Mutations that affect the function of this protein cause increased rates of cell division and a predisposition towards the development of malignancy. Several BRCA1 mutations, including point mutations, deletions, and insertions, have been identifie ...
... BRCA1 appears to encode a tumor suppressor protein. Mutations that affect the function of this protein cause increased rates of cell division and a predisposition towards the development of malignancy. Several BRCA1 mutations, including point mutations, deletions, and insertions, have been identifie ...
Applications of Recombinant DNA to Pathologic Diagnosis
... The process that produces a complementary strand of RNA from DNA. Plasmid: ...
... The process that produces a complementary strand of RNA from DNA. Plasmid: ...
Biochemistry of Cells - Warren County Public Schools
... per person per year Cellulose, found in plant cell walls, is the most abundant organic compound on Earth ...
... per person per year Cellulose, found in plant cell walls, is the most abundant organic compound on Earth ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
Organic Molecules Worksheet
... groups of amino acids are joined together, a protein is formed. 23. What are some of the functions of proteins? __________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is the monomer of proteins? ___________________________ ...
... groups of amino acids are joined together, a protein is formed. 23. What are some of the functions of proteins? __________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ 24. What is the monomer of proteins? ___________________________ ...
protein synthesis
... directly to the location by internal targeting sequence Protein destined for the inner mitochondrial membrane contain prosequence that guides first into the mitochondrial matrix. After removal of the pro-sequence by processing peptidase, the proteins are directed by second targeting signal sequenc ...
... directly to the location by internal targeting sequence Protein destined for the inner mitochondrial membrane contain prosequence that guides first into the mitochondrial matrix. After removal of the pro-sequence by processing peptidase, the proteins are directed by second targeting signal sequenc ...
Brief Answer Key (up to 2/9)
... 6.) What two interactions are occurring in the DNA double helix? Explain each. Together, both yield what structural benefit for the helix? a. Complementary base pairing and Base stacking by hydrophobic interactions b. Provides stability 7.) The directionality of the nucleotide sequence is read in wh ...
... 6.) What two interactions are occurring in the DNA double helix? Explain each. Together, both yield what structural benefit for the helix? a. Complementary base pairing and Base stacking by hydrophobic interactions b. Provides stability 7.) The directionality of the nucleotide sequence is read in wh ...
FREE Sample Here
... The final shape of a protein is important to its function. When proteins are exposed to extremes in heat and pH, they undergo an irreversible change in shape called denaturation which destroys their ability to function. Levels of Protein Organization The primary structure of a polypeptide is the seq ...
... The final shape of a protein is important to its function. When proteins are exposed to extremes in heat and pH, they undergo an irreversible change in shape called denaturation which destroys their ability to function. Levels of Protein Organization The primary structure of a polypeptide is the seq ...
CHAPTER 8
... The non-structural protein (NS1) that is encoded in the 3’ portion of the genome serves (1) attached to the 5’ end of the viral DNA during replication; (2) serves as a helicase during replication and DNA packaging; (3) serves as a site-specific nickase; (4) mediates arrest of the cell in the G1 phas ...
... The non-structural protein (NS1) that is encoded in the 3’ portion of the genome serves (1) attached to the 5’ end of the viral DNA during replication; (2) serves as a helicase during replication and DNA packaging; (3) serves as a site-specific nickase; (4) mediates arrest of the cell in the G1 phas ...
Chapter 3
... strand till it reaches the previous RNA primer, where it stops, to continue further downstream the replication fork with the next primer. This results in a strand that consists of DNA fragments, called Okazaki fragments, interrupted by short RNA fragments. The enzyme that produces the leading and la ...
... strand till it reaches the previous RNA primer, where it stops, to continue further downstream the replication fork with the next primer. This results in a strand that consists of DNA fragments, called Okazaki fragments, interrupted by short RNA fragments. The enzyme that produces the leading and la ...
Nanotechnology for Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
... MEMS can be designed with structures that range from micrometers to nanometers in size. MEMS can have moving parts and can also integrate electrical circuits as part of the features on the chip. Microfabrication has generated MEMS with a wide variety of applications that has impacted multiple fields ...
... MEMS can be designed with structures that range from micrometers to nanometers in size. MEMS can have moving parts and can also integrate electrical circuits as part of the features on the chip. Microfabrication has generated MEMS with a wide variety of applications that has impacted multiple fields ...
File - Ms. Adam`s science site
... C. She will have more product because the enzyme works more efficiently. D. She will have more product because the enzyme is at its optimum pH. 2. Which is represented by Structure X below? A. substrate B. product C. enzyme D. complex ...
... C. She will have more product because the enzyme works more efficiently. D. She will have more product because the enzyme is at its optimum pH. 2. Which is represented by Structure X below? A. substrate B. product C. enzyme D. complex ...
PCR - UCLA EEB
... keep track of which one you’ve used. 3. Set up everything in groups of 8 when possible (e.g. 8 samples, 8 tubes, 8 tips). Use tip one for sample one in tube one. This will help you keep track of which sample you are on. 4. Keep lids on whenever possible. 5. Reagents must be completely thawed and mix ...
... keep track of which one you’ve used. 3. Set up everything in groups of 8 when possible (e.g. 8 samples, 8 tubes, 8 tips). Use tip one for sample one in tube one. This will help you keep track of which sample you are on. 4. Keep lids on whenever possible. 5. Reagents must be completely thawed and mix ...
CHM 365 Name: Exam 2 Oct. 13, 2004 Do all of the questions. Part I
... Circle all of the following that are true statements about the transition state of a reaction: a) The transition state concentration is equal to the rate of the reaction. b) The transition state is located at the height of a free energy diagram. c) The energy required to raise the average energy of ...
... Circle all of the following that are true statements about the transition state of a reaction: a) The transition state concentration is equal to the rate of the reaction. b) The transition state is located at the height of a free energy diagram. c) The energy required to raise the average energy of ...
PCR_HB
... POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION • Primers (may be specific or random) • Thermostable polymerase – Taq pol – Pfu pol – Vent pol ...
... POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION • Primers (may be specific or random) • Thermostable polymerase – Taq pol – Pfu pol – Vent pol ...
Adobe PDF - Boston University Physics
... depends both on r and ,. As it follows from our analysis, the length distribution of various DTR differ significantly from each other in various organisms. Varying psr, ,d, we find even better agreement with experimental data [Fig. 1(b)] for each particular case. The nonuniversality of psr, ,d is bi ...
... depends both on r and ,. As it follows from our analysis, the length distribution of various DTR differ significantly from each other in various organisms. Varying psr, ,d, we find even better agreement with experimental data [Fig. 1(b)] for each particular case. The nonuniversality of psr, ,d is bi ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.