Resonant Effects in Collisions of Relativistic Electrons in the Field of
... onances occur only when photons (of the spontaneous and external field) propagate nonparallel to each other. In the sequel, we restricted our consideration of resonances to the range of intensities where η Ⰶ 1. It is demonstrated that, within a sufficiently broad range of electron energies and scatt ...
... onances occur only when photons (of the spontaneous and external field) propagate nonparallel to each other. In the sequel, we restricted our consideration of resonances to the range of intensities where η Ⰶ 1. It is demonstrated that, within a sufficiently broad range of electron energies and scatt ...
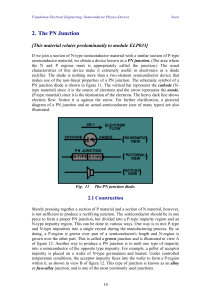
ELECTRONIC MATERIALS Lecture 10
... added later. At this stage, we need to build up a few layers of silicon (which conducts electricity) alternating with a few layers of an insulator (which doesn't conduct electricity). These two types of material will be stacked, like layers of frosting between layers of cake. Later, we'll etch away ...
... added later. At this stage, we need to build up a few layers of silicon (which conducts electricity) alternating with a few layers of an insulator (which doesn't conduct electricity). These two types of material will be stacked, like layers of frosting between layers of cake. Later, we'll etch away ...
chapter 7 multielectron atoms outline
... The agreement of approx. with exact is actually even better than it looks. The two plots were perfectly superimposed and I had to add on a small constant to exact so that you could see the two curves. ...
... The agreement of approx. with exact is actually even better than it looks. The two plots were perfectly superimposed and I had to add on a small constant to exact so that you could see the two curves. ...
quantum
... physical entity measured. Feynman et al. also wrote concerning Gedankenexperiment 2: the jolt given to the electron when the photon is scattered by it is such as to change the electron’s motion enough so that if it might have gone to where P12 [the electron distribution] was at a maximum [in Gedanke ...
... physical entity measured. Feynman et al. also wrote concerning Gedankenexperiment 2: the jolt given to the electron when the photon is scattered by it is such as to change the electron’s motion enough so that if it might have gone to where P12 [the electron distribution] was at a maximum [in Gedanke ...
Electron Attraction Mediated by Coulomb Repulsion
... organic molecule model system proposed by Little1, comprising two parts: the ‘system’ - a one dimensional conducting chain (individual lattice sites marked green), and the ‘medium’ – an array of side-chain ‘polarizers’ (purple) each having a single electron that can hop between a site close and a si ...
... organic molecule model system proposed by Little1, comprising two parts: the ‘system’ - a one dimensional conducting chain (individual lattice sites marked green), and the ‘medium’ – an array of side-chain ‘polarizers’ (purple) each having a single electron that can hop between a site close and a si ...
Pauli Exclusion Principle
... 7-69 The wavelengths of the photons emitted by potassium corresponding to transitions from the 4P3/2 and 4P1/2 states to the ground state are 766.41 nm and 769.90 nm. (a) Calculate the energies of these photons in electron volts. (b) The difference in energies of these photons equals the difference ...
... 7-69 The wavelengths of the photons emitted by potassium corresponding to transitions from the 4P3/2 and 4P1/2 states to the ground state are 766.41 nm and 769.90 nm. (a) Calculate the energies of these photons in electron volts. (b) The difference in energies of these photons equals the difference ...
Electron-beam lithography

Electron-beam lithography (often abbreviated as e-beam lithography) is the practice of scanning a focused beam of electrons to draw custom shapes on a surface covered with an electron-sensitive film called a resist (""exposing""). The electron beam changes the solubility of the resist, enabling selective removal of either the exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist by immersing it in a solvent (""developing""). The purpose, as with photolithography, is to create very small structures in the resist that can subsequently be transferred to the substrate material, often by etching.The primary advantage of electron-beam lithography is that it can draw custom patterns (direct-write) with sub-10 nm resolution. This form of maskless lithography has high resolution and low throughput, limiting its usage to photomask fabrication, low-volume production of semiconductor devices, and research & development.