Chapter 2
... In our cells, 90% of the substances are water. Of the remaining molecules, 50 percent are proteins. Proteins determine the functions of cells. Red blood cells, for example, have to be able to carry oxygen. They can do so because they produce protein haemoglobin, which transports oxygen. Some protein ...
... In our cells, 90% of the substances are water. Of the remaining molecules, 50 percent are proteins. Proteins determine the functions of cells. Red blood cells, for example, have to be able to carry oxygen. They can do so because they produce protein haemoglobin, which transports oxygen. Some protein ...
Document
... Examples right. Top, a 1H-15N HSQC of an acyl carrier protein in the apo-form (no fatty acid bound). In the lower panel the effect of increasing fatty acid chain length is monitored. ...
... Examples right. Top, a 1H-15N HSQC of an acyl carrier protein in the apo-form (no fatty acid bound). In the lower panel the effect of increasing fatty acid chain length is monitored. ...
Document
... • 21. Which of the following statements is false? a) A reaction may not occur at a detectable rate even though it has a favorable equilibrium. b) After a reaction, the enzyme involved becomes available to catalyze the reaction again. c) For S P, a catalyst shifts the reaction equilibrium to the righ ...
... • 21. Which of the following statements is false? a) A reaction may not occur at a detectable rate even though it has a favorable equilibrium. b) After a reaction, the enzyme involved becomes available to catalyze the reaction again. c) For S P, a catalyst shifts the reaction equilibrium to the righ ...
File - miss marsh science
... Proteins are made up of chains of small molecules called amino acids. There are over 20 different kinds of amino acid. Proteins are used by the body for growth and repair. ...
... Proteins are made up of chains of small molecules called amino acids. There are over 20 different kinds of amino acid. Proteins are used by the body for growth and repair. ...
Slide
... • One amino acid, cysteine, can form a covalent bond with another cysteine (called a disulfide bond or bridge) • Apart from the bonds within an amino acid residue and the peptide bonds that connect residues, disulfide bonds are the only common covalent bonds within a protein • In a typical cell ...
... • One amino acid, cysteine, can form a covalent bond with another cysteine (called a disulfide bond or bridge) • Apart from the bonds within an amino acid residue and the peptide bonds that connect residues, disulfide bonds are the only common covalent bonds within a protein • In a typical cell ...
Chemistry PPT
... throughout human history. • However, sugars are not the only substances perceived as sweet; there are other chemicals that can trigger the same sensation. • We perceive sweetness when molecules of a substance attach to the “sweet” taste receptors on our tongue, triggering a message to the brain. • M ...
... throughout human history. • However, sugars are not the only substances perceived as sweet; there are other chemicals that can trigger the same sensation. • We perceive sweetness when molecules of a substance attach to the “sweet” taste receptors on our tongue, triggering a message to the brain. • M ...
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LAB QUESTIONS Laboratory
... PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LAB QUESTIONS Laboratory evaluation of serum proteins and enzymes ...
... PATHOPHYSIOLOGY LAB QUESTIONS Laboratory evaluation of serum proteins and enzymes ...
1.2a Chemistry of Life
... throughout human history. • However, sugars are not the only substances perceived as sweet; there are other chemicals that can trigger the same sensation. • We perceive sweetness when molecules of a substance attach to the “sweet” taste receptors on our tongue, triggering a message to the brain. • M ...
... throughout human history. • However, sugars are not the only substances perceived as sweet; there are other chemicals that can trigger the same sensation. • We perceive sweetness when molecules of a substance attach to the “sweet” taste receptors on our tongue, triggering a message to the brain. • M ...
Analysis on Organic Compounds Submitted by WWW
... acids differ with respect to the nature of the chemical group that is attached to the base structure. Examples of amino acids are alanine, valine, glutamic acid, tryptophan, tyrosine, and histidine. Amino acids are linked to form a protein by the removal of water molecules (Figure ). The links forg ...
... acids differ with respect to the nature of the chemical group that is attached to the base structure. Examples of amino acids are alanine, valine, glutamic acid, tryptophan, tyrosine, and histidine. Amino acids are linked to form a protein by the removal of water molecules (Figure ). The links forg ...
Membrane Protein : Integral/Peripheral
... • Hypotonic IV’s are used to treat true dehydration (water loss) • Water will move into our cells ...
... • Hypotonic IV’s are used to treat true dehydration (water loss) • Water will move into our cells ...
File
... "Transcription and the Genetic Code." Science Online. Facts On File, Inc. Web. 19 Nov. 2013. ...
... "Transcription and the Genetic Code." Science Online. Facts On File, Inc. Web. 19 Nov. 2013. ...
Organelle Definition and Mechanism of Production Protein Targeting
... 1. Polyribosomes represent an assembly line of protein synthesis on one mRNA, and clearly many copies are made in parallel. For this problem, we have induced synthesis of a protein by a stimulus. We want to determine how many proteins per cell are present at steady state if the half-time of the prot ...
... 1. Polyribosomes represent an assembly line of protein synthesis on one mRNA, and clearly many copies are made in parallel. For this problem, we have induced synthesis of a protein by a stimulus. We want to determine how many proteins per cell are present at steady state if the half-time of the prot ...
Biology Biochemistry
... Monomers are basic structures of macromolecules! ______________________________ are long chains of carbon atoms connected to each other with double or single bonds. o Lipids are mostly composed of _______________ and _______________ with a few ________________ atoms. Two forms of fatty acids: satura ...
... Monomers are basic structures of macromolecules! ______________________________ are long chains of carbon atoms connected to each other with double or single bonds. o Lipids are mostly composed of _______________ and _______________ with a few ________________ atoms. Two forms of fatty acids: satura ...
Protein Folding I and II
... Disulfide Bond Formation - Proteins with disulfide bonds have a built-in advantage if they are denatured with their disulfide bonds intact intact. The intact disulfide bonds eliminate many degrees of freedom associated with denaturation, denaturation so fewer events need to occur to bring about the ...
... Disulfide Bond Formation - Proteins with disulfide bonds have a built-in advantage if they are denatured with their disulfide bonds intact intact. The intact disulfide bonds eliminate many degrees of freedom associated with denaturation, denaturation so fewer events need to occur to bring about the ...
Hanson Homework 2011 Key
... have their oligosaccharide chains facing the outside of the cell. True. The oligosaccharide chains are added in the lumens of the ER and Golgi apparatus, which are topologically equivalent to the outside of the cell. This basic topology is conserved in all membrane budding and fusion events. Thus, o ...
... have their oligosaccharide chains facing the outside of the cell. True. The oligosaccharide chains are added in the lumens of the ER and Golgi apparatus, which are topologically equivalent to the outside of the cell. This basic topology is conserved in all membrane budding and fusion events. Thus, o ...
Slide 1
... that are active against mutant viruses Accuracy of binding-site prediction can be improved using a combination of shape descriptors for the interfaces We use geometrical, topological and functional descriptors in combination for ligand binding site prediction of HIV-1 protease ...
... that are active against mutant viruses Accuracy of binding-site prediction can be improved using a combination of shape descriptors for the interfaces We use geometrical, topological and functional descriptors in combination for ligand binding site prediction of HIV-1 protease ...
optional activity key File
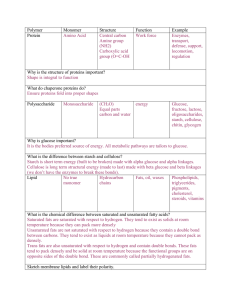
... What is the chemical difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids? Saturated fats are saturated with respect to hydrogen. They tend to exist as solids at room temperature because they can pack more densely Unsaturated fats are not saturated with respect to hydrogen because they contain a ...
... What is the chemical difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids? Saturated fats are saturated with respect to hydrogen. They tend to exist as solids at room temperature because they can pack more densely Unsaturated fats are not saturated with respect to hydrogen because they contain a ...
Molecular Biology and Chemistry - Systems Biology Research Group
... contortions caused by the bonding between the side chains of the various ...
... contortions caused by the bonding between the side chains of the various ...
PPT - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... Atmospheres and Chemistry reducing: CH4 , NH3, H2O, H2. or CO2, N2, H2 or CO, N2, H2 There is hydrogen gas and/or hydrogen is present combined with other elements (methane, ammonia, water) neutral: CO or CO2 , N2 , H2O no hydrogen or oxygen gas oxidizing: O2, CO2, N2 ...
... Atmospheres and Chemistry reducing: CH4 , NH3, H2O, H2. or CO2, N2, H2 or CO, N2, H2 There is hydrogen gas and/or hydrogen is present combined with other elements (methane, ammonia, water) neutral: CO or CO2 , N2 , H2O no hydrogen or oxygen gas oxidizing: O2, CO2, N2 ...
Regulator of tumour suppression found Research Highlights
... translocation of p27 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm — the place where p27 is broken down by degradation machinery. Taken together, the findings showed that p38 is a negative regulator of the cell cycle inhibitor p27. The reduction or absence of p27 in the nucleus can lead to a host of ...
... translocation of p27 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm — the place where p27 is broken down by degradation machinery. Taken together, the findings showed that p38 is a negative regulator of the cell cycle inhibitor p27. The reduction or absence of p27 in the nucleus can lead to a host of ...
Anti-c-myc antibody 9E10 - Protein Engineering, Design and Selection
... both without glutamic acid of position 1 and glutamine of position 2 lead to a binding signal comparable to that of the untruncated peptide. A drastic effect amounting to the complete loss of detectable binding signal is associated with further shortening by omitting the lysine at position 3. The sh ...
... both without glutamic acid of position 1 and glutamine of position 2 lead to a binding signal comparable to that of the untruncated peptide. A drastic effect amounting to the complete loss of detectable binding signal is associated with further shortening by omitting the lysine at position 3. The sh ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE
... MEMBRANE PROTEINS • INTEGRAL or TRANS – MEMBRANE PROTEINS • LIPID-ANCHORED MEMBRANE PROTEINS • PERIPHERAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS ...
... MEMBRANE PROTEINS • INTEGRAL or TRANS – MEMBRANE PROTEINS • LIPID-ANCHORED MEMBRANE PROTEINS • PERIPHERAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.