Proteins - Cook Biology
... • There are 20 different amino acids because there are 20 different side chains. ...
... • There are 20 different amino acids because there are 20 different side chains. ...
Water
... as the mRNA is moved through the ribosome one codon at a time. (When completed, the polypeptide is released from the ribosome.) ...
... as the mRNA is moved through the ribosome one codon at a time. (When completed, the polypeptide is released from the ribosome.) ...
Representations of 3D Structures
... lengths/angles and standard information about atom-atom interactions such as minimum distance (i.e. Van der Waals radii) •With all this information you can generate a model of the structure. Important: NMR gives you a number of possible solutions (all almost identical, rmsd <1Å), This can range from ...
... lengths/angles and standard information about atom-atom interactions such as minimum distance (i.e. Van der Waals radii) •With all this information you can generate a model of the structure. Important: NMR gives you a number of possible solutions (all almost identical, rmsd <1Å), This can range from ...
Vitamins
... one plant protein low in one amino acid, with another plant protein high in that amino acid. Another way is to combine a plant protein with a small amount of animal protein. When complementary proteins are eaten together or within the course of the day all essential amino acids are provided. ...
... one plant protein low in one amino acid, with another plant protein high in that amino acid. Another way is to combine a plant protein with a small amount of animal protein. When complementary proteins are eaten together or within the course of the day all essential amino acids are provided. ...
Ch. 3 Review Guide
... Explain the processes of dehydration synthesis and the process of hydrolysis ...
... Explain the processes of dehydration synthesis and the process of hydrolysis ...
Biochemistry: Monomers and Polymers
... Def. of Amino Acid • Amino acids are molecules that contain C, H, O, N, and sometimes sulfur. – Our bodies are able to make 12 of the 20 amino acids, the rest come from what you eat. – The amino acid monomers are linked together by peptide bonds to form protein polymers. ...
... Def. of Amino Acid • Amino acids are molecules that contain C, H, O, N, and sometimes sulfur. – Our bodies are able to make 12 of the 20 amino acids, the rest come from what you eat. – The amino acid monomers are linked together by peptide bonds to form protein polymers. ...
Lecture 5
... Subset of turn-lovers. Glycine is special because it is so flexible, so it can easily make the sharp turns and bends needed in a b-turn. Proline is special because it is so rigid; you could say that it is pre-bend for the b-turn. Aspartic acid, asparagine, and serine have in common that they have sh ...
... Subset of turn-lovers. Glycine is special because it is so flexible, so it can easily make the sharp turns and bends needed in a b-turn. Proline is special because it is so rigid; you could say that it is pre-bend for the b-turn. Aspartic acid, asparagine, and serine have in common that they have sh ...
- Peptide Machines, Inc.
... clogged lines, and overfills so typical of other instruments. The use of stock solutions of AA's eliminates the need for pre-fill cartridges or barcoding. ...
... clogged lines, and overfills so typical of other instruments. The use of stock solutions of AA's eliminates the need for pre-fill cartridges or barcoding. ...
Organization: The 6 Essential Elements
... small subunits called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, each with a specific side chain of chemicals. Amino acids bond to other amino acids to form a long chain called a protein. These chains of amino acids fold into a particular shape. The shape of a protein will ...
... small subunits called amino acids. There are 20 different amino acids, each with a specific side chain of chemicals. Amino acids bond to other amino acids to form a long chain called a protein. These chains of amino acids fold into a particular shape. The shape of a protein will ...
Jumbo_2860g_strawberry_2014 copy - Supplements
... It’s been shown that people tend to overestimate their actual nutrient consumption when trying to gain muscle and brawn. In other words, they eat less than they think and they need for steady and significant progress! Everybody seeks the magic bullet while ignoring the fact that nothing is more powe ...
... It’s been shown that people tend to overestimate their actual nutrient consumption when trying to gain muscle and brawn. In other words, they eat less than they think and they need for steady and significant progress! Everybody seeks the magic bullet while ignoring the fact that nothing is more powe ...
Publications de l`équipe
... Valentina Mercanti, Anna Marchetti, Emmanuelle Lelong, Franck Perez, Lelio Orci, Pierre Cosson ...
... Valentina Mercanti, Anna Marchetti, Emmanuelle Lelong, Franck Perez, Lelio Orci, Pierre Cosson ...
protein - Humble ISD
... A student performed several chemical tests of 4 unknown foods. The results are given below. Which unknown is most likely from egg white and why? ...
... A student performed several chemical tests of 4 unknown foods. The results are given below. Which unknown is most likely from egg white and why? ...
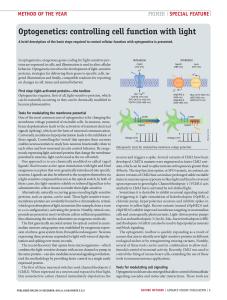
Optogenetics: controlling cell function with light
... from plants, can be fused to cellular effector proteins to create lightsensitive variants. The LOV2 domain uses naturally encoded flavin as a chromophore and is the basis of light-activated fusion proteins such as LOV2-Rac. Blue light induces a change in the conformation of the LOV2 domain, which re ...
... from plants, can be fused to cellular effector proteins to create lightsensitive variants. The LOV2 domain uses naturally encoded flavin as a chromophore and is the basis of light-activated fusion proteins such as LOV2-Rac. Blue light induces a change in the conformation of the LOV2 domain, which re ...
Introduction to Protein Folding and Molecular Simulation
... If 100 psec (10-10 sec) were required to convert from a conformation to another one, a random search of all conformations would require 5 x 1047 x 10-10 sec ≒ 1.6 x 1030 years. However, folding of proteins takes place in msec to sec order. Therefore, proteins fold not via a random search but a more ...
... If 100 psec (10-10 sec) were required to convert from a conformation to another one, a random search of all conformations would require 5 x 1047 x 10-10 sec ≒ 1.6 x 1030 years. However, folding of proteins takes place in msec to sec order. Therefore, proteins fold not via a random search but a more ...
Gene Expression
... between DNA and the three types of RNA. Transcription uses the DNA gene code to produce a strand of RNA, while translation uses the mRNA to produce a protein/polypeptide. Enzymes are necessary for the processes of transcription and translation to occur. The mRNA codon chart can be used to predict th ...
... between DNA and the three types of RNA. Transcription uses the DNA gene code to produce a strand of RNA, while translation uses the mRNA to produce a protein/polypeptide. Enzymes are necessary for the processes of transcription and translation to occur. The mRNA codon chart can be used to predict th ...
biomolecule ppt
... LIPIDS (fats) ● Functions: o Lipids can be used to store energy for later use o Phospholipids are important parts of biological membranes ...
... LIPIDS (fats) ● Functions: o Lipids can be used to store energy for later use o Phospholipids are important parts of biological membranes ...
II. Lecture Section 2 CELL SPECIALIZATION: Regulation of
... c. Epigenetic modification can be copied and inherited 1. Changes to chromatin structure can be directly inherited 2. Add unique features to eukaryotic chromosome function d. Transcription factors regulate promoter activation 1. Transcription initiation in eukaryotes requires many proteins 2. RNA po ...
... c. Epigenetic modification can be copied and inherited 1. Changes to chromatin structure can be directly inherited 2. Add unique features to eukaryotic chromosome function d. Transcription factors regulate promoter activation 1. Transcription initiation in eukaryotes requires many proteins 2. RNA po ...
Protein Synthesis: Comprehesive Review PowerPoint Slides
... transcription and translation // three type of ribonucleic acids required for protein synthesis – messenger RNA (mRNA) is assembled • a mirror-image copy of the gene is made • migrates from the nucleus to cytoplasm • its code is read by the ribosomes – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • cytoplasmic organelles c ...
... transcription and translation // three type of ribonucleic acids required for protein synthesis – messenger RNA (mRNA) is assembled • a mirror-image copy of the gene is made • migrates from the nucleus to cytoplasm • its code is read by the ribosomes – Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) • cytoplasmic organelles c ...
33511-33521
... genome): “extracellular”, “immune response”, “blood coagulation”, “lipid transport”, “complement activation”, “regulation of blood pressure”, as expected; also: cytoskeletal proteins, receptors and transporters. Proteins from most cellular locations and molecular processes are recognized. Under-repr ...
... genome): “extracellular”, “immune response”, “blood coagulation”, “lipid transport”, “complement activation”, “regulation of blood pressure”, as expected; also: cytoskeletal proteins, receptors and transporters. Proteins from most cellular locations and molecular processes are recognized. Under-repr ...
Chapter 17 Power Point
... • Both help protect mRNA from degradation by enzymes • Both facilitate the attachment of mRNA to the ribosome ...
... • Both help protect mRNA from degradation by enzymes • Both facilitate the attachment of mRNA to the ribosome ...
051229
... comparison parallels that of sequence alignment. It has been shown that despite primary sequence diversity, protein structures of related sequences possess a structural core of αhelices and β-sheets and vary in the loop regions.To determine the characteristic properties for each target sequence from ...
... comparison parallels that of sequence alignment. It has been shown that despite primary sequence diversity, protein structures of related sequences possess a structural core of αhelices and β-sheets and vary in the loop regions.To determine the characteristic properties for each target sequence from ...
Components of Food
... Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction which can convert an oil to a semisolid fat by adding hydrogen to some of the carboxylic acid C=C double bond , thus decreasing the degree of unsaturation. ...
... Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction which can convert an oil to a semisolid fat by adding hydrogen to some of the carboxylic acid C=C double bond , thus decreasing the degree of unsaturation. ...
RNA
... Primary structure: the amino acid sequence Secondary structure: local structures stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The most common examples are the alpha helix, beta sheet and turns. Tertiary structure: the overall shape of a single protein molecule; most commonly the formation of a hydrophobic core, bu ...
... Primary structure: the amino acid sequence Secondary structure: local structures stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The most common examples are the alpha helix, beta sheet and turns. Tertiary structure: the overall shape of a single protein molecule; most commonly the formation of a hydrophobic core, bu ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.