1 - LWW.com
... monoclonal antibody (clone 247-3F6) at a concentration of 0.5 µg/ml at 4˚C. They were washed and incubated with peroxidase-labeled rabbit anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) for 1 hour at room temperature. Then, the membranes were incubated with chemiluminescence Luminol Reagent (Supersignal, Pierce, ...
... monoclonal antibody (clone 247-3F6) at a concentration of 0.5 µg/ml at 4˚C. They were washed and incubated with peroxidase-labeled rabbit anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) for 1 hour at room temperature. Then, the membranes were incubated with chemiluminescence Luminol Reagent (Supersignal, Pierce, ...
Isolation and Amino Acid Sequence of Two New PR
... glucanase) have not been explored. Genes encoding PR-4 proteins were studied in potato, tomato, tobacco, Arabidopsis, and rubber tree (Broekaert et al., 1990; Friedrich et al., 1991; Linthorst et al., 1991; Potter et al., 1993; Stanford et al., 1989), while mature proteins have been characterized on ...
... glucanase) have not been explored. Genes encoding PR-4 proteins were studied in potato, tomato, tobacco, Arabidopsis, and rubber tree (Broekaert et al., 1990; Friedrich et al., 1991; Linthorst et al., 1991; Potter et al., 1993; Stanford et al., 1989), while mature proteins have been characterized on ...
2.1 KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their
... 3. Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers, and can be found in meats, cheeses, eggs, and fish. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. ...
... 3. Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers, and can be found in meats, cheeses, eggs, and fish. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. ...
Protein - standish
... differently shaped beads. Each bead is a small amino acid. These amino acids can join together to make thousands of different proteins. Scientists have found many different amino acids in protein, but 22 of them are very important to human health. Of those 22 amino acids, your body can make 13 of th ...
... differently shaped beads. Each bead is a small amino acid. These amino acids can join together to make thousands of different proteins. Scientists have found many different amino acids in protein, but 22 of them are very important to human health. Of those 22 amino acids, your body can make 13 of th ...
Macromolecules biologyjunction
... are made of subunits called amino acids and are used to build cells and do much of the work inside organisms. They also act as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). Use your SATP2 ...
... are made of subunits called amino acids and are used to build cells and do much of the work inside organisms. They also act as enzymes helping to control metabolic reactions in organisms. Amino acids contain two functional groups, the carboxyl group (-COOH) and the amino group (-NH2). Use your SATP2 ...
Module 1: Review of General and Organic Chemistry
... e. Will either isozyme work near its maximal rate under normal blood glucose levels? If so, which one and why? ...
... e. Will either isozyme work near its maximal rate under normal blood glucose levels? If so, which one and why? ...
Amino Acid composition of vegetables and fruits from
... from a variety of plants were found to give favorable balance of essential and nonessential amino acids, comparable to animal products (', 2). Even the potato tuber, which is commonly considered an "energy food", has also been found to contain protein of high biological value (3, 41. Since the amino ...
... from a variety of plants were found to give favorable balance of essential and nonessential amino acids, comparable to animal products (', 2). Even the potato tuber, which is commonly considered an "energy food", has also been found to contain protein of high biological value (3, 41. Since the amino ...
classsssssss
... abnormal in these enzymes. The patient is most likely to have which of the following findings? • A. citrullinemia • B. Methylmalonic aciduria • C. homocystinuria • D. orotic aciduria • E. lactic acidosis ...
... abnormal in these enzymes. The patient is most likely to have which of the following findings? • A. citrullinemia • B. Methylmalonic aciduria • C. homocystinuria • D. orotic aciduria • E. lactic acidosis ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... site, with the correct anticodon and the correct amino acid. A peptide bond is formed between the amino acids and water is removed. ...
... site, with the correct anticodon and the correct amino acid. A peptide bond is formed between the amino acids and water is removed. ...
Organic Compounds
... • pH – too high or too low the H+ or OH – ions react with the amino acid side chains (R groups) – improper folding occurs – reaction slows • Salt conc. – too much or too little causes improper folding of protein • Substrate concentration – lower the substrate conc., the slower the reaction ...
... • pH – too high or too low the H+ or OH – ions react with the amino acid side chains (R groups) – improper folding occurs – reaction slows • Salt conc. – too much or too little causes improper folding of protein • Substrate concentration – lower the substrate conc., the slower the reaction ...
ANPS 019 Black 09-02
... Activation energy is the amount of energy needed to begin a reaction Enzymes make reaction more likely Most reactions require enzymes Enzymes reduce energy of activation, making it more likely a reaction will occur Enzymes are not changed or used up in the reaction, so one enzyme can catalyze the sa ...
... Activation energy is the amount of energy needed to begin a reaction Enzymes make reaction more likely Most reactions require enzymes Enzymes reduce energy of activation, making it more likely a reaction will occur Enzymes are not changed or used up in the reaction, so one enzyme can catalyze the sa ...
File
... 2. Which condition is necessary for enzymes to function properly in the human body? (1) These catalysts must have a specific shape. (3) Body temperature must be above 40°C. (2) These catalysts must be able to reproduce. (4) Body pH must be above 10. 3. The term “substrate” is most commonly used to d ...
... 2. Which condition is necessary for enzymes to function properly in the human body? (1) These catalysts must have a specific shape. (3) Body temperature must be above 40°C. (2) These catalysts must be able to reproduce. (4) Body pH must be above 10. 3. The term “substrate” is most commonly used to d ...
File
... 1.Test for Starch: - to a food add three or four drops of iodine, if starch is present the solution will change color to dark blue. 2. Test for Glucose: -take some food in a test tube and add some Benedict’s solution. - put the test tube in a beaker full of water and place it on a tripod with a buns ...
... 1.Test for Starch: - to a food add three or four drops of iodine, if starch is present the solution will change color to dark blue. 2. Test for Glucose: -take some food in a test tube and add some Benedict’s solution. - put the test tube in a beaker full of water and place it on a tripod with a buns ...
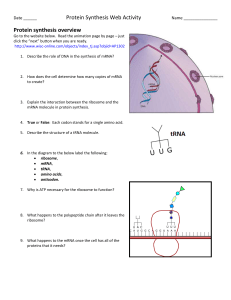
Transcription - smithlhhsb121
... The interaction of tRNA and mRNA takes place in a ribosome Consists of two protein subunits and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Within the ribosome are three binding sites ◦ P site (peptidyl-tRNA site) where the tRNA holding the polypepetide chain ◦ A site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) where next tRNA in line is held ...
... The interaction of tRNA and mRNA takes place in a ribosome Consists of two protein subunits and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Within the ribosome are three binding sites ◦ P site (peptidyl-tRNA site) where the tRNA holding the polypepetide chain ◦ A site (aminoacyl-tRNA site) where next tRNA in line is held ...
MB207_12 - MB207Jan2010
... • In most cells, Golgi apparatus is located close to the nucleus whereas the network of ER tubules extends from the nucleus throughout the entire cytosol. • The localization of both ER and Golgi apparatus depends on an intact microtubule array. ...
... • In most cells, Golgi apparatus is located close to the nucleus whereas the network of ER tubules extends from the nucleus throughout the entire cytosol. • The localization of both ER and Golgi apparatus depends on an intact microtubule array. ...
Soy Protein in Milk Replacers
... Problems with soy protein. One of the biggest problems with using soy proteins in milk replacers is the presence of anti-nutritional factors in soybeans. These include trypsin inhibitor, glycinin and βconglycinin. Trypsin inhibitor can reduce digestibility by binding trypsin, an enzyme in the digest ...
... Problems with soy protein. One of the biggest problems with using soy proteins in milk replacers is the presence of anti-nutritional factors in soybeans. These include trypsin inhibitor, glycinin and βconglycinin. Trypsin inhibitor can reduce digestibility by binding trypsin, an enzyme in the digest ...
Kids Building Bricks - Johnston County Schools
... • From DNA to mRNA • Occurs in the nucleus • Enzymes make a RNA copy of a segment of DNA –Just like DNA replication except A pairs with U, not with T ...
... • From DNA to mRNA • Occurs in the nucleus • Enzymes make a RNA copy of a segment of DNA –Just like DNA replication except A pairs with U, not with T ...
3. What are macromolecules?
... worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. A special type of lipid called phospholipids help make up the cell membrane. Two layers of these phospholipids make up the membrane. Phospholipids have a "water-loving" hydrophilic head and two ...
... worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. A special type of lipid called phospholipids help make up the cell membrane. Two layers of these phospholipids make up the membrane. Phospholipids have a "water-loving" hydrophilic head and two ...
Name: Proteins Activity Amino Acids, Building Blocks of Proteins
... by using models. 7. Cut out the four amino acids. Attempt to join the amino acids. 8. Can the amino acid models easily join to form a protein molecule? 9. Join the molecules by removing as many –OH groups and –H groups as needed from the amino acids. All four amino acid molecules can be joined in th ...
... by using models. 7. Cut out the four amino acids. Attempt to join the amino acids. 8. Can the amino acid models easily join to form a protein molecule? 9. Join the molecules by removing as many –OH groups and –H groups as needed from the amino acids. All four amino acid molecules can be joined in th ...
Curriculum for Excellence Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Nature`s Che
... Amino acids join by a condensation reaction to form proteins. The link joining amino acid residues in polypeptide chains is a peptide (amide) link. Most enzymes are proteins and act as biological catalysts. During digestion, enzymes break proteins into smaller peptide chains and amino acids. ...
... Amino acids join by a condensation reaction to form proteins. The link joining amino acid residues in polypeptide chains is a peptide (amide) link. Most enzymes are proteins and act as biological catalysts. During digestion, enzymes break proteins into smaller peptide chains and amino acids. ...
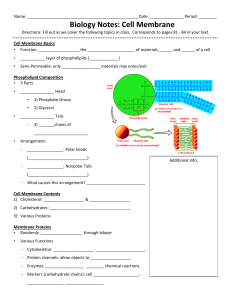
Biology Notes: Cell Membrane
... • Semi‐Permeable: only _________________ materials may enter/exit ...
... • Semi‐Permeable: only _________________ materials may enter/exit ...
Protein structure prediction Haixu Tang School of Informatics
... are based on neural networks. The overall idea is that neural networks can be trained to recognize amino acid patterns in known secondary structure units, and to use these patterns to distinguish between the different types of secondary structure. Neural networks classify “input vectors” or “example ...
... are based on neural networks. The overall idea is that neural networks can be trained to recognize amino acid patterns in known secondary structure units, and to use these patterns to distinguish between the different types of secondary structure. Neural networks classify “input vectors” or “example ...
Acids and Bases (cont.)
... – Enzymes allow chemical reactions to proceed quickly at body temperatures – Three steps are involved in enzyme action: 1. Substrate binds to enzyme’s active site, temporarily forming enzyme-substrate complex 2. Complex undergoes rearrangement of substrate, resulting in final product 3. Product is r ...
... – Enzymes allow chemical reactions to proceed quickly at body temperatures – Three steps are involved in enzyme action: 1. Substrate binds to enzyme’s active site, temporarily forming enzyme-substrate complex 2. Complex undergoes rearrangement of substrate, resulting in final product 3. Product is r ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.