Chapter 5
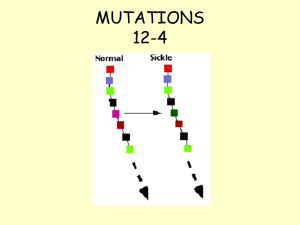
... Chapter 5 1. Sickle-cell anemia is an example of _____________________ because _________________________. a. stabilizing selection/ there is only one common phenotype in populations where malaria is prevalent. b. directional selection/ malaria is promoting the loss of the sickle allele in population ...
... Chapter 5 1. Sickle-cell anemia is an example of _____________________ because _________________________. a. stabilizing selection/ there is only one common phenotype in populations where malaria is prevalent. b. directional selection/ malaria is promoting the loss of the sickle allele in population ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... (d) When a small polypeptide S was broken down in this way, three different amino acids were produced according to the following reaction. ...
... (d) When a small polypeptide S was broken down in this way, three different amino acids were produced according to the following reaction. ...
Astrovirus Replication: An Overview
... with different degrees of similarity.36 Consistent with the capsid polyprotein domain organization, studies using antibodies revealed that VP34 would express conserved epitopes shared by all serotypes, while VP29 and VP26 contained the serotype-specific neutralizing epitopes.24,37,38 Thus, it is rea ...
... with different degrees of similarity.36 Consistent with the capsid polyprotein domain organization, studies using antibodies revealed that VP34 would express conserved epitopes shared by all serotypes, while VP29 and VP26 contained the serotype-specific neutralizing epitopes.24,37,38 Thus, it is rea ...
Genetics Class- Ch. 10 Notes
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Enzymes - CEA Workshop Teacher Notes.pptx
... • Some objects and their mirror images are non-‐superimposable (just like your les and right hands). • When a molecule cannot be superimposed on its mirror image the molecule is described ...
... • Some objects and their mirror images are non-‐superimposable (just like your les and right hands). • When a molecule cannot be superimposed on its mirror image the molecule is described ...
Enzyme Power Point
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
Identification of eight novel coagulation factor XIII subunit A
... are shown in Figure 2(A-F). Tyr167 is situated in the !-sandwich domain. It is the first amino acid of the short !-strand ranging from Tyr167 to Thr172. The tyrosine side chain extends into the loop formed by the amino acids Gly33-Leu45. In the figure, there is a gap in the loop since Arg37 and Gly3 ...
... are shown in Figure 2(A-F). Tyr167 is situated in the !-sandwich domain. It is the first amino acid of the short !-strand ranging from Tyr167 to Thr172. The tyrosine side chain extends into the loop formed by the amino acids Gly33-Leu45. In the figure, there is a gap in the loop since Arg37 and Gly3 ...
BIOL 106 Introduction to Cell Biology
... Recognize the structures, properties, and roles of the four major classes of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) and their role in biology. Learning Objectives Describe the special bonding properties of carbon that allow it to form an endless variety of organic mol ...
... Recognize the structures, properties, and roles of the four major classes of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) and their role in biology. Learning Objectives Describe the special bonding properties of carbon that allow it to form an endless variety of organic mol ...
Molecular evolution of paclitaxel biosynthetic genes TS and
... Plants synthesize an enormous number of secondary compounds that provide an increasingly exploited reservoir for the generation of pharmaceutically active agents (Hartmann et al. 2005), and many more await discovery. In the conifer genus Taxus, paclitaxel (Taxol), a well-known anti-cancer agent, and ...
... Plants synthesize an enormous number of secondary compounds that provide an increasingly exploited reservoir for the generation of pharmaceutically active agents (Hartmann et al. 2005), and many more await discovery. In the conifer genus Taxus, paclitaxel (Taxol), a well-known anti-cancer agent, and ...
Genetics Test Review
... Use a Punnett square to predict the phenotypic and genotypic outcome (offspring) of a cross between a plant heterozygous/hybrid for yellow (Yy) peas and a plant homozygous/purebred for green (yy) peas. Problem #2 - In pea plants, yellow peas are dominant over green peas. Use a Punnett square to pred ...
... Use a Punnett square to predict the phenotypic and genotypic outcome (offspring) of a cross between a plant heterozygous/hybrid for yellow (Yy) peas and a plant homozygous/purebred for green (yy) peas. Problem #2 - In pea plants, yellow peas are dominant over green peas. Use a Punnett square to pred ...
Chemistry as a Game of Molecular Construction. The Bond-Click Way Brochure
... 8.2.6 Solubility and Insolubility of Ionic Materials 240 8.3 The Use of Ionic Matter in Living Organisms 242 8.3.1 Soluble Ionic Material Takes Care of Biological Communication 242 8.3.2 The Insoluble Ionic Material Makes Our Skeleton and Teeth 243 8.4 Covalent Molecules that Form Ions in Solution: ...
... 8.2.6 Solubility and Insolubility of Ionic Materials 240 8.3 The Use of Ionic Matter in Living Organisms 242 8.3.1 Soluble Ionic Material Takes Care of Biological Communication 242 8.3.2 The Insoluble Ionic Material Makes Our Skeleton and Teeth 243 8.4 Covalent Molecules that Form Ions in Solution: ...
... Choice A: The aminoacyl synthetase that attaches Ala to the correct tRNA can also, by mistake, attach the amino acid Gly. If Gly is attached, then it is removed by hydrolysis at a separate editing site on the enzyme. Based on the structure of these amino acids, provide a sketch or description of the ...
Jump to Terms beginning with: A B Ca-Cn Co
... A process whereby only one immunoglobulin light chain and one heavy chain gene are transcribed in any one cell; the other genes are repressed. ...
... A process whereby only one immunoglobulin light chain and one heavy chain gene are transcribed in any one cell; the other genes are repressed. ...
EXTENDED CONCEPT OF KNOWLEDGE FOR EVOLUTIONARY
... skepticism — do we have any real knowledge at all? If we do not limit ourselves by the traditional concept of knowledge as belief (or proposition), we can give a certain answer, yes we do! There are many things that we certainly can do (if we just want to) — in many respects we are capable of doing ...
... skepticism — do we have any real knowledge at all? If we do not limit ourselves by the traditional concept of knowledge as belief (or proposition), we can give a certain answer, yes we do! There are many things that we certainly can do (if we just want to) — in many respects we are capable of doing ...
ZIRGAN (ganciclovir ophthalmic gel) 0.15% Treats Herpetic
... when they leave the house to instill it every 2 hours. In addition, trifluridine is one of the few remaining ophthalmic drugs that are preserved with thimerosal. MECHANISMS OF ACTION ZIRGAN gel 0.15% works in two ways. It is phosphorylated primarily by the viral enzyme thymidine kinase, which allows ...
... when they leave the house to instill it every 2 hours. In addition, trifluridine is one of the few remaining ophthalmic drugs that are preserved with thimerosal. MECHANISMS OF ACTION ZIRGAN gel 0.15% works in two ways. It is phosphorylated primarily by the viral enzyme thymidine kinase, which allows ...
RECOMBINEERING: A POWERFUL NEW TOOL FOR MOUSE
... genome will be completed and annotated. The next challenge will be to determine how each of these genes functions alone and with other genes in the genome, to understand the developmental programme of a human. Given that there are many genes that need to be characterized and the fact that a lot of t ...
... genome will be completed and annotated. The next challenge will be to determine how each of these genes functions alone and with other genes in the genome, to understand the developmental programme of a human. Given that there are many genes that need to be characterized and the fact that a lot of t ...
CYP74C3 and CYP74A1, plant cytochrome P450 enzymes whose
... detergent micelles and that the protein was entirely watersoluble. In the same work, however, it was reported that the specific activity of the enzyme was enhanced 2–3-fold by detergent, but the molecular mechanism responsible for this activation is unknown. The molecular mechanisms and primary dete ...
... detergent micelles and that the protein was entirely watersoluble. In the same work, however, it was reported that the specific activity of the enzyme was enhanced 2–3-fold by detergent, but the molecular mechanism responsible for this activation is unknown. The molecular mechanisms and primary dete ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.